Scabies
| Scabies | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Seven-year itch[1] | |
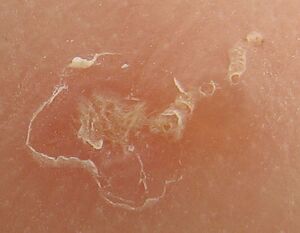 | |
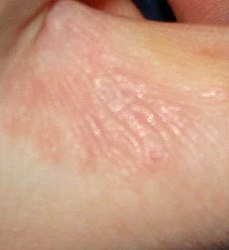
| Magnified view of a burrowing trail of the scabies mite. The scaly patch on the left was caused by scratching and marks the mite's entry point into the skin. The mite has burrowed to the top-right, where it can be seen as a dark spot at the end. | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease, dermatology |
| Symptoms | itchiness, pimple-like rash[2] |
| Usual onset | 2–6 weeks (first infection), ~1 day (subsequent infections)[2] |
| Causes | Sarcoptes scabiei mite spread by close contact[3] |
| Risk factors | Crowded living conditions (child care facilities, group homes, prisons), lack of access to water[3][4] |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms[5] |
| Differential diagnosis | Seborrheic dermatitis, dermatitis herpetiformis, pediculosis, atopic dermatitis[6] |
| Medication | Permethrin, crotamiton, lindane, ivermectin[7] |
| Frequency | 204 million / 2.8% (2015)[8] |
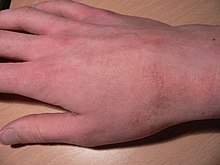
Scabies (also known as the seven-year itch) is a contagious skin infestation by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei.[1][3] The most common symptoms are severe itchiness and a pimple-like rash.[2] Occasionally, tiny burrows may appear on the skin.[2] In a first-ever infection, infected person will usually develop symptoms within two to six weeks.[2] During a second infection, symptoms may begin within 24 hours.[2] These symptoms can be present across most of the body or just certain areas such as the wrists, between fingers, or along the waistline.[2] The head may be affected, but this is typically only in young children.[2] The itch is often worse at night, or following a hot shower.[9] Scratching may cause skin breakdown and an additional bacterial infection in the skin.[2]
Scabies is caused by infection with the female mite Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis, an ectoparasite.[3] The mites burrow into the skin to live and deposit eggs.[3] The symptoms of scabies are due to an allergic reaction to the mites.[2] Often, only between 10 and 15 mites are involved in an infection.[2] Scabies is most often spread during a relatively long period of direct skin contact with an infected person (at least 10 minutes) such as that which may occur during sex or living together.[3][10] Spread of disease may occur even if the person has not developed symptoms yet.[11] Crowded living conditions, such as those found in child-care facilities, group homes, and prisons, increase the risk of spread.[3] Areas with a lack of access to water also have higher rates of disease.[4] Crusted scabies is a more severe form of the disease.[3] It typically only occurs in those with a poor immune system and people may have millions of mites, making them much more contagious.[3] In these cases, spread of infection may occur during brief contact or by contaminated objects.[3] The mite is very small and usually not directly visible.[3] Diagnosis is based on the signs and symptoms.[5]
A number of medications are available to treat those infected, including permethrin, crotamiton, and lindane creams and ivermectin pills.[7] Sexual contacts within the last month and people who live in the same house should also be treated at the same time.[11] Generally, repeat treatment after a week is suggested.[9] Bedding and clothing used in the last three days should be washed in hot water and dried in a hot dryer.[11] As the mite does not live for more than three days away from human skin, more washing is not needed.[11] Symptoms may continue for two to four weeks following treatment.[11] If after this time symptoms continue, retreatment may be needed.[11]
Scabies is one of the three most common skin disorders in children, along with ringworm and bacterial skin infections.[12] As of 2015, it affects about 204 million people (2.8% of the world population).[8] It is equally common in both sexes.[13] The young and the old are more commonly affected.[5] It also occurs more commonly in the developing world and tropical climates.[5] The word scabies is from Latin: scabere, "to scratch".[14] Other animals do not spread human scabies.[3] Infection in other animals is typically caused by slightly different but related mites and is known as sarcoptic mange.[15]
Signs and symptoms

