Haloperidol
 Haloperidol 5mg/ml solution for injection | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌhæloʊˈpɛrɪdɒl/ |
| Trade names | Haldol, Serenace, others |
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Typical antipsychotic |
| Main uses | Psychosis, mania[1] |
| Side effects | Movement disorder, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, QT prolongation[2] |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | by mouth, IM, IV, depot (as decanoate ester) |
| Defined daily dose | 3.3 to 8 mg[3] |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682180 |
| Legal | |
| License data |
|
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Bioavailability | 60–70% (by mouth)[4] |
| Protein binding | ~90%[4] |
| Metabolism | Liver-mediated[4] |
| Elimination half-life | 14–26 hours (IV), 20.7 hours (IM), 14–37 hours (oral)[4] |
| Excretion | Biliary (hence in feces) and in urine[4][5] |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H23ClFNO2 |
| Molar mass | 375.87 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Haloperidol, marketed under the trade name Haldol among others, is a typical antipsychotic medication.[2] Haloperidol is used in the treatment of schizophrenia, tics in Tourette syndrome, mania in bipolar disorder, nausea and vomiting, delirium, agitation, acute psychosis, and hallucinations in alcohol withdrawal.[2][6][7] It may be used by mouth or injection into a muscle or a vein.[2] Haloperidol typically works within 30 to 60 minutes.[2] A long-acting formulation may be used as an injection every four weeks in people with schizophrenia or related illnesses, who either forget or refuse to take the medication by mouth.[2]
Haloperidol may result in a movement disorder known as tardive dyskinesia which may be permanent.[2] Neuroleptic malignant syndrome and QT interval prolongation may occur.[2] In older people with psychosis due to dementia it results in an increased risk of death.[2] When taken during pregnancy it may result in problems in the infant.[2][8] It should not be used in people with Parkinson's disease.[2]
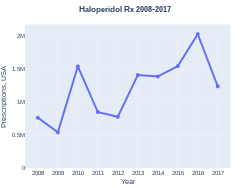
Haloperidol was discovered in 1958 by Paul Janssen.[9] It was made from pethidine (meperidine).[10] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[11] It is the most commonly used typical antipsychotic.[12] It is relatively inexpensive.[13][14][15] In 2017, it was the 296th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than one million prescriptions.[16][17]
Medical uses
Haloperidol is used in the control of the symptoms of:
- Acute psychosis, such as drug-induced psychosis caused by LSD, psilocybin, amphetamines, ketamine,[18] and phencyclidine,[19] and psychosis associated with high fever or metabolic disease. Some evidence, however, has found haloperidol to worsen psychosis due to psilocybin.[20]
- Adjunctive treatment of alcohol and opioid withdrawal
- Agitation and confusion associated with cerebral sclerosis
- Alcohol-induced psychosis
- Hallucinations in alcohol withdrawal[6]
- Hyperactive delirium (to control the agitation component of delirium)
- Hyperactivity, aggression
- Otherwise uncontrollable, severe behavioral disorders in children and adolescents
- Schizophrenia[21]
- Therapeutic trial in personality disorders, such as borderline personality disorder
- Treatment of intractable hiccups[22][23]
- Treatment of neurological disorders, such as tic disorders such as Tourette syndrome, and chorea
- Treatment of severe nausea and emesis in postoperative and palliative care, especially for palliating adverse effects of radiation therapy and chemotherapy in oncology
Haloperidol was considered indispensable for treating psychiatric emergency situations,[24][25] although the newer atypical drugs have gained a greater role in a number of situations as outlined in a series of consensus reviews published between 2001 and 2005.[26][27][28]
In a 2013 comparison of 15 antipsychotics in schizophrenia, haloperidol demonstrated standard effectiveness. It was 13–16% more effective than ziprasidone, chlorpromazine, and asenapine, approximately as effective as quetiapine and aripiprazole, and 10% less effective than paliperidone.[29] A 2013 systematic review compared haloperidol to placebo in schizophrenia:[30]
| Summary | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haloperidol often causes troublesome adverse effects. If there is no other antipsychotic drug, using haloperidol to offset the consequences of untreated schizophrenia is justified. Where a choice of drug is available, however, an alternative antipsychotic with less likelihood of adverse effects such as parkinsonism, akathisia and acute dystonias may be more desirable.[30] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Animal experiments indicate haloperidol is not teratogenic, but is embryotoxic in high doses. In humans, no controlled studies exist. Reports in pregnant women revealed possible damage to the fetus, although most of the women were exposed to multiple drugs during pregnancy. In addition, neonates exposed to antipsychotics are at risk for extrapyramidal and withdrawal symptoms following delivery, such as agitation, hypertonia, hypotonia, tremor, somnolence, respiratory distress, and feeding disorder. Haloperidol should be given during pregnancy only if the benefit to the mother outweighs the potential fetal risk.[21]
Haloperidol is excreted in breast milk. A few studies have examined the impact on breastfed infants and in most cases, there were no effects on infant growth and development.[31]
Other considerations

During long-term treatment of chronic psychiatric disorders, the daily dose should be reduced to the lowest level needed for maintenance of remission. Sometimes, it may be indicated to terminate haloperidol treatment gradually.[32] In addition, during long-term use, routine monitoring including measurement of BMI, blood pressure, fasting blood sugar, and lipids, is recommended due to the risk of side effects.[33]
