Kangri cancer
| Kangri cancer | |
|---|---|
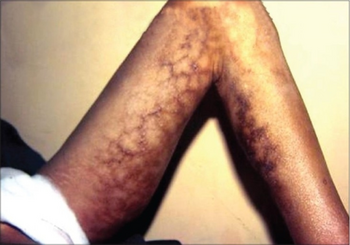 | |
| Erythema abigne on medial aspect of thigh and leg | |
| Specialty | Dermatology/oncology |
Kangri cancer is a type of squamous-cell carcinoma of the skin. It is found only in Kashmir in the northwest of the Indian subcontinent. It occurs on the lower abdomen and inner thighs and is due to the use of a kanger, a ceramic pot covered with wicker-work, carried as a source of warmth during cold weather. One of the earliest records of the condition was made in 1881 by surgeons at the Kashmir Mission Hospital and its cause was recognized in the early 20th century by Arthur Neve.[1][2]
Despite current knowledge of the cause of this condition, cases are still being reported.[3]
Other conditions associated with prolonged use of kangri in this fashion include erythema ab igne, a reticulate hypermelanosis with erythema.
Signs and symptoms
Most cases (80%) of squamous cell carcinoma attributed to ultraviolet radiation present in areas of the skin that are usually more exposed to sunlight (e.g., head, face, neck).[4] Although a particular form of squamous cell carcinoma, Kangri cancer is more often associated with the abdomen, thigh, and leg regions due to the usage and positioning of kangri pots, which come in close contact with these anatomical features.[5][6]
Over time, the use of kangri pots to keep warm results in erythema ab igne, a precancerous keratotic growth that “take the shape of superficial, serpegenous, reticular blackish brown colored lesions.”[6] Eventually, the cells at the lesion site become more irregular in shape and form; the lesions ulcerate and may become itchy and bloody. The resulting irregular growth is the presentation of kangri cancer.[4][6]
Risk factors
Use of the kangri pot is the principal cause of kangri cancer. The pot holds hot wood and charcoal, and is put in direct contact with the skin of the abdomen and the thigh areas as a way to keep warm during winter in northern India.[6] Elements that are believed to contribute to the development of kangri cancer are heat, burning wood particles, smoke, soot, and tar of burnt chinar leaves.[7][8]
In one study, researchers found that kangri cancer patients had a history of using a kangri for 5-6 hours a day, 3-4 months a year.[9]
Genetics
Beyond the behavioral risk factor of prolonged usage of kangri pots, researchers have begun to look at genetic mutations that may make some people more predisposed to develop kangri cancer.
- In one study, people with kangri cancer were found to be approximately twice as likely as a control group to have a mutation in the TP53 gene (codon 72 polymorphism). Patients with higher grade tumors exhibited more proline amino acid mutations at this site.[10]
- Another study confirmed the association of kangri Cancer and TP53, finding substitutions and insertions in 40% of the kangri cancer patients studied. The researchers observed a significant correlation with mutation status and age as well as with the presence of affected lymph nodes in patients. TP53 may, in the future, serve as “potential molecular marker and prognostic tool” for kangri cancer. Furthermore, PTEN mutations were found in two of thirty patients studied; though due to the small sample size, no useful conclusions could be postulated.[5]
- Two polymorphisms of the HSP70 gene were discovered to be correlated with poor prognosis in cases of kangri cancer; the “Hsp70-2 A/G or G/G and Hsp70homC/C genotypes” could potentially be utilized to measure risk of kangri cancer development as well as to predict prognosis.[11]
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of this condition can be done via the following:[citation needed]
- Medical history
- Physical examination
- Medical imaging
- Biopsy
Treatment
Surgery
In the treatment of kangri cancer, surgery is, most often, the first-line course of action to remove the primary tumor.[6]
Radiotherapy
External beam radiotherapy has been used in one person to prevent the relapse and growth of tumor metastases to the head and neck regions. The prophylactic applications of radiation have been noted as “encouraging” in this one case, reducing some tumors and eliminating others.[6]
Another study with a couple of the same authors found that radiotherapy after surgery helped with the reduction and cure of head and neck tumors in additional cases. The researchers suggest that external beam radiotherapy should be part of the treatment course for patients who have or at risk of developing tumors in the head and neck areas.[4]
Prognosis
A research article from 1923 noted that the average life expectancy of those with kangri cancer was about fifteen months, though there have been records of people dying within one year and living for more than twenty years with kangri cancer.[7] Updated life expectancy is not found in more recent scientific publications.