The characteristic symptoms of a scabies infection include intense itching and superficial burrows.[17] Because the host develops the symptoms as a reaction to the mites' presence over time, typically a delay of four to six weeks occurs between the onset of infestation and the onset of itching. Similarly, symptoms often persist for one to several weeks after successful eradication of the mites. As noted, those re-exposed to scabies after successful treatment may exhibit symptoms of the new infestation in a much shorter period—as little as one to four days.[18]
Itching
In the classic scenario, the itch is made worse by warmth, and is usually experienced as being worse at night, possibly because distractions are fewer.[17] As a symptom, it is less common in the elderly.[17]
Rash
The superficial burrows of scabies usually occur in the area of the finger webs, feet, ventral wrists, elbows, back, buttocks, and external genitals.[17] Except in infants and the immunosuppressed, infection generally does not occur in the skin of the face or scalp. The burrows are created by excavation of the adult mite in the epidermis.[17]
In most people, the trails of the burrowing mites are linear or S-shaped tracks in the skin often accompanied by rows of small, pimple-like mosquito or insect bites. These signs are often found in crevices of the body, such as on the webs of fingers and toes, around the genital area, in stomach folds of the skin, and under the breasts of women.[19]
Symptoms typically appear two to six weeks after infestation for individuals never before exposed to scabies. For those having been previously exposed, the symptoms can appear within several days after infestation. However, symptoms may appear after several months or years.[20] Acropustulosis, or blisters and pustules on the palms and soles of the feet, are characteristic symptoms of scabies in infants.[19]
-
Scabies of the foot
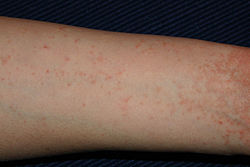
-
Scabies of the arm
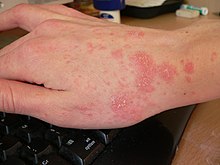
-
Scabies of the hand
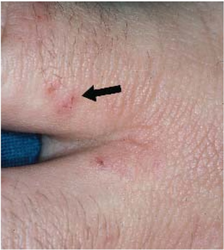
-
Scabies of the finger
-
Scabies infestation with visible burrow
Crusted scabies

The elderly, disabled, and people with an impaired immune system, such as those with HIV, cancer, or those on immunosuppressive medications, are susceptible to crusted scabies (also called Norwegian scabies).[17][20][21] On those with weaker immune systems, the host becomes a more fertile breeding ground for the mites, which spread over the host's body, except the face. The mites in crusted scabies are not more virulent than in noncrusted scabies; however, they are much more numerous (up to two million). People with crusted scabies exhibit scaly rashes, slight itching, and thick crusts of skin that contain large numbers of scabies mites. For this reason, persons with crusted scabies are more contagious to others than those with typical scabies.[3][22] Such areas make eradication of mites particularly difficult, as the crusts protect the mites from topical miticides/scabicides, necessitating prolonged treatment of these areas.[citation needed]
Cause
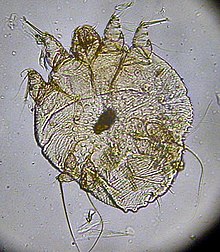
Scabies mite

In the 18th century, Italian biologists Giovanni Cosimo Bonomo and Diacinto Cestoni (1637–1718) described the mite now called Sarcoptes scabiei, variety hominis, as the cause of scabies. Sarcoptes is a genus of skin parasites and part of the larger family of mites collectively known as scab mites. These organisms have eight legs as adults, and are placed in the same phylogenetic class (Arachnida) as spiders and ticks.[citation needed]
S. scabiei mites are under 0.5 mm in size, but are sometimes visible as pinpoints of white. Gravid females tunnel into the dead, outermost layer (stratum corneum) of a host's skin and deposit eggs in the shallow burrows. The eggs hatch into larvae in three to ten days. These young mites move about on the skin and molt into a "nymphal" stage, before maturing as adults, which live three to four weeks in the host's skin. Males roam on top of the skin, occasionally burrowing into the skin. In general, the total number of adult mites infesting a healthy hygienic person with noncrusted scabies is small, about 11 females in burrows, on average.[23]
The movement of mites within and on the skin produces an intense itch, which has the characteristics of a delayed cell-mediated inflammatory response to allergens. IgE antibodies are present in the serum and the site of infection, which react to multiple protein allergens in the body of the mite. Some of these cross-react to allergens from house dust mites. Immediate antibody-mediated allergic reactions (wheals) have been elicited in infected persons, but not in healthy persons; immediate hypersensitivity of this type is thought to explain the observed far more rapid allergic skin response to reinfection seen in persons having been previously infected (especially having been infected within the previous year or two).[24]
