Ipratropium/salbutamol
| Combination of | |
|---|---|
| Ipratropium bromide | Muscarinic antagonist |
| Salbutamol | Short-acting β2-adrenergic agonist |
| Names | |
| Trade names | Combivent, DuoNeb, Breva, others |
| Clinical data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | Inhalation |
| Defined daily dose | not established[2] |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Professional Drug Facts |
| MedlinePlus | a601063 |
| Legal | |
| License data | |
| Legal status | |
Ipratropium/salbutamol, sold under the brand name Combivent among others, is a combination medication used to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).[3][4] It contains ipratropium (an anticholinergic) and salbutamol (albuterol, a β2-adrenergic agonist).[3] It is taken by inhalation.[5]
Common side effects include sore throat, muscle cramps, and nausea.[3] Other side effects may include bronchospasm, allergic reactions, and upper respiratory tract infections.[3] Safety in pregnancy is unclear.[1] Each medication typically decreases bronchospasm and does so via different mechanisms.[3]
The combination was approved for medical use in the United States in 1996.[5] It is available as a generic medication.[4] Sixty doses in the United Kingdom costs the NHS about 18 £ as of 2019.[4] In the United States the wholesale cost of this amount is about US$9.50.[6] In 2017, it was the 172nd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than three million prescriptions.[7][8]
Medical uses
Dosage
It may be used as 1 inhalation every 4 to 6 hours for COPD.[9] It is available under the brand Combivent Respimat.[9]
The defined daily dose is not established.[2]
Society and culture
Inhalers prior to 2013 contained a chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) based propellant; however, these were removed from the market and replaced with ones that do not contain CFCs.[10] The new version also releases little green house gases, as opposed to single medication salbutamol or ipratropium MDIs.[9]
Cost
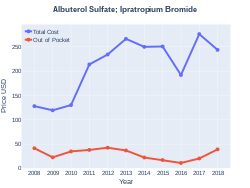
In Canada 120 doses costs about 50 CAD as of 2023.[9] Sixty doses in the United Kingdom costs the NHS about 18 £ as of 2019.[4] In the United States the wholesale cost of this amount is about US$9.50.[6]
-
Albuterol/ipratropium costs (US)
-
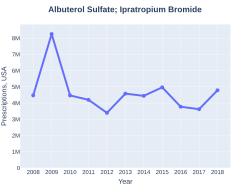
Albuterol/ipratropium prescriptions (US)
Usage
In 2017, it was the 172nd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than three million prescriptions.[7][8]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Albuterol / ipratropium Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 19 April 2019. Retrieved 19 April 2019.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "WHOCC - ATC/DDD Index". www.whocc.no. Archived from the original on 1 July 2021. Retrieved 9 September 2020.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 "DailyMed - ipratropium bromide and albuterol sulfate inhalant". dailymed.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 17 May 2020. Retrieved 18 April 2019.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. p. 247. ISBN 9780857113382.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Ipratropium and Albuterol - FDA prescribing information, side effects and uses". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 19 April 2019. Retrieved 18 April 2019.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "NADAC as of 2019-02-27". Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Archived from the original on 2019-03-06. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "The Top 300 of 2020". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 12 February 2021. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "Albuterol Sulfate; Ipratropium Bromide - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 11 April 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 "BC Inhalers". www.bcinhalers.ca. Archived from the original on 30 June 2023. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
- ↑ Research, Center for Drug Evaluation and (3 November 2018). "Phase Out of Combivent Inhalation Aerosol - Questions and Answers". FDA. Archived from the original on 27 March 2023. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|---|
- DailyMed Archived 2020-05-17 at the Wayback Machine
- Consumer Medication Information from PubMed Archived 2012-12-03 at the Wayback Machine
- National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Expert Panel 3. Expert panel report 3: guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma. Bethesda (MD): National Institutes of Health. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; 2007 Aug. NIH Publication No. 07-4051.
- Pages using duplicate arguments in template calls
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Chemical articles without CAS registry number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs missing an ATC code
- Drugs that are a combination of chemicals
- Webarchive template wayback links
- Beta-adrenergic agonists
- Bronchodilators
- Combination drugs
- Muscarinic antagonists
- RTT