Filariasis
| Filariasis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Life cycle of Wuchereria bancrofti, a parasite that causes filariasis | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Frequency | 120 million people worldwide[1] |
Filariasis is a parasitic disease caused by an infection with roundworms of the Filarioidea type.[2] These are spread by blood-feeding insects such as black flies and mosquitoes. They belong to the group of diseases called helminthiases.
These parasites exist in the wild in subtropical parts of southern Asia, Africa, the South Pacific, and parts of South America. One does not acquire them in the Northern Hemisphere like Europe or the US.[3]
Eight known filarial worms have humans as a definitive host. These are divided into three groups according to the part of the body they affect:
- Lymphatic filariasis is caused by the worms Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi, and Brugia timori. These worms occupy the lymphatic system, including the lymph nodes; in chronic cases, these worms lead to the syndrome of elephantiasis.
- Subcutaneous filariasis is caused by Loa loa (the eye worm), Mansonella streptocerca, and Onchocerca volvulus. These worms occupy the layer just under the skin. L. loa causes Loa loa filariasis, while O. volvulus causes river blindness.
- Serous cavity filariasis is caused by the worms Mansonella perstans and Mansonella ozzardi, which occupy the serous cavity of the abdomen. Dirofilaria immitis, the dog heartworm, rarely infects humans.
The adult worms, which usually stay in one tissue, release early larval forms known as microfilariae into the person's blood. These circulating microfilariae can be taken up during a blood meal by an insect vector; in the vector, they develop into infective larvae that can be spread to another person.
Individuals infected by filarial worms may be described as either "microfilaraemic" or "amicrofilaraemic", depending on whether microfilariae can be found in their peripheral blood. Filariasis is diagnosed in microfilaraemic cases primarily through direct observation of microfilariae in the peripheral blood. Occult filariasis is diagnosed in amicrofilaraemic cases based on clinical observations and, in some cases, by finding a circulating antigen in the blood.
Signs and symptoms
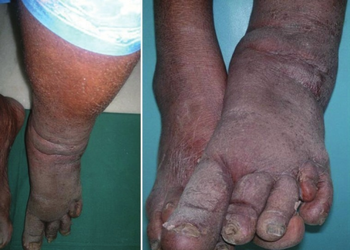
The most spectacular symptom of lymphatic filariasis is elephantiasis – edema with thickening of the skin and underlying tissues—which was the first disease discovered to be transmitted by mosquito bites.[4] Elephantiasis results when the parasites lodge in the lymphatic system.[citation needed]
Elephantiasis affects mainly the lower extremities, while the ears, mucous membranes, and amputation stumps are affected less frequently. However, different species of filarial worms tend to affect different parts of the body; Wuchereria bancrofti can affect the legs, arms, vulva, breasts, and scrotum (causing hydrocele formation), while Brugia timori rarely affects the genitals.[citation needed] Those who develop the chronic stages of elephantiasis are usually free from microfilariae (amicrofilaraemic), and often have adverse immunological reactions to the microfilariae, as well as the adult worms.[4]
The subcutaneous worms present with rashes, urticarial papules, and arthritis, as well as hyper- and hypopigmentation macules. Onchocerca volvulus manifests itself in the eyes, causing "river blindness" (onchocerciasis), one of the leading causes of blindness in the world.[citation needed] Serous cavity filariasis presents with symptoms similar to subcutaneous filariasis, in addition to abdominal pain, because these worms are also deep-tissue dwellers.[citation needed]
Cause
Human filarial nematode worms have complicated life cycles, which primarily consists of five stages. After the male and female worms mate, the female gives birth to live microfilariae by the thousands. The microfilariae are taken up by the vector insect (intermediate host) during a blood meal. In the intermediate host, the microfilariae molt and develop into third-stage (infective) larvae. Upon taking another blood meal, the vector insect, such as Culex pipiens, injects the infectious larvae into the dermis layer of the skin. After about one year, the larvae molt through two more stages, maturing into the adult worms.[citation needed]
Diagnosis
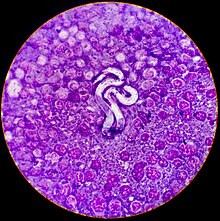
Filariasis is usually diagnosed by identifying microfilariae on Giemsa stained, thin and thick blood film smears, using the "gold standard" known as the finger prick test. The finger prick test draws blood from the capillaries of the finger tip; larger veins can be used for blood extraction, but strict windows of the time of day must be observed. Blood must be drawn at appropriate times, which reflect the feeding activities of the vector insects. Examples are W. bancrofti, whose vector is a mosquito; night is the preferred time for blood collection. Loa loa's vector is the deer fly; daytime collection is preferred.[6] This method of diagnosis is only relevant to microfilariae that use the blood as transport from the lungs to the skin. Some filarial worms, such as M. streptocerca and O. volvulus, produce microfilariae that do not use the blood; they reside in the skin only. For these worms, diagnosis relies upon skin snips and can be carried out at any time.[citation needed]
Concentration methods
Various concentration methods are applied: membrane filter, Knott's concentration method, and sedimentation technique.[citation needed]
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and antigenic assays, which detect circulating filarial antigens, are also available for making the diagnosis. The latter are particularly useful in amicrofilaraemic cases. Spot tests for antigen[7] are far more sensitive, and allow the test to be done anytime, rather in the late hours.