Transmission
Scabies is contagious and can be contracted through prolonged physical contact with an infested person.[25] This includes sexual intercourse, although a majority of cases are acquired through other forms of skin-to-skin contact. Less commonly, scabies infestation can happen through the sharing of clothes, towels, and bedding, but this is not a major mode of transmission; individual mites can survive for only two to three days, at most, away from human skin at room temperature.[26][27] As with lice, a latex condom is ineffective against scabies transmission during intercourse, because mites typically migrate from one individual to the next at sites other than the sex organs.[28]
Healthcare workers are at risk of contracting scabies from patients, because they may be in extended contact with them.[29]
Pathophysiology
The symptoms are caused by an allergic reaction of the host's body to mite proteins, though exactly which proteins remains a topic of study. The mite proteins are also present from the gut, in mite feces, which are deposited under the skin. The allergic reaction is both of the delayed (cell-mediated) and immediate (antibody-mediated) type, and involves IgE (antibodies are presumed to mediate the very rapid symptoms on reinfection).[23] The allergy-type symptoms (itching) continue for some days, and even several weeks, after all mites are killed. New lesions may appear for a few days after mites are eradicated. Nodular lesions from scabies may continue to be symptomatic for weeks after the mites have been killed.[23]
Rates of scabies are negatively related to temperature and positively related to humidity.[30]
Diagnosis
Scabies may be diagnosed clinically in geographical areas where it is common when diffuse itching presents along with either lesions in two typical spots or itchiness is present in another household member.[12] The classical sign of scabies is the burrow made by a mite within the skin.[12] To detect the burrow, the suspected area is rubbed with ink from a fountain pen or a topical tetracycline solution, which glows under a special light. The skin is then wiped with an alcohol pad. If the person is infected with scabies, the characteristic zigzag or S pattern of the burrow will appear across the skin; however, interpreting this test may be difficult, as the burrows are scarce and may be obscured by scratch marks.[12] A definitive diagnosis is made by finding either the scabies mites or their eggs and fecal pellets.[12] Searches for these signs involve either scraping a suspected area, mounting the sample in potassium hydroxide and examining it under a microscope, or using dermoscopy to examine the skin directly.[17]
Differential diagnosis
Symptoms of early scabies infestation mirror other skin diseases, including dermatitis, syphilis, erythema multiforme, various urticaria-related syndromes, allergic reactions, ringworm-related diseases, and other ectoparasites such as lice and fleas.[31]
Prevention
Mass-treatment programs that use topical permethrin or oral ivermectin have been effective in reducing the prevalence of scabies in a number of populations.[12] No vaccine is available for scabies. The simultaneous treatment of all close contacts is recommended, even if they show no symptoms of infection (asymptomatic), to reduce rates of recurrence.[12] Since mites can survive for only two to three days without a host, other objects in the environment pose little risk of transmission except in the case of crusted scabies. Therefore cleaning is of little importance.[12] Rooms used by those with crusted scabies require thorough cleaning.[32]
Management
A number of medications are effective in treating scabies. Treatment should involve the entire household, and any others who have had recent, prolonged contact with the infested individual.[12] Options to control itchiness include antihistamines and prescription anti-inflammatory agents.[33] Bedding, clothing and towels used during the previous three days should be washed in hot water and dried in a hot dryer.[34]
Permethrin
Permethrin, a pyrethroid insecticide, is the most effective treatment for scabies,[35] and remains the treatment of choice.[12][36] It is applied from the neck down, usually before sleep, and left on for about eight to 14 hours, then washed off in the morning.[12] Care should be taken to coat the entire skin surface, not just symptomatic areas; any patch of skin left untreated can provide a "safe haven" for one or more mites to survive. One application is normally sufficient, as permethrin kills eggs and hatchlings, as well as adult mites, though many physicians recommend a second application three to seven days later as a precaution. Crusted scabies may require multiple applications, or supplemental treatment with oral ivermectin (below).[12][36][37] Permethrin may cause slight irritation of the skin that is usually tolerable.[17]