However, in 2013, it was noted that the progression from erythema ab igne to squamous cell carcinoma was between one and two decades.[9]
It has been reported that about one-third to one-half of patients with kangri cancer show metastasis to local lymph nodes.[4]
Epidemiology
The first case of kangri cancer was reportedly recognized in 1819.[6]
The incidence of kangri cancer is higher for those over age 50.[4][9]
There is no definitive predominance of kangri cancer in either males or females. Some studies may point to higher prevalence in males while others observed higher prevalence in females.[4][9]
In scientific literature, kangri cancer has only been attributed to the Kashmir region of northern India due to the traditional use of kangri pots. Kangri cancer is limited to this population, and thus, relatively little is known still, and there is much to be studied about the condition.[6][9][10]
In 2017, a local Kashmir media outlet, The Kashmir Reader, reported that researchers and health care providers are optimistic about the reduced incidence of kangri cancer, citing the rise of thermal clothing and electric heating sources that are now used in place of kangri pots to keep warm.[12]
See also
References
- ↑ Neve A (1900) Indian med. Gaz. 35, 81
- ↑ McCulloch HD (1910). "'Kangri cancer': A physiological aspect". Br Med J. 2 (2595): 912–913. doi:10.1136/bmj.2.2595.912-b. PMC 2336016.
- ↑ Wani I (2010). "Kangri cancer". Surgery. 147 (4): 586–588. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2009.10.025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 Teli, Mohmad Ashraf; Khan, N. A.; Darzi, M. Ashraf; Gupta, Meenu; Tufail, A. (2009-01-01). "Recurrence pattern in squamous cell carcinoma of skin of lower extremities and abdominal wall (Kangri cancer) in Kashmir valley of Indian subcontinent: impact of various treatment modalities". Indian Journal of Dermatology. 54 (4): 342–346. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.57610. ISSN 1998-3611. PMC 2807710. PMID 20101335.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Hussain, Ishraq; ul Rehman, Shakeel; Afroze, Dil; Zahoor, Lubna; Abdullah, Safiya; Hafiz, Adil; Shah, Zafar A.; Iqbal, Shabir; Shaffi, Mohammad (2009-05-31). "Mutational spectrum of conserved regions of TP53 and PTEN genes in Kangri cancer (of the skin) in the Kashmiri population". Mutation Research. 676 (1–2): 5–10. doi:10.1016/j.mrgentox.2009.02.011. ISSN 0027-5107. PMID 19486858.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 Teli, Ma; Darzi, Ma; Gupta, M.; Katoch, Ss (2008-07-01). "Recurrent Kangri cancer treated with external beam radiotherapy on a cobalt unit". Indian Journal of Cancer. 45 (3): 134–135. doi:10.4103/0019-509x.44074. ISSN 0019-509X. PMID 19018122. Archived from the original on 2021-09-29. Retrieved 2021-02-02.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Neve, E. F. (1923-12-29). "Kangri-Burn Cancer". British Medical Journal. 2 (3287): 1255–1256. doi:10.1136/bmj.2.3287.1255. ISSN 0007-1447. PMC 2317796. PMID 20771404.
- ↑ Gothoskar, S. V.; Ranadive, K. J. (1966-12-01). "Experimental studies on the aetiology of "Kangri cancer"". British Journal of Cancer. 20 (4): 751–755. doi:10.1038/bjc.1966.86. ISSN 0007-0920. PMC 2008146. PMID 5964606.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 Hassan, Iffat; Sajad, Peerzada; Reshi, Ruby (2013-05-01). "Histopathological analysis of the cutaneous changes due to kangri use in kashmiri population: a hospital based study". Indian Journal of Dermatology. 58 (3): 188–190. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.110825. ISSN 1998-3611. PMC 3667279. PMID 23723467.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Pandith, Arshad A.; Khan, Nighat P.; Rashid, Nargis; Azad, Niyaz; Zaroo, Inam; Hafiz, Adil; Siddiqi, Mushtaq A. (2012-08-01). "Impact of codon 72 Arg > Pro single nucleotide polymorphism in TP53 gene in the risk of kangri cancer: a case control study in Kashmir". Tumor Biology. 33 (4): 927–933. doi:10.1007/s13277-012-0318-2. ISSN 1423-0380. PMID 22249977.
- ↑ Rehman, Shakeel Ul; Sameer, A. Syed; Zahoor, Lubna; Syeed, Nidda; Nanda, Mahoor S.; Hafiz, Adil; Shah, Zaffar A.; Siddiqi, Mushtaq A. (2009-05-01). "Polymorphic analysis of MHClinked Heat Shock Protein 70 genes: Their susceptibility and prognostic implication in Kangri cancer cases of Kashmiri population". Indian Journal of Human Genetics. 15 (2): 65–71. doi:10.4103/0971-6866.55218. ISSN 0971-6866. PMC 2910951. PMID 20680154.
- ↑ Correspondent, Reader (2017-02-05). "Specific to Kashmir, Kangri cancer on decline". Kashmir Reader. Archived from the original on 2017-04-22. Retrieved 2017-04-21.