Other forms of therapy (psychotherapy, occupational therapy/ergotherapy, or social rehabilitation) should be instituted.[citation needed] PET imaging studies have suggested low doses are preferable. Clinical response was associated with at least 65% occupancy of D2 receptors, while greater than 72% was likely to cause hyperprolactinaemia and over 78% associated with extrapyramidal side effects. Doses of haloperidol greater than 5 mg increased the risk of side effects without improving efficacy.[34] Patients responded with doses under even 2 mg in first-episode psychosis.[35] For maintenance treatment of schizophrenia, an international consensus conference recommended a reduction dosage by about 20% every 6 months until a minimal maintenance dose is established.[33]
- Depot forms are also available; these are injected deeply intramuscularly at regular intervals. The depot forms are not suitable for initial treatment, but are suitable for patients who have demonstrated inconsistency with oral dosages.[citation needed]
The decanoate ester of haloperidol (haloperidol decanoate) has a much longer duration of action, so is often used in people known to be noncompliant with medication by mouth. A dose is given by intramuscular injection once every two to four weeks.[36] The IUPAC name of haloperidol decanoate is [4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-oxobutyl]piperidin-4-yl] decanoate.
Topical formulations of haloperidol should not be used as treatment for nausea because research does not indicate this therapy is more effective than alternatives.[37]
Dosage
The defined daily dose of haloperidol is 8 mg by mouth.[38] The defined daily dose is 3.3 to 8 mg when given by injection.[3] Typical doses for schizophrenia are 5 to 20 mg per day by mouth but may be started as low as 1 mg per day.[2] Between 2 and 5 mg may be used by injection into a muscle for those who are significantly agitated.[2] Lower doses should be used in older people.[1] The maximum recommended dose of the short acting formulation by injection is 15 mg per day in adults and 5 mg in older people.[39] A long acting injection into a muscle can be given every 3 to 4 weeks at 10 times the dose a person is taking by mouth.[40]
For acute psychosis treatment should generally last at least three months while for chronic psychosis treatment should generally last at least a year.[1] Treatment for an episoid of mania may be from 3 to 6 weeks.[1] Treatment should be stopped gradually.[1]
Side effects
Sources for the following lists of side effects:[41][42][43][44]
As haloperidol is a high-potency typical antipsychotic, it tends to produce significant extrapyramidal side effects. According to a 2013 meta-analysis of the comparative efficacy and tolerability of 15 antipsychotic drugs it was the most prone of the 15 for causing extrapyramidal side effects.[29]
With more than 6 months of use 14 percent of users gain weight.[45] Haloperidol may be neurotoxic.[46]
Common (>1% incidence)
- Extrapyramidal side effects including:
- Akathisia (motor restlessness)
- Dystonia (continuous spasms and muscle contractions)
- Muscle rigidity
- Parkinsonism (characteristic symptoms such as rigidity)
- Hypotension
- Anticholinergic side effects such as: (These adverse effects are more common than with lower-potency typical antipsychotics, such as chlorpromazine and thioridazine.)
- Blurred vision
- Constipation
- Dry mouth
- Somnolence (which is not a particularly prominent side effect, as is supported by the results of the aforementioned meta-analysis.[29])
Unknown frequency
- Anemia
- Headache
- Increased respiratory rate
- Orthostatic hypotension
- Prolonged QT interval
- Visual disturbances
Rare (<1% incidence)
- Acute hepatic failure
- Agitation
- Agranulocytosis
- Anaphylactic reaction
- Anorexia
- Bronchospasm
- Cataracts
- Cholestasis
- Confusional state
- Depression
- Dermatitis exfoliative
- Dyspnea
- Edema
- Extrasystoles
- Face edema
- Gynecomastia
- Hepatitis
- Hyperglycemia
- Hypersensitivity
- Hyperthermia
- Hypoglycemia
- Hyponatremia
- Hypothermia
- Increased sweating
- Injection site abscess
- Insomnia
- Itchiness
- Jaundice
- Laryngeal edema
- Laryngospasm
- Leukocytoclastic vasculitis
- Leukopenia
- Liver function test abnormal
- Nausea
- Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
- Neutropenia
- Pancytopenia
- Photosensitivity reaction
- Priapism
- Psychotic disorder
- Pulmonary embolism
- Rash
- Retinopathy
- Seizure
- Sudden death
- Tardive dyskinesia
- Thrombocytopenia
- Torsades de pointes
- Urinary retention
- Urticaria
- Ventricular fibrillation
- Ventricular tachycardia
- Vomiting
Contraindications
- Pre-existing coma, acute stroke
- Severe intoxication with alcohol or other central depressant drugs
- Known allergy against haloperidol or other butyrophenones or other drug ingredients
- Known heart disease, when combined will tend towards cardiac arrest[citation needed]
Special cautions
- A multiple-year study suggested this drug and other neuroleptic antipsychotic drugs commonly given to people with Alzheimer's with mild behavioral problems often make their condition worse and its withdrawal was even beneficial for some cognitive and functional measures.[47]
- Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis: analysis of 17 trials showed the risk of death in this group of patients was 1.6 to 1.7 times that of placebo-treated patients. Most of the causes of death were either cardiovascular or infectious in nature. It is not clear to what extent this observation is attributed to antipsychotic drugs rather than the characteristics of the patients. The drug bears a boxed warning about this risk.[21]
- Impaired liver function, as haloperidol is metabolized and eliminated mainly by the liver
- In patients with hyperthyreosis, the action of haloperidol is intensified and side effects are more likely.