Ivermectin
Oral ivermectin is effective in eradicating scabies, often in a single dose.[4][12] It is the treatment of choice for crusted scabies, and is sometimes prescribed in combination with a topical agent.[12][17] It has not been tested on infants, and is not recommended for children under six years of age.[17]
Topical ivermectin preparations have been shown to be effective for scabies in adults, though only one such formulation is available in the United States at present, and it is not FDA-approved as a scabies treatment.[38] It has also been useful for sarcoptic mange (the veterinary analog of human scabies).[39][40] conditions.
Others
Other treatments include lindane, benzyl benzoate, crotamiton, malathion, and sulfur preparations.[12][17] Lindane is effective, but concerns over potential neurotoxicity have limited its availability in many countries.[17] It is banned in California,[41] but may be used in other states as a second-line treatment.[42] Sulfur ointments or benzyl benzoate are often used in the developing world due to their low cost;[17] Some 10% sulfur solutions have been shown to be effective,[43] and sulfur ointments are typically used for at least a week, though many people find the odor of sulfur products unpleasant.[17] Crotamiton has been found to be less effective than permethrin in limited studies.[17] Crotamiton or sulfur preparations are sometimes recommended instead of permethrin for children, due to concerns over dermal absorption of permethrin.[12]
-
Day 4
-
Day 8 (treatment begins)
-
Day 12 (under treatment)
-
Healed
Communities
Scabies is endemic in many developing countries,[44] where it tends to be particularly problematic in rural and remote areas. In such settings, community-wide control strategies are required to reduce the rate of disease, as treatment of only individuals is ineffective due to the high rate of reinfection. Large-scale mass drug administration strategies may be required where coordinated interventions aim to treat whole communities in one concerted effort.[45] Although such strategies have shown to be able to reduce the burden of scabies in these kinds of communities, debate remains about the best strategy to adopt, including the choice of drug.[45][46]
The resources required to implement such large-scale interventions in a cost-effective and sustainable way are significant. Furthermore, since endemic scabies is largely restricted to poor and remote areas, it is a public health issue that has not attracted much attention from policy makers and international donors.[45][46]
Epidemiology
Scabies is one of the three most common skin disorders in children, along with tinea and pyoderma.[12] As of 2010, it affects about 100 million people (1.5% of the population) and its frequency is not related to gender.[13] The mites are distributed around the world and equally infect all ages, races, and socioeconomic classes in different climates.[22] Scabies is more often seen in crowded areas with unhygienic living conditions.[47] Globally as of 2009, an estimated 300 million cases of scabies occur each year, although various parties claim the figure is either over- or underestimated.[20][48] About 1–10% of the global population is estimated to be infected with scabies, but in certain populations, the infection rate may be as high as 50–80%.[12]
History

Scabies has been observed in humans since ancient times. Archeological evidence from Egypt and the Middle East suggests scabies was present as early as 494 BC.[18][49] In the fourth century BC, Aristotle reported on "lice" that "escape from little pimples if they are pricked" – a description consistent with scabies.[50] Arab physician, Ibn Zuhr is believed to have been the first to discover the scabies mites.[51]
The Roman encyclopedist and medical writer Aulus Cornelius Celsus (c. 25 BC – 50 AD) is credited with naming the disease "scabies" and describing its characteristic features.[50] The parasitic etiology of scabies was documented by the Italian physician Giovanni Cosimo Bonomo (1663–1696) in his 1687 letter, "Observations concerning the fleshworms of the human body".[50] Bonomo's description established scabies as one of the first human diseases with a well-understood cause.[18][49]
In Europe in the late 19th through mid-20th centuries, a sulfur-bearing ointment called by the medical eponym of Wilkinson's ointment was widely used for topical treatment of scabies. The contents and origins of several versions of the ointment were detailed in correspondence published in the British Medical Journal in 1945.[52]