Lymph node aspirate and chylous fluid may also yield microfilariae. Medical imaging, such as CT or MRI, may reveal "filarial dance sign" in the chylous fluid; X-ray tests can show calcified adult worms in lymphatics. The DEC provocation test is performed to obtain satisfying numbers of parasites in daytime samples. Xenodiagnosis is now obsolete, and eosinophilia is a nonspecific primary sign.[citation needed]
Treatment

The recommended treatment for people outside the United States is albendazole combined with ivermectin.[8][9] A combination of diethylcarbamazine and albendazole is also effective.[8][10] Side effects of the drugs include nausea, vomiting, and headaches.[11] All of these treatments are microfilaricides; they have no effect on the adult worms. While the drugs are critical for treatment of the individual, proper hygiene is also required.[12] There is good evidence that albendazole alone; or addition of albendazole to diethylcarbamazine or ivermectin, makes minimal difference in clearing microfilaria or adult worms from blood circulation.[13] Diethylcarbamazine-medicated salt is effective in controlling lymphatic filariasis while maintaining its coverage at 90% in the community for six months.[14]
Different trials were made to use the known drug at its maximum capacity in absence of new drugs. In a study from India, it was shown that a formulation of albendazole had better anti-filarial efficacy than albendazole itself.[15][non-primary source needed]
In 2003, the common antibiotic doxycycline was suggested for treating elephantiasis.[16] Filarial parasites have symbiotic bacteria in the genus Wolbachia, which live inside the worm and seem to play a major role in both its reproduction and the development of the disease. This drug has shown signs of inhibiting the reproduction of the bacteria, further inducing sterility.[10] Clinical trials in June 2005 by the Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine reported an eight-week course almost completely eliminated microfilaraemia.[17][non-primary source needed] [18]
Society and culture
Research teams
In 2015 William C. Campbell and Satoshi Ōmura were co-awarded half of that year's Nobel prize in Physiology or Medicine for the discovery of the drug avermectin, which, in the further developed form ivermectin, has decreased the occurrence of lymphatic filariasis.[18]
Prospects for elimination
Filarial diseases in humans offer prospects for elimination by means of vermicidal treatment. If the human link in the chain of infection can be broken, then notionally the disease could be wiped out in a season. In practice it is not quite so simple, and there are complications in that multiple species overlap in certain regions and double infections are common. This creates difficulties for routine mass treatment because people with onchocerciasis in particular react badly to treatment for lymphatic filariasis.[19]
Other animals
Filariasis can also affect domesticated animals, such as cattle, sheep, and dogs.
Cattle
- Verminous hemorrhagic dermatitis is a clinical disease in cattle due to Parafilaria bovicola.
- Intradermal onchocerciasis of cattle results in losses in leather due to Onchocerca dermata, O. ochengi, and O. dukei. O. ochengi is closely related to human O. volvulus (river blindness), sharing the same vector, and could be useful in human medicine research.
- Stenofilaria assamensis and others cause different diseases in Asia, in cattle and zebu.
Horses
- "Summer bleeding" is hemorrhagic subcutaneous nodules in the head and upper forelimbs, caused by Parafilaria multipapillosa (North Africa, Southern and Eastern Europe, Asia and South America).[20]
Dogs
- Heart filariasis is caused by Dirofilaria immitis.
See also
- Ascariasis
- Eradication of infectious diseases
- Helminthiasis
- List of parasites (human)
- Neglected tropical diseases
References
- ↑ Morris-Jones, Rachael (2019). "18. Tropical dermatology". In Morris-Jones, Rachael (ed.). ABC of Dermatology (7th ed.). Hoboken: Wiley Blackwell. pp. 153–154. ISBN 978-1-119-48899-6. Archived from the original on 16 May 2022. Retrieved 17 May 2022.
- ↑ Center for Disease Control and Prevention. "Lymphatic Filariasis". Archived from the original on 27 May 2010. Retrieved 18 July 2010.
- ↑ "CDC — Lymphatic Filariasis FAQ". Archived from the original on 15 February 2015. Retrieved 13 March 2022.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Lymphatic filariasis". Health Topics A to Z. Source: The World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 18 September 2011. Retrieved 24 March 2013.