- IV injections: risk of hypotension or orthostatic collapse
- Patients at special risk for the development of QT prolongation (hypokalemia, concomitant use of other drugs causing QT prolongation)
- Patients with a history of leukopenia: a complete blood count should be monitored frequently during the first few months of therapy and discontinuation of the drug should be considered at the first sign of a clinically significant decline in white blood cells.[21]
- Pre-existing Parkinson's disease[48] or dementia with Lewy bodies
Interactions
- Amiodarone: Q-Tc interval prolongation (potentially dangerous change in heart rhythm).[49]
- Amphetamine and methylphenidate: counteracts increased action of norepinephrine and dopamine in patients with narcolepsy or ADD/ADHD
- Epinephrine: action antagonized, paradoxical decrease in blood pressure may result
- Guanethidine: antihypertensive action antagonized
- Levodopa: decreased action of levodopa
- Lithium: rare cases of the following symptoms have been noted: encephalopathy, early and late extrapyramidal side effects, other neurologic symptoms, and coma.[50]
- Methyldopa: increased risk of extrapyramidal side effects and other unwanted central effects
- Other central depressants (alcohol, tranquilizers, narcotics): actions and side effects of these drugs (sedation, respiratory depression) are increased. In particular, the doses of concomitantly used opioids for chronic pain can be reduced by 50%.
- Other drugs metabolized by the CYP3A4 enzyme system: inducers such as carbamazepine, phenobarbital, and rifampicin decrease plasma levels and inhibitors such as quinidine, buspirone, and fluoxetine increase plasma levels[21]
- Tricyclic antidepressants: metabolism and elimination of tricyclics significantly decreased, increased toxicity noted (anticholinergic and cardiovascular side effects, lowering of seizure threshold)
Discontinuation
The British National Formulary recommends a gradual withdrawal when discontinuing antipsychotics to avoid acute withdrawal syndrome or rapid relapse.[51] Symptoms of withdrawal commonly include nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite.[52] Other symptoms may include restlessness, increased sweating, and trouble sleeping.[52] Less commonly there may be a feeling of the world spinning, numbness, or muscle pains.[52] Symptoms generally resolve after a short period of time.[52]
There is tentative evidence that discontinuation of antipsychotics can result in psychosis.[53] It may also result in reoccurrence of the condition that is being treated.[54] Rarely tardive dyskinesia can occur when the medication is stopped.[52]
Overdose
Symptoms
Symptoms are usually due to side effects. Most often encountered are:
- Anticholinergic side effects (dry mouth, constipation, paralytic ileus, difficulties in urinating, decreased perspiration)
- Coma in severe cases, accompanied by respiratory depression and massive hypotension, shock
- Hypotension or hypertension
- Rarely, serious ventricular arrhythmia (torsades de pointes), with or without prolonged QT-time
- Sedation
- Severe extrapyramidal side effects with muscle rigidity and tremors, akathisia, etc.
Treatment
Treatment is mostly symptomatic and involves intensive care with stabilization of vital functions. In early detected cases of oral overdose, induction of emesis, gastric lavage, and the use of activated charcoal can be tried. In the case of a severe overdose, antidotes such as bromocriptine or ropinirole may be used to treat the extrapyramidal effects caused by haloperidol, acting as dopamine receptor agonists.[citation needed] ECG and vital signs should be monitored especially for QT prolongation and severe arrhythmias should be treated with antiarrhythmic measures.[21]
Prognosis
In general, the prognosis of overdose is good, provided the person has survived the initial phase. An overdose of haloperidol can be fatal.[55]
Pharmacology
Haloperidol is a typical butyrophenone type antipsychotic that exhibits high affinity dopamine D2 receptor antagonism and slow receptor dissociation kinetics.[56] It has effects similar to the phenothiazines.[23] The drug binds preferentially to D2 and α1 receptors at low dose (ED50 = 0.13 and 0.42 mg/kg, respectively), and 5-HT2 receptors at a higher dose (ED50 = 2.6 mg/kg). Given that antagonism of D2 receptors is more beneficial on the positive symptoms of schizophrenia and antagonism of 5-HT2 receptors on the negative symptoms, this characteristic underlies haloperidol's greater effect on delusions, hallucinations and other manifestations of psychosis.[57] Haloperidol's negligible affinity for histamine H1 receptors and muscarinic M1 acetylcholine receptors yields an antipsychotic with a lower incidence of sedation, weight gain, and orthostatic hypotension though having higher rates of treatment emergent extrapyramidal symptoms.