Society and culture

The International Alliance for the Control of Scabies was started in 2012,[5][46][53] and brings together over 150 researchers, clinicians, and public-health experts from more than 15 different countries. It has managed to bring the global health implications of scabies to the attention of the World Health Organization.[46] Consequently, the WHO has included scabies on its official list of neglected tropical diseases and other neglected conditions.[54]
Scabies in animals

Scabies may occur in a number of domestic and wild animals; the mites that cause these infestations are of different subspecies from the one typically causing the human form.[17] These subspecies can infest animals that are not their usual hosts, but such infections do not last long.[17] Scabies-infected animals suffer severe itching and secondary skin infections. They often lose weight and become frail.[23]
The most frequently diagnosed form of scabies in domestic animals is sarcoptic mange, caused by the subspecies Sarcoptes scabiei canis, most commonly in dogs and cats. Sarcoptic mange is transmissible to humans who come into prolonged contact with infested animals,[55] and is distinguished from human scabies by its distribution on skin surfaces covered by clothing. Scabies-infected domestic fowl suffer what is known as "scaly leg". Domestic animals that have gone feral and have no veterinary care are frequently afflicted with scabies and a host of other ailments.[56] Nondomestic animals have also been observed to suffer from scabies. Gorillas, for instance, are known to be susceptible to infection by contact with items used by humans.[57]
Research
Moxidectin is being evaluated as a treatment for scabies.[58] It is established in veterinary medicine to treat a range of parasites, including sarcoptic mange. Its advantage over ivermectin is its longer half life in humans and, thus, potential duration of action.[59] Tea tree oil appears to be effective in the laboratory setting.[60]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Gates, Robert H. (2003). Infectious disease secrets (2nd ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier, Hanley Belfus. p. 355. ISBN 978-1-56053-543-0. Archived from the original on 2021-08-29. Retrieved 2020-07-30.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 "Parasites – Scabies Disease". Center for Disease Control and Prevention. November 2, 2010. Archived from the original on 2 May 2015. Retrieved 18 May 2015.
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 "Epidemiology & Risk Factors". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. November 2, 2010. Archived from the original on 29 April 2015. Retrieved 18 May 2015.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "WHO -Water-related Disease". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 2010-10-22. Retrieved 2010-10-10.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 "Scabies". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 18 May 2015. Retrieved 18 May 2015.
- ↑ Ferri, Fred F. (2010). "Chapter S". Ferri's differential diagnosis : a practical guide to the differential diagnosis of symptoms, signs, and clinical disorders (2nd ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Mosby. ISBN 978-0323076999.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Parasites – Scabies Medications". Center for Disease Control and Prevention. November 2, 2010. Archived from the original on 30 April 2015. Retrieved 18 May 2015.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence, Collaborators. (8 October 2016). "Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015". Lancet. 388 (10053): 1545–1602. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6. PMC 5055577. PMID 27733282.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Bolognia, Jean L.; Schaffer, Julie V.; Duncan, Karynne O.; Ko, Christine (2022). "71. Infestations: scabies". Dermatology Essentials (2nd ed.). Elsevier. pp. 733–737. ISBN 978-0-323-70971-2. Archived from the original on 2024-02-12. Retrieved 2024-02-12.
- ↑ Dressler, C; Rosumeck, S; Sunderkötter, C; Werner, RN; Nast, A (14 November 2016). "The Treatment of Scabies". Deutsches Ärzteblatt International. 113 (45): 757–62. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2016.0757. PMC 5165060. PMID 27974144.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 11.5 "Parasites - Scabies Treatment". Center for Disease Control and Prevention. November 2, 2010. Archived from the original on 28 April 2015. Retrieved 18 May 2015.