- ↑ Wheeler L. "Microfilaria of Dirofilaria immitis (Heartworms) Surrounded by Neoplastic Lymphocytes". Flickr. Archived from the original on 17 May 2022. Retrieved 2 December 2017.
- ↑ Metzger, Wolfram Gottfried; Mordmüller, Benjamin (April 2014). "Loa loa—does it deserve to be neglected?". The Lancet Infectious Diseases. 14 (4): 353–357. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70263-9. PMID 24332895. Archived from the original on 12 February 2022. Retrieved 13 March 2022.
- ↑ "Seva Fila" (PDF). JB Tropical Disease Research Centre & Department of Biochemistry, Mahatma Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 March 2012. Retrieved 13 March 2022.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 The Carter Center, Lymphatic Filariasis Elimination Program, archived from the original on 20 July 2008, retrieved 17 July 2008
- ↑ U.S. Centers for Disease Control, Lymphatic Filariasis Treatment, archived from the original on 4 May 2010, retrieved 17 July 2008
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Taylor MJ, Hoerauf A, Bockarie M (October 2010). "Lymphatic filariasis and onchocerciasis". Lancet. 376 (9747): 1175–85. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(10)60586-7. PMID 20739055. S2CID 29589578.
- ↑ Turkington CA. "Filariasis". The Gale Encyclopedia of Public Health. 1: 351–353.
- ↑ Hewitt K, Whitworth JA (1 August 2005). "Filariasis". Medicine. 33 (8): 61–64. doi:10.1383/medc.2005.33.8.61.
- ↑ Macfarlane CL, Budhathoki SS, Johnson S, Richardson M, Garner P (January 2019). "Albendazole alone or in combination with microfilaricidal drugs for lymphatic filariasis". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1 (1): CD003753. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003753.pub4. PMC 6354574. PMID 30620051.
- ↑ Adinarayanan S, Critchley J, Das PK, Gelband H, et al. (Cochrane Infectious Diseases Group) (January 2007). "Diethylcarbamazine (DEC)-medicated salt for community-based control of lymphatic filariasis". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (1): CD003758. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003758.pub2. PMC 6532694. PMID 17253495.
- ↑ Gaur RL, Dixit S, Sahoo MK, Khanna M, Singh S, Murthy PK (April 2007). "Anti-filarial activity of novel formulations of albendazole against experimental brugian filariasis". Parasitology. 134 (Pt 4): 537–44. doi:10.1017/S0031182006001612. PMID 17078904. S2CID 24567214.
- ↑ Hoerauf A, Mand S, Fischer K, Kruppa T, Marfo-Debrekyei Y, Debrah AY, Pfarr KM, Adjei O, Buttner DW (2003), "Doxycycline as a novel strategy against bancroftian filariasis-depletion of Wolbachia endosymbionts from Wuchereria bancrofti and stop of microfilaria production", Med Microbiol Immunol (Berl), 192 (4): 211–6, doi:10.1007/s00430-002-0174-6, PMID 12684759, S2CID 23349595
- ↑ Taylor MJ, Makunde WH, McGarry HF, Turner JD, Mand S, Hoerauf A (2005), "Macrofilaricidal activity after doxycycline treatment of Wuchereria bancrofti: a double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial", Lancet, 365 (9477): 2116–21, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)66591-9, PMID 15964448, S2CID 21382828
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Andersson J, Forssberg H, Zierath JR (5 October 2015), "Avermectin and Artemisinin - Revolutionary Therapies against Parasitic Diseases" (PDF), The Nobel Assembly at Karolinska Institutet, archived (PDF) from the original on 5 October 2015, retrieved 5 October 2015
- ↑ Ndeffo-Mbah ML, Galvani AP (April 2017). "Global elimination of lymphatic filariasis". The Lancet. Infectious Diseases. 17 (4): 358–359. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(16)30544-8. PMID 28012944.
- ↑ Pringle H (3 March 2011), The Emperor and the Parasite, archived from the original on 6 December 2019, retrieved 9 March 2011
Further reading
- "Special issue", Indian Journal of Urology, 21 (1), January–June 2005, archived from the original on 10 July 2020, retrieved 13 March 2022
- "Filariasis". Therapeutics in Dermatology. June 2012. Archived from the original on 24 April 2015. Retrieved 24 July 2012.
External links
| Classification |
|---|
- Pages with script errors
- Use dmy dates from May 2020
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from May 2021
- Articles with unsourced statements from May 2010
- Articles with unsourced statements from July 2020
- All pages needing factual verification
- Wikipedia articles needing factual verification from October 2015
- Webarchive template wayback links
- Animal diseases
- Insect-borne diseases
- Neglected tropical diseases
- Helminthiases
- Tropical diseases
- Veterinary helminthology
- Parasitic diseases