Haloperidol acts on these receptors: (Ki)
- D1 (silent antagonist) — Unknown efficiency[citation needed]
- D5 (silent antagonist) — Unknown efficiency[citation needed]
- D2 (inverse agonist) — 0.74 nM[58]
- D3 (inverse agonist) — 0.2 nM[59]
- D4 (inverse agonist) — 5–9 nM[60]
- σ1 (irreversible inactivation by haloperidol metabolite HPP+) – 3 nM[61]
- σ2 (agonist): 54 nM[62]
- 5HT1A receptor agonist – 1927 nM[63]
- 5HT2A (silent antagonist) – 53 nM[63]
- 5HT2C (silent antagonist) – 10,000 nM[63]
- 5HT6 (silent antagonist) – 3666 nM[63]
- 5HT7 (irreversible silent antagonist) — 377.2 nM[63]
- H1 (silent antagonist) — 1,800 nM[63]
- M1 (silent antagonist) — 10,000 nM[63]
- α1A (silent antagonist) — 12 nM[63]
- α2A (silent antagonist) — 1130 nM[63]
- α2B (silent antagonist) — 480 nM[63]
- α2C (silent antagonist) — 550 nM[63]
- NR1/NR2B subunit containing NMDA receptor (antagonist; ifenprodil site): IC50 — 2,000 nM[64]
Pharmacokinetics
By mouth
The bioavailability of oral haloperidol ranges from 60–70%. However, there is a wide variance in reported mean Tmax and T1/2 in different studies, ranging from 1.7 to 6.1 hours and 14.5 to 36.7 hours respectively.[4]
Intramuscular
The drug is well and rapidly absorbed with a high bioavailability when injected intramuscularly. The Tmax is 20 minutes in healthy individuals and 33.8 minutes in patients with schizophrenia. The mean T1/2 is 20.7 hours.[4] The decanoate injectable formulation is for intramuscular administration only and is not intended to be used intravenously. The plasma concentrations of haloperidol decanoate reach a peak at about six days after the injection, falling thereafter, with an approximate half-life of three weeks.[65] The decanote is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines as an alternative to fluphenazine.[66]
Intravenous
The bioavailability is 100% in intravenous (IV) injection, and the very rapid onset of action is seen within seconds. The T1/2 is 14.1 to 26.2 hours. The apparent volume of distribution is between 9.5 and 21.7 L/kg.[4] The duration of action is four to six hours.
Therapeutic concentrations
Plasma levels of five to 15 micrograms per liter are typically seen for therapeutic response (Ulrich S, et al. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1998). The determination of plasma levels is rarely used to calculate dose adjustments but can be useful to check compliance.
The concentration of haloperidol in brain tissue is about 20-fold higher compared to blood levels. It is slowly eliminated from brain tissue,[67] which may explain the slow disappearance of side effects when the medication is stopped.[67][68]
Distribution and metabolism
Haloperidol is heavily protein bound in human plasma, with a free fraction of only 7.5 to 11.6%. It is also extensively metabolized in the liver with only about 1% of the administered dose excreted unchanged in the urine. The greatest proportion of the hepatic clearance is by glucuronidation, followed by reduction and CYP-mediated oxidation, primarily by CYP3A4.[4]
History
Haloperidol was discovered by Paul Janssen.[69] It was developed in 1958 at the Belgian company Janssen Pharmaceutica and submitted to the first of clinical trials in Belgium later that year.[70][71]
Haloperidol was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on 12 April 1967; it was later marketed in the U.S. and other countries under the brand name Haldol by McNeil Laboratories.[70]
Society and culture
Cost
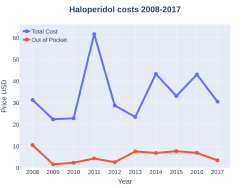
Haloperidol is relatively inexpensive, being up to 100 fold less expensive than newer antipsychotics.[14][13] The daily defined dose for haloperidol is 8 mg.[72] In low and middle income countries the typical wholesale cost for 5 mg tablets is less $US0.01 when bought at least 1000 at a time.[72] The cost to the NHS in the United Kingdom is about £1.20 for 30 0.5 mg capsules and £15.00 for 38 5 mg tablets as of 2019.[73] The solution for injection is about £3.50 per 5 mg.[73] The wholesale cost in the United States is $US0.25 per 0.5 mg tablet and $0.53 per 5 mg tablet as of 2020.[74]
-
Haloperidol costs (US)
-
Haloperidol prescriptions (US)
Brand names
Haloperidol is the INN, BAN, USAN, AAN approved name.