- ↑ 12.00 12.01 12.02 12.03 12.04 12.05 12.06 12.07 12.08 12.09 12.10 12.11 12.12 12.13 12.14 12.15 12.16 12.17 Andrews RM, McCarthy J, Carapetis JR, Currie BJ (December 2009). "Skin disorders, including pyoderma, scabies, and tinea infections". Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 56 (6): 1421–40. doi:10.1016/j.pcl.2009.09.002. PMID 19962029.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Vos, T (Dec 15, 2012). "Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010". Lancet. 380 (9859): 2163–96. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2. PMC 6350784. PMID 23245607. Archived from the original on January 12, 2019. Retrieved July 30, 2020.
- ↑ Mosby's Medical, Nursing & Allied Health Dictionary (4 ed.). Mosby-Year Book Inc. 1994. p. 1395. ISBN 9780801672255.
- ↑ Georgis' Parasitology for Veterinarians (10 ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. 2014. p. 68. ISBN 9781455739882. Archived from the original on 2021-08-29. Retrieved 2020-07-30.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 CDC web site > DPDx – Laboratory Identification of Parasites of Public Health Concern > Scabies "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2009-02-20. Retrieved 2009-02-09.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ 17.00 17.01 17.02 17.03 17.04 17.05 17.06 17.07 17.08 17.09 17.10 17.11 17.12 17.13 17.14 17.15 17.16 Hay RJ (2009). "Scabies and pyodermas—diagnosis and treatment". Dermatol Ther. 22 (6): 466–74. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8019.2009.01270.x. PMID 19889132.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 Markell, Edward K.; John, David C.; Petri, William H. (2006). Markell and Voge's medical parasitology (9th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. ISBN 978-0-7216-4793-7.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 "Scabies" (PDF). DermNet NZ. New Zealand Dermatological Society Incorporated. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-03-27.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 Bouvresse, S.; Chosidow, O. (Apr 2010). "Scabies in healthcare settings". Curr Opin Infect Dis. 23 (2): 111–18. doi:10.1097/QCO.0b013e328336821b. PMID 20075729. S2CID 206001293.
- ↑ Hicks MI, Elston DM (2009). "Scabies". Dermatol Ther. 22 (4): 279–92. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8019.2009.01243.x. PMID 19580575.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 "DPDx – Scabies". Laboratory Identification of Parasites of Public Health Concern. CDC. Archived from the original on 2009-02-20.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 23.2 23.3 Walton, SF; Currie, BJ (April 2007). "Problems in Diagnosing Scabies, a Global Disease in Human and Animal Populations". Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 20 (2): 268–79. doi:10.1128/CMR.00042-06. PMC 1865595. PMID 17428886.
- ↑ Walton SF, Currie BJ (2007). "Problems in Diagnosing Scabies, a Global Disease in Human and Animal Populations". Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 20 (2): 268–79. doi:10.1128/CMR.00042-06. PMC 1865595. PMID 17428886.
- ↑ Carol Turkington; Jeffrey S. Dover, M.D. (2006). The Encyclopedia of Skin and Skin Disorders. New York: Facts on File inc. ISBN 978-0-8160-6403-8.
- ↑ "Scabies Causes". WebMD. October 2010. Archived from the original on 2010-09-22. Retrieved 2010-10-09.
- ↑ Chosidow O (April 2006). "Clinical practices. Scabies". N. Engl. J. Med. 354 (16): 1718–27. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp052784. PMID 16625010.
- ↑ "Scabies – Fast Facts". American Social Health Association. Archived from the original on 2011-04-22. Retrieved 2010-10-09.
- ↑ FitzGerald, Deirdre; Grainger, Rachel J.; Reid, Alex (2014). "Interventions for preventing the spread of infestation in close contacts of people with scabies". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2 (2): CD009943. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009943.pub2. ISSN 1469-493X. PMID 24566946.
