Giemsa stain
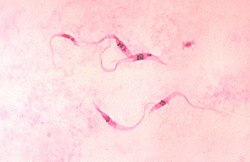

Giemsa stain (/ˈɡiːmzə/), named after German chemist and bacteriologist Gustav Giemsa, is a nucleic acid stain used in cytogenetics and for the histopathological diagnosis of malaria and other parasites.[1]
Uses

It is specific for the phosphate groups of DNA and attaches itself to regions of DNA where there are high amounts of adenine-thymine bonding. Giemsa stain is used in Giemsa banding, commonly called G-banding, to stain chromosomes and often used to create a karyogram (chromosome map). It can identify chromosomal aberrations such as translocations and rearrangements.[citation needed]
It stains the trophozoite Trichomonas vaginalis, which presents with greenish discharge and motile cells on wet prep.[citation needed]
Giemsa stain is also a differential stain, such as when it is combined with Wright stain to form Wright-Giemsa stain. It can be used to study the adherence of pathogenic bacteria to human cells. It differentially stains human and bacterial cells purple and pink respectively. It can be used for histopathological diagnosis of the Plasmodium species that cause malaria[2] and some other spirochete and protozoan blood parasites. It is also used to stain Wolbachia cells in host tissue.[3]
Giemsa stain is a classic blood film stain for peripheral blood smears and bone marrow specimens. Erythrocytes stain pink, platelets show a light pale pink, lymphocyte cytoplasm stains sky blue, monocyte cytoplasm stains pale blue, and leukocyte nuclear chromatin stains magenta. It is also used to visualize the classic "safety pin" shape in Yersinia pestis.

Giemsa stain is also used to visualize chromosomes. This is particularly relevant for detection of Cytomegalovirus infection, where the classical finding would be an "owl-eye" viral inclusion.[4]
Giemsa stains the fungus Histoplasma, Chlamydia bacteria, and can be used to identify mast cells.[5]
Generation
Giemsa's solution is a mixture of methylene blue, eosin, and Azure B. The stain is usually prepared from commercially available Giemsa powder.
A thin film of the specimen on a microscope slide is fixed in pure methanol for 30 seconds, by immersing it or by putting a few drops of methanol on the slide. The slide is immersed in a freshly prepared 5% Giemsa stain solution for 20–30 minutes (in emergencies 5–10 minutes in 10% solution can be used), then flushed with tap water and left to dry.[6]
See also
- Biological stains and staining protocols
- Histology
- Leishman stain
- Microscopy
- Romanowsky stain
- Wright's stain
References
- ^ Zipfel, E.; Grezes, J. -R.; Naujok, A.; Seiffert, W.; Wittekind, D. H.; Zimmermann, H. W. (1984). "Über Romanowsky-Farbstoffe und den Romanowsky-Giemsa-Effekt". Histochemistry. 81 (4): 337–351. doi:10.1007/bf00514328. ISSN 0301-5564.
- ^ Shapiro, Howard M.; Mandy, Francis (August 2007). "Cytometry in malaria: moving beyond Giemsa". Cytometry Part A. 71 (9): 643–645. doi:10.1002/cyto.a.20453. PMID 17712779. S2CID 12831277.
- ^ Riegler, Markus; O’Neill, Scott L. (2006). "The Genus Wolbachia". In Dworkin, Martin; Falkow, Stanley; Rosenberg, Eugene; Schleifer, Karl-Heinz; Stackebrandt, Erko (eds.). The Prokaryotes. Springer. pp. 547–561. doi:10.1007/0-387-30745-1_22. ISBN 978-0-387-30745-9.
- ^ Woods, G. L.; Walker, D. H. (July 1996). "Detection of infection or infectious agents by use of cytologic and histologic stains". Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 9 (3): 382–404. doi:10.1128/cmr.9.3.382. ISSN 0893-8512. PMC 172900. PMID 8809467.
- ^ Damsgaard, T. E.; Olesen, Anne Braae; Sørensen, Flemming Brandt; Thestrup-Pedersen, Kristian; Schiøtz, Peter Oluf (April 1997). "Mast cells and atopic dermatitis. Stereological quantification of mast cells in atopic dermatitis and normal human skin". Archives of Dermatological Research. 289 (5): 256–260. doi:10.1007/s004030050189. PMID 9164634. S2CID 229476.
- ^ "4.2.2.2. Giemsa stain". impact-malaria.com. Archived from the original on 2013-10-29. Retrieved 28 Oct 2013.