It is sold under the tradenames Aloperidin, Bioperidolo, Brotopon, Dozic, Duraperidol (Germany), Einalon S, Eukystol, Haldol (common tradename in the US and UK), Halosten, Keselan, Linton, Peluces, Serenace and Sigaperidol.[citation needed]
-
Haloperidol, 10-mg oral tablet
-
Haldol decanoate 50 mg/ml solution for injection into muscle[75]
Veterinary use
Haloperidol is also used on many different kinds of animals for nonselective tranquilization and diminishing behavioral arousal, in veterinary and other settings including captivity management.[76]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 "HALOPERIDOL oral - Essential drugs". medicalguidelines.msf.org. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 30 August 2020.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 "Haloperidol". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 2 January 2015. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "WHOCC - ATC/DDD Index". www.whocc.no. Archived from the original on 6 August 2020. Retrieved 30 August 2020.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 Kudo, S; Ishizaki T (December 1999). "Pharmacokinetics of haloperidol: an update". Clinical Pharmacokinetics. 37 (6): 435–56. doi:10.2165/00003088-199937060-00001. PMID 10628896.
- ↑ "Product Information Serenace" (PDF). TGA eBusiness Services. Aspen Pharma Pty Ltd. 29 September 2011. Archived from the original on 14 March 2017. Retrieved 29 May 2014.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Schuckit, MA (27 November 2014). "Recognition and management of withdrawal delirium (delirium tremens)". The New England Journal of Medicine. 371 (22): 2109–13. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1407298. PMID 25427113. Archived from the original on 13 February 2020. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ Plosker, GL (1 July 2012). "Quetiapine: a pharmacoeconomic review of its use in bipolar disorder". PharmacoEconomics. 30 (7): 611–31. doi:10.2165/11208500-000000000-00000. PMID 22559293.
- ↑ "Prescribing medicines in pregnancy database". Australian Government. 3 March 2014. Archived from the original on 8 April 2014. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
- ↑ Sneader, Walter (2005). Drug discovery : a history (Rev. and updated ed.). Chichester: Wiley. p. 124. ISBN 978-0-471-89979-2. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015.
- ↑ Ravina, Enrique (2011). The evolution of drug discovery: from traditional medicines to modern drugs (1. Aufl. ed.). Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. p. 62. ISBN 978-3-527-32669-3. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015.
- ↑ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ↑ Stevens, Andrew (2004). Health care needs assessment: the epidemiologically based needs assessment reviews (2nd ed.). Abingdon: Radcliffe Medical. p. 202. ISBN 978-1-85775-892-4. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Adams, James G. (2012). Emergency Medicine E-Book: Clinical Essentials (Expert Consult -- Online). Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 1635. ISBN 978-1-4557-3394-1. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 19 April 2020.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 I, Escobar Javier; Humberto, Marin (2013). Clinical Psychopharmacology: A Practical Approach. World Scientific. p. 69. ISBN 978-981-4578-37-0. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 19 April 2020.
- ↑ Hitchings, Andrew; Lonsdale, Dagan; Burrage, Daniel; Baker, Emma (2014). The Top 100 Drugs e-book: Clinical Pharmacology and Practical Prescribing. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 75. ISBN 978-0-7020-5515-7. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 19 April 2020.
- ↑ "The Top 300 of 2020". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 12 February 2021. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ↑ "Haloperidol - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 8 July 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ↑ Giannini, A. James; Underwood, Ned A.; Condon, Maggie (2000). "Acute Ketamine Intoxication Treated by Haloperidol". American Journal of Therapeutics. 7 (6): 389–91. doi:10.1097/00045391-200007060-00008. PMID 11304647.
- ↑ Giannini, A. James; Eighan, Michael S.; Loiselle, Robert H.; Giannini, Matthew C. (1984). "Comparison of Haloperidol and Chlorpromazine in the Treatment of Phencyclidine Psychosis". The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 24 (4): 202–4. doi:10.1002/j.1552-4604.1984.tb01831.x. PMID 6725621.
- ↑ Johnson, M; Richards, W; Griffiths, R (August 2008). "Human hallucinogen research: guidelines for safety". Journal of Psychopharmacology. Thousand Oaks, California: SAGE Publications. 22 (6): 603–20. doi:10.1177/0269881108093587. PMC 3056407. PMID 18593734.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 21.3 21.4 21.5 "Haldol Official FDA information, side effects and uses". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 5 October 2013. Retrieved 3 October 2013.
- ↑ Joint Formulary Committee (2013). British National Formulary (BNF) (65 ed.). London, England: Pharmaceutical Press. pp. 229–30. ISBN 978-0-85711-084-8.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Brayfield, A, ed. (13 December 2013). "Haloperidol". Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. London, UK: Pharmaceutical Press. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 29 May 2014.
- ↑ Cavanaugh, SV (1986). "Psychiatric emergencies". The Medical Clinics of North America. 70 (5): 1185–202. doi:10.1016/S0025-7125(16)30919-1. PMID 3736271.