- ↑ Liu, Jui-Ming; Wang, Hsiao-Wei; Chang, Fung-Wei; Liu, Yueh-Ping; Chiu, Feng-Hsiang; Lin, Yi-Chun; Cheng, Kuan-Chen; Hsu, Ren-Jun (2016). "The effects of climate factors on scabies. A 14-year population-based study in Taiwan". Parasite. 23: 54. doi:10.1051/parasite/2016065. ISSN 1776-1042. PMC 5134670. PMID 27905271. Archived from the original on 2020-07-27. Retrieved 2020-07-30.

- ↑ Arlian, LG (1989). "Biology, host relations, and epidemiology of Sarcoptes scabiei". Annual Review of Entomology. 34 (1): 139–61. doi:10.1146/annurev.en.34.010189.001035. PMID 2494934.
- ↑ "Prevention and Control – Scabies". Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Archived from the original on 2010-03-07. Retrieved 2010-10-09.
- ↑ Vañó-Galván, S; Moreno-Martin, P (2008). "Generalized pruritus after a beach vacation. Diagnosis: scabies". Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine. 75 (7): 474, 478. doi:10.3949/ccjm.75.7.474. PMID 18646583.
- ↑ "Parasites - Scabies". cdc.gov. November 2, 2010. Archived from the original on 11 December 2014. Retrieved 11 December 2014.
- ↑ Strong M, Johnstone PW (2007). Strong M (ed.). "Interventions for treating scabies". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (3): CD000320. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000320.pub2. PMC 6532717. PMID 17636630.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 "Scabies". Illinois Department of Public Health. January 2008. Archived from the original on 2010-12-05. Retrieved 2010-10-07.
- ↑ The Pill Book. Bantam Books. 2010. pp. 867–69. ISBN 978-0-553-59340-2.
- ↑ Victoria J, Trujillo R (2001). "Topical ivermectin: a new successful treatment for scabies". Pediatr Dermatol. 18 (1): 63–65. doi:10.1046/j.1525-1470.2001.018001063.x. PMID 11207977.
- ↑ Soll M. D., d'Assonville J. A., Smith C. J. Z. (1992). "Efficacy of topically applied invermectin against sarcoptic mange (Sarcoptes scabiei var.bovis) of cattle". Parasitology Research. 78 (2): 120–122. doi:10.1007/BF00931652. PMID 1557323. S2CID 28579947.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Carr, Patrick C.; Brodell, Robert T. (17 March 2016). "Scabies". New England Journal of Medicine. 374 (11): e13. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm1500116. ISSN 0028-4793. PMID 26981951.
- ↑ Humphreys, EH; Janssen, S; Heil, A; Hiatt, P; Solomon, G; Miller, MD (March 2008). "Outcomes of the California ban on pharmaceutical lindane: clinical and ecologic impacts". Environmental Health Perspectives. 116 (3): 297–302. doi:10.1289/ehp.10668. PMC 2265033. PMID 18335094.
- ↑ "FDA Public Health Advisory: Safety of Topical Lindane Products for the Treatment of Scabies and Lice". Fda.gov. 2009-04-30. Archived from the original on 2010-11-26. Retrieved 2010-11-14.
- ↑ Jin-Gang A, Sheng-Xiang X, Sheng-Bin X, et al. (March 2010). "Quality of life of patients with scabies". J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 24 (10): 1187–91. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2010.03618.x. PMID 20236379.
- ↑ Andrews, RM; McCarthy, J; Carapetis, JR; Currie, BJ (Dec 2009). "Skin disorders, including pyoderma, scabies, and tinea infections". Pediatric Clinics of North America. 56 (6): 1421–40. doi:10.1016/j.pcl.2009.09.002. PMID 19962029.
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 45.2 Hay, RJ; Steer, AC; Chosidow, O; Currie, BJ (Apr 2013). "Scabies: a suitable case for a global control initiative". Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases. 26 (2): 107–09. doi:10.1097/QCO.0b013e32835e085b. PMID 23302759. S2CID 26416151.
