Clemizole
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.486 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
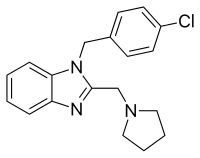
| Formula | C19H20ClN3 |
| Molar mass | 325.84 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Clemizole is an H1 antagonist.
Synthesis
Benzimidazoles substituted with an alkylamine at position 2 have a venerable history as H1 antihistaminic agents. The standard starting material for many benzimidazoles consists of phenylenediamine, or its derivatives.

Reaction of that compound with chloroacetic acid can be rationalized by invoking initial formation of the chloromethyl amide. Imide formation with the remaining free amino group closes the ring to afford 2-chloromethyl benzimidazole (3). Displacement of halogen with pyrrolidine affords the alkylation product. The proton on the fused imidazole nitrogen is then removed by reaction with sodium hydride. Treatment of the resulting anion with α,4-dichlorotoluene gives the H1 antihistaminic agent clemizole (5).
See also
References
- ^ Jerchel D, Fischer H, Kracht M (1952). "Zur Darstellung der Benzimidazole". Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie. 575 (2): 162–173. doi:10.1002/jlac.19525750204.
- ^ GB 703272, Schenck M, Heinz W, issued 1954, assigned to Schering AG
- ^ US 2689853, Schenck M, Heinz W, issued 1954, assigned to Schering AG
- Articles with short description
- Short description matches Wikidata
- Drugs not assigned an ATC code
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Drugs with no legal status
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Benzimidazoles
- Chloroarenes
- H1 receptor antagonists
- 1-Pyrrolidinyl compounds
- All stub articles
- Respiratory system drug stubs