- ↑ Currier, Glenn W. (2003). "The Controversy over 'Chemical Restraint' In Acute Care Psychiatry". Journal of Psychiatric Practice. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 9 (1): 59–70. doi:10.1097/00131746-200301000-00006. PMID 15985915.
- ↑ Allen, MH; Currier, GW; Hughes, DH; Reyes-Harde, M; Docherty, JP (2001). "The Expert Consensus Guideline Series. Treatment of behavioral emergencies". Postgraduate Medicine (Spec No): 1–88, quiz 89–90. PMID 11500996.
- ↑ Allen, Michael H.; Currier, Glenn W.; Hughes, Douglas H.; Docherty, John P.; Carpenter, Daniel; Ross, Ruth (2003). "Treatment of Behavioral Emergencies: A Summary of the Expert Consensus Guidelines". Journal of Psychiatric Practice. 9 (1): 16–38. doi:10.1097/00131746-200301000-00004. PMID 15985913.
- ↑ Allen, Michael H.; Currier, Glenn W.; Carpenter, Daniel; Ross, Ruth W.; Docherty, John P. (2005). "Introduction: Methods, Commentary, and Summary". Journal of Psychiatric Practice. 11: 5–25. doi:10.1097/00131746-200511001-00002. PMID 16319571.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 29.2 Leucht, Stefan; Cipriani, Andrea; Spineli, Loukia; Mavridis, Dimitris; Örey, Deniz; Richter, Franziska; Samara, Myrto; Barbui, Corrado; Engel, Rolf R; Geddes, John R; Kissling, Werner; Stapf, Marko Paul; Lässig, Bettina; Salanti, Georgia; Davis, John M (2013). "Comparative efficacy and tolerability of 15 antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis". The Lancet. 382 (9896): 951–62. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60733-3. PMID 23810019.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 Adams, C; Bergman, H; Irving, C (2013). "Haloperidol versus placebo for schizophrenia". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 11 (11): CD003082.pub3. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003082.pub3. PMID 24242360. Archived from the original on 20 August 2017.
- ↑ "LACTMED: Haloperidol". 31 October 2018. Archived from the original on 19 January 2019. Retrieved 18 January 2019.
- ↑ "Haloperidol at Chemeurope". Archived from the original on 12 June 2012.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 Work Group on Schizophrenia. "Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Schizophrenia Second Edition". Archived from the original on 27 March 2012. Retrieved 21 April 2014.
- ↑ Oosthuizen, P.; Emsley, R. A.; Turner, J.; Keyter, N. (2001). "Determining the optimal dose of haloperidol in first-episode psychosis". Journal of Psychopharmacology. 15 (4): 251–5. doi:10.1177/026988110101500403. PMID 11769818.
- ↑ Tauscher, Johannes; Kapur, Shitij (2001). "Choosing the Right Dose of Antipsychotics in Schizophrenia". CNS Drugs. 15 (9): 671–8. doi:10.2165/00023210-200115090-00001. PMID 11580306.
- ↑ Goodman and Gilman's Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 10th edition (McGraw-Hill, 2001).[page needed]
- ↑ American Academy of Hospice and Palliative Medicine. "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question". Choosing Wisely: An Initiative of the ABIM Foundation. American Academy of Hospice and Palliative Medicine. Archived from the original on 1 September 2013. Retrieved 1 August 2013., which cites
- Smith, Thomas J.; Ritter, Joseph K.; Poklis, Justin L.; Fletcher, Devon; Coyne, Patrick J.; Dodson, Patricia; Parker, Gwendolyn (2012). "ABH Gel is Not Absorbed from the Skin of Normal Volunteers". Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 43 (5): 961–6. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2011.05.017. PMID 22560361.
- Weschules, Douglas J. (2005). "Tolerability of the Compound ABHR in Hospice Patients". Journal of Palliative Medicine. 8 (6): 1135–43. doi:10.1089/jpm.2005.8.1135. PMID 16351526.
- ↑ "Single Drug Information – International Medical Products Price Guide". Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 5 August 2020.
- ↑ "HALOPERIDOL injectable - Essential drugs". medicalguidelines.msf.org. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 2 September 2020.
- ↑ "HALOPERIDOL decanoate injectable - Essential drugs". medicalguidelines.msf.org. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 2 September 2020.
- ↑ Product Information [Internet]. 2011 [cited 2013 Sep 29]. Available from: "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 14 March 2017. Retrieved 29 May 2014.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ HALDOL® Injection For Intramuscular Injection Only Product Information [Internet]. Janssen; 2011 [cited 2013 Sep 29]. Available from: "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 14 March 2017. Retrieved 29 September 2013.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ Truven Health Analytics, Inc. DrugPoint® System (Internet) [cited 2013 Sep 29]. Greenwood Village, CO: Thomsen Healthcare; 2013.
- ↑ Joint Formulary Committee. British National Formulary (BNF) 65. Pharmaceutical Pr; 2013.
