Cevimeline
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | se vim' e leen[1] |
| Trade names | Evoxac |
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Muscarinic agonist[1] |
| Main uses | Dry mouth[1] |
| Side effects | Increased sweating, runny nose, nausea, diarrhea, headaches, dizziness, visual disturbances, tiredness[1] |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | By mouth (capsules) |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a608025 |
| Legal | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Protein binding | <20% |
| Chemical and physical data | |
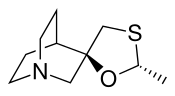
| Formula | C10H17NOS |
| Molar mass | 199.31 g·mol−1 |
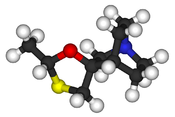
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Cevimeline, sold under the brand name Evoxac, is a medication used to treat dry mouth due to Sjögren's syndrome or radiation therapy.[1] It is similar to pilocarpine.[2] It is taken by mouth.[1]
Side effects are usually mild and may include increased sweating, runny nose, nausea, diarrhea, headaches, dizziness, visual disturbances, and tiredness.[1] Safety in pregnancy is unclear.[2] It is a muscarinic agonist, which results in increased saliva production.[1]
Cevimeline was approved for medical use in the United States in 2000.[2] It is available as a generic medication.[3] In the United States a month of medication costs about 52 USD as of 2021.[3]
Medical use
Dosage
The typical dose is 30 mg three times daily.[1]
Side effects
Known side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, excessive sweating, rash, headache, runny nose, cough, drowsiness, hot flashes, blurred vision, and difficulty sleeping.[4]
Contraindications include asthma and angle closure glaucoma.[citation needed]
Mechanism of action
By activating the M3 receptors of the parasympathetic nervous system, cevimeline stimulates secretion by the salivary glands, thereby alleviating dry mouth.
See also
- Pilocarpine — a similar parasympathomimetic medication for dry mouth (xerostomia)
- Bethanechol — a similar muscarinic parasympathomimetic with longer-lasting effect
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 "Cevimeline". LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. 2012. Archived from the original on 6 May 2021. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Cevimeline Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 28 January 2021. Retrieved 3 January 2022. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "AHFS2022" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Cevimeline Prices, Coupons & Savings Tips - GoodRx". GoodRx. Archived from the original on 26 September 2016. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
- ↑ [1] Archived 2017-09-30 at the Wayback Machine MedicineNet: Cevimeline. Accessed 10/12/2007
External links
| Identifiers: |
|
|---|
- Pages using duplicate arguments in template calls
- Pages with reference errors
- Webarchive template wayback links
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Chemical articles without CAS registry number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs missing an ATC code
- Drugboxes which contain changes to verified fields
- Drugboxes which contain changes to watched fields
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from December 2010
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- Articles with changed EBI identifier
- Muscarinic agonists
- Oxathiolanes
- Quinuclidines
- Spiro compounds
- Daiichi Sankyo
- RTT