Clonorchiasis
| Clonorchiasis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Differential symptoms of parasite infection by raw fish: Clonorchis sinensis (a trematode/fluke), Anisakis (a nematode/roundworm) and Diphyllobothrium a (cestode/tapeworm),[1] all have gastrointestinal, but otherwise distinct, symptoms.[2][3][4][5] | |
Clonorchiasis is an infectious disease caused by the Chinese liver fluke (Clonorchis sinensis) and two related species. Clonorchiasis is a known risk factor for the development of cholangiocarcinoma, a neoplasm of the biliary system.[citation needed]
Symptoms of opisthorchiasis caused by Opisthorchis viverrini and by O. felineus are indistinguishable from clonorchiasis caused by Clonorchis sinensis,[6] leading some to argue that the disease by these three parasites should be referred to collectively as clonorchiasis.[6]
Signs and symptoms
The clinical presentation of Clonorchiasis is as follows:[7]
- Fever
- Epigastric pain
- Jaundice
- Diarrhea
Cause
Clonorchiasis sinensis is a trematode (fluke) which is part of the phylum Platyhelminthes. The parasitic worm is as long as 10 to 25 mm and lives in the bile ducts of the liver. It is a hermaphroditic fluke that requires two intermediate hosts. The eggs of the worms are passed in fecal matter into a body of water and are then ingested by mollusks. The water snail is the first intermediate host, in which a miracidium (an embryonated egg discharged in stool) goes through its developmental stages (sporocyst, rediae and cercariae). Freshwater fish are a second intermediate host for the parasitic worm. They become infected when the larva (cercaria) of the worm leaves the snail and penetrates the flesh of the fish. Humans then become infected by eating infected fish that has been undercooked, smoked, pickled, or salted, and from there the cycle repeats.
Clonorchiasis is endemic in the Far East, especially in Korea, Japan, Taiwan, and Southern China. Clonorchiasis has been reported in areas to which it is not endemic (including the United States). In such cases, the infection follows the ingestion of undercooked or pickled freshwater fish imported from one of the endemic areas and containing metacercariae.[8]
Diagnosis
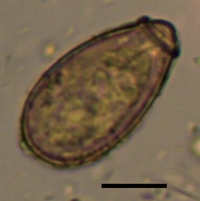
Adult C. sinensis worms can inhabit the bile ducts of humans for 20–25 years without any clear clinical symptoms. This, in addition to the nonspecific symptoms infected persons may develop, can lead to missed diagnoses.[citation needed]
Patients are diagnosed when C. sinensis eggs are found in stools. The formalin-ether concentration technique (FECT) method of stool examination is most effective at diagnosing light cases of infection, while the Kato-Katz (KK) method is more suitable for the diagnosing of persons with clonorchiasis. Serological methods that use enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) can help differentiate the eggs of C. sinensis from other flukes.[9]
Treatment
Praziquantil is the treatment of choice for clonorchiasis.[medical citation needed]
References
- ↑ WaiSays: About Consuming Raw Fish Archived 2018-04-19 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved on April 14, 2009
- ↑ For Chlonorchiasis: Public Health Agency of Canada – Clonorchis sinensis – Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) Archived 2010-12-06 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved on April 14, 2009
- ↑ For Anisakiasis: WrongDiagnosis: Symptoms of Anisakiasis Archived 2021-09-28 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved on April 14, 2009
- ↑ For Diphyllobothrium: MedlinePlus > Diphyllobothriasis Archived 2016-07-04 at the Wayback Machine Updated by: Arnold L. Lentnek, MD. Retrieved on April 14, 2009
- ↑ For symptoms of diphyllobothrium due to vitamin B12-deficiency University of Maryland Medical Center > Megaloblastic (Pernicious) Anemia Archived 2011-11-26 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved on April 14, 2009
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 King, Sandie; Scholz, Tomáš (2001). "Trematodes of the family Opisthorchiidae: A minireview". The Korean Journal of Parasitology. 39 (3): 209–21. doi:10.3347/kjp.2001.39.3.209. PMC 2721069. PMID 11590910..
- ↑ "Clonorchiasis - Infectious Diseases". MSD Manual Professional Edition. Archived from the original on 21 May 2022. Retrieved 4 November 2022.
- ↑ "Clonorchiasis". CDC – DPDx. Archived from the original on 2013-02-16.
- ↑ Tang, Ze-Li; et al. (6 Jul 2016). "Current status and perspectives of Clonorchis sinensis and clonorchiasis: epidemiology, pathogenesis, omics, prevention and control". Infectious Diseases of Poverty. 5 (5): 71. doi:10.1186/s40249-016-0166-1. PMC 4933995. PMID 27384714.
External links
| Classification |
|---|
- Pages with script errors
- Webarchive template wayback links
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from March 2022
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- Articles with unsourced statements from July 2020
- Articles with unsourced statements from September 2022
- Hepatology
- Helminthiases
- Foodborne illnesses
- Tropical diseases