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 January 2017. Retrieved 30 September 2016.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ Nasrallah, Henry A.; Chen, Alexander T. (August 2017). "Multiple neurotoxic effects of haloperidol resulting in neuronal death". Annals of Clinical Psychiatry. 29 (3): 195–202. ISSN 1547-3325. PMID 28738100.
- ↑ Ballard, Clive; Lana, Marisa Margallo; Theodoulou, Megan; Douglas, Simon; McShane, Rupert; Jacoby, Robin; Kossakowski, Katja; Yu, Ly-Mee; Juszczak, Edmund; on behalf of the Investigators DART AD (2008). Brayne, Carol (ed.). "A Randomised, Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Trial in Dementia Patients Continuing or Stopping Neuroleptics (The DART-AD Trial)". PLoS Medicine. 5 (4): e76. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0050076. PMC 2276521. PMID 18384230.
Neuroleptics provided no benefit for patients with mild behavioural problems, but were associated with a marked deterioration in verbal skills
- Lay summary in: "Medication 'worsens Alzheimer's'". BBC News Online. 1 April 2008.
- ↑ Leentjens, Albert FG; Van Der Mast, Rose C (2005). "Delirium in elderly people: An update". Current Opinion in Psychiatry. 18 (3): 325–30. doi:10.1097/01.yco.0000165603.36671.97. PMID 16639157.
- ↑ Bush, S. E.; Hatton, R. C.; Winterstein, A. G.; Thomson, M. R.; Woo, G. W. (2008). "Effects of concomitant amiodarone and haloperidol on Q-Tc interval prolongation". American Journal of Health-System Pharmacy. 65 (23): 2232–6. doi:10.2146/ajhp080039. PMID 19020191.
- ↑ Sandyk, R; Hurwitz, MD (1983). "Toxic irreversible encephalopathy induced by lithium carbonate and haloperidol. A report of 2 cases". South African Medical Journal. 64 (22): 875–6. PMID 6415823.
- ↑ Joint Formulary Committee, BMJ, ed. (March 2009). "4.2.1". British National Formulary (57 ed.). United Kingdom: Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain. p. 192. ISBN 978-0-85369-845-6.
Withdrawal of antipsychotic drugs after long-term therapy should always be gradual and closely monitored to avoid the risk of acute withdrawal syndromes or rapid relapse.
- ↑ 52.0 52.1 52.2 52.3 52.4 Haddad, Peter; Haddad, Peter M.; Dursun, Serdar; Deakin, Bill (2004). Adverse Syndromes and Psychiatric Drugs: A Clinical Guide. OUP Oxford. pp. 207–216. ISBN 9780198527480. Archived from the original on 22 April 2021. Retrieved 14 July 2019.
- ↑ Moncrieff J (July 2006). "Does antipsychotic withdrawal provoke psychosis? Review of the literature on rapid onset psychosis (supersensitivity psychosis) and withdrawal-related relapse". Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. 114 (1): 3–13. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.2006.00787.x. PMID 16774655.
- ↑ Sacchetti, Emilio; Vita, Antonio; Siracusano, Alberto; Fleischhacker, Wolfgang (2013). Adherence to Antipsychotics in Schizophrenia. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 85. ISBN 9788847026797. Archived from the original on 22 April 2021. Retrieved 14 July 2019.
- ↑ "Haloperidol at Drugs.com". Archived from the original on 22 November 2011.
- ↑ Seeman, P; Tallerico, T (1998). "Antipsychotic drugs which elicit little or no Parkinsonism bind more loosely than dopamine to brain D2 receptors, yet occupy high levels of these receptors". Molecular Psychiatry. 3 (2): 123–34. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4000336. PMID 9577836.
- ↑ Schotte, A; Janssen PF; Megens AA; Leysen JE (1993). "Occupancy of central neurotransmitter receptors by risperidone, clozapine and haloperidol, measured ex vivo by quantitative autoradiography". Brain Research. 631 (2): 191–202. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(93)91535-z. PMID 7510574.
- ↑ Leysen, JE; Janssen, PM; Gommeren, W; Wynants, J; Pauwels, PJ; Janssen, PA (1992). "In vitro and in vivo receptor binding and effects on monoamine turnover in rat brain regions of the novel antipsychotics risperidone and ocaperidone". Molecular Pharmacology. 41 (3): 494–508. PMID 1372084. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 23 September 2012.
- ↑ Malmberg, Åsa; Mikaels, Åsa; Mohell, Nina (1998). "Agonist and Inverse Agonist Activity at the Dopamine D3 Receptor Measured by Guanosine 5′-[γ-Thio]Triphosphate-[35S] Binding". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 285 (1): 119–26. PMID 9536001. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 23 September 2012.
- ↑ Leysen, JE; Janssen, PM; Megens, AA; Schotte, A (1994). "Risperidone: A novel antipsychotic with balanced serotonin-dopamine antagonism, receptor occupancy profile, and pharmacologic activity". The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 55 (Suppl): 5–12. PMID 7520908.