- ↑ 46.0 46.1 46.2 46.3 Engelman, D; Kiang, K; Chosidow, O; McCarthy, J; Fuller, C; Lammie, P; Hay, R; Steer, A; Members Of The International Alliance For The Control Of, Scabies (2013). "Toward the global control of human scabies: introducing the International Alliance for the Control of Scabies". PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 7 (8): e2167. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0002167. PMC 3738445. PMID 23951369.
- ↑ Green MS (1989). "Epidemiology of scabies". Epidemiol Rev. 11 (1): 126–50. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036033. PMID 2509232.
- ↑ Hicks, MI; Elston, DM (Jul–Aug 2009). "Scabies". Dermatologic Therapy. 22 (4): 279–92. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8019.2009.01243.x. PMID 19580575.
- ↑ 49.0 49.1 "Scabies homepage". Stanford University. Archived from the original on 2010-05-13. Retrieved 2010-10-09.
- ↑ 50.0 50.1 50.2 Roncalli RA (July 1987). "The history of scabies in veterinary and human medicine from biblical to modern times". Vet. Parasitol. 25 (2): 193–98. doi:10.1016/0304-4017(87)90104-X. PMID 3307123.
- ↑ "Ibn Zuhr". Archived from the original on 2020-02-29.
- ↑ Goldsmith, WN (1945), "Wilkinson's ointment", Br Med J, 1 (4392): 347–48, doi:10.1136/bmj.1.4392.347-c, PMC 2056959.
- ↑ "International Alliance for the Control of Scabies". International Alliance for the Control of Scabies. Archived from the original on 2 February 2014. Retrieved 1 February 2014.
- ↑ "The 17 neglected tropical diseases". Neglected tropical diseases. World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 1 February 2014.
- ↑ Borgman W (June 30, 2006). Dog mange called scabies can transfer to humans. Orlando Sentinel archive Dog mange called scabies can transfer to humans - Orlando Sentinel at the Wayback Machine (archived 2015-02-16). Retrieved February 16, 2015.
- ↑ "Bali Animal Welfare Association". Archived from the original on 2010-02-26. Retrieved 2009-07-28.
- ↑ "Uganda: Out of the Wild". Frontline. PBS. Archived from the original on 2013-11-05. Transcript | A Death In Tehran | FRONTLINE | PBS (section on rare diseases in Uganda). Retrieved Nov 4, 2013.
{{cite episode}}: Cite uses deprecated parameter|transcripturl=(help) - ↑ Mounsey, Kate E.; Bernigaud, Charlotte; Chosidow, Olivier; McCarthy, James S. (2016-03-17). "Prospects for Moxidectin as a New Oral Treatment for Human Scabies". PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 10 (3): e0004389. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0004389. ISSN 1935-2727. PMC 4795782. PMID 26985995.
- ↑ Prichard, Roger; Ménez, Cécile; Lespine, Anne (2012-12-01). "Moxidectin and the avermectins: Consanguinity but not identity". International Journal for Parasitology. Drugs and Drug Resistance. 2: 134–53. doi:10.1016/j.ijpddr.2012.04.001. ISSN 2211-3207. PMC 3862425. PMID 24533275.
- ↑ Thomas, Jackson; Dettwiller, Pascale; Spelman, Tim; Carson, Christine F.; Davey, Rachel C.; Baby, Kavya E.; Cooper, Gabrielle M.; Kyle, Greg; Naunton, Mark (2016-02-03). "Therapeutic Potential of Tea Tree Oil for Scabies". The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 94 (2): 258–266. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.14-0515. ISSN 0002-9637. PMC 4751955. PMID 26787146.
External links
- American Academy of Dermatology pamphlet on Scabies Archived 2013-03-20 at the Wayback Machine
- Scabies FAQ from the National Pediculosis Association Archived 2019-06-05 at the Wayback Machine
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
- Pages with script errors
- CS1 maint: archived copy as title
- CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list
- Webarchive template wayback links
- CS1 errors: deprecated parameters
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Articles containing Latin-language text
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from July 2020
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- Parasitic infestations, stings, and bites of the skin
- Arthropod infestations
- Neglected tropical diseases
- Tropical diseases
- Articles containing video clips
- RTT
- RTTID