- ↑ Cobos, Enrique J.; Del Pozo, Esperanza; Baeyens, José M. (2007). "Irreversible blockade of sigma-1 receptors by haloperidol and its metabolites in guinea pig brain and SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells". Journal of Neurochemistry. 102 (3): 812–25. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04533.x. PMID 17419803.
- ↑ Colabufo, Nicolaantonio; Berardi, Francesco; Contino, Marialessandra; Niso, Mauro; Abate, Carmen; Perrone, Roberto; Tortorella, Vincenzo (2004). "Antiproliferative and cytotoxic effects of some σ2 agonists and σ1 antagonists in tumour cell lines". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 370 (2): 106–13. doi:10.1007/s00210-004-0961-2. PMID 15322732.
- ↑ 63.00 63.01 63.02 63.03 63.04 63.05 63.06 63.07 63.08 63.09 63.10 Kroeze, Wesley K; Hufeisen, Sandra J; Popadak, Beth A; Renock, Sean M; Steinberg, Seanna; Ernsberger, Paul; Jayathilake, Karu; Meltzer, Herbert Y; Roth, Bryan L (2003). "H1-Histamine Receptor Affinity Predicts Short-Term Weight Gain for Typical and Atypical Antipsychotic Drugs". Neuropsychopharmacology. 28 (3): 519–26. doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1300027. PMID 12629531.
- ↑ Ilyin, VI; Whittemore, ER; Guastella, J; Weber, E; Woodward, RM (1996). "Subtype-selective inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors by haloperidol". Molecular Pharmacology. 50 (6): 1541–50. PMID 8967976. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 23 September 2012.
- ↑ "drugs.com". Archived from the original on 10 August 2011.
- ↑ World Health Organization (2023). The selection and use of essential medicines 2023: web annex A: World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 23rd list (2023). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/371090. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2023.02.
- ↑ 67.0 67.1 Kornhuber, Johannes; Schultz, Andreas; Wiltfang, Jens; Meineke, Ingolf; Gleiter, Christoph H.; Zöchling, Robert; Boissl, Karl-Werner; Leblhuber, Friedrich; Riederer, Peter (1999). "Persistence of Haloperidol in Human Brain Tissue". The American Journal of Psychiatry. 156 (6): 885–90. doi:10.1176/ajp.156.6.885. PMID 10360127.
- ↑ Kornhuber, Johannes; Wiltfang, Jens; Riederer, Peter; Bleich, Stefan (2006). "Neuroleptic drugs in the human brain: Clinical impact of persistence and region-specific distribution". European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience. 256 (5): 274–80. doi:10.1007/s00406-006-0661-7. PMID 16788768.
- ↑ Healy, David (1996). The psychopharmacologists. Vol. 1. London: Chapman and Hall. ISBN 978-1-86036-008-4.[page needed]
- ↑ 70.0 70.1 Granger, Bernard; Albu, Simona (2005). "The Haloperidol Story". Annals of Clinical Psychiatry. 17 (3): 137–40. doi:10.1080/10401230591002048. PMID 16433054.
- ↑ Lopez-Munoz, Francisco; Alamo, Cecilio (2009). "The Consolidation of Neuroleptic Therapy: Janssen, the Discovery of Haloperidol and Its Introduction into Clinical Practice". Brain Research Bulletin. 79 (2): 130–141. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2009.01.005. PMID 19186209.
- ↑ 72.0 72.1 "Single Drug Information – International Medical Products Price Guide". MSH. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 19 April 2020.
- ↑ 73.0 73.1 British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. p. 383. ISBN 9780857113382.
- ↑ "NADAC as of 2020-04-15 | Data.Medicaid.gov". Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Archived from the original on 13 May 2021. Retrieved 19 April 2020.
- ↑ "Haldol Decanoate - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) - (emc)". www.medicines.org.uk. Archived from the original on 24 December 2021. Retrieved 26 December 2021.
- ↑ "The Use of Haloperidol as a Long-Acting Neuroleptic in Game Capture Operations". Archived from the original on 21 June 2020. Retrieved 20 June 2020.
External links
| External sites: | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers: |
|
- Pages using duplicate arguments in template calls
- Wikipedia articles needing page number citations from September 2012
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- CS1 maint: archived copy as title
- Use dmy dates from November 2017
- Use American English from November 2017
- All Wikipedia articles written in American English
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Chemical articles without CAS registry number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs missing an ATC code
- Drugboxes which contain changes to watched fields
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from April 2013
- 4-Hydroxypiperidines
- Antiemetics
- Belgian inventions
- Butyrophenone antipsychotics
- Chemical substances for emergency medicine
- Chloroarenes
- Fluoroarenes
- Johnson & Johnson brands
- Janssen Pharmaceutica
- NMDA receptor antagonists
- Prolactin releasers
- Suspected embryotoxicants
- Suspected fetotoxicants
- Tertiary alcohols
- Typical antipsychotics
- World Health Organization essential medicines
- RTT

![Haldol decanoate 50 mg/ml solution for injection into muscle[75]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b3/Haldol_Decanoate.jpg/165px-Haldol_Decanoate.jpg)