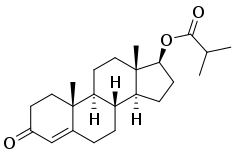
Estradiol benzoate/testosterone isobutyrate
 | |
 | |
| Combination of | |
|---|---|
| Estradiol benzoate | Estrogen |
| Testosterone isobutyrate | Androgen; Anabolic steroid |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Femandren M, Folivirin |
| Other names | EB/TiB; EB/TiB |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
Estradiol benzoate/testosterone isobutyrate (EB/TiB), sold under the brand names Femandren M and Folivirin, is an injectable combination medication of estradiol benzoate (EB), an estrogen, and testosterone isobutyrate (TiB), an androgen/anabolic steroid, which is used in menopausal hormone therapy for women.[1][2][3][4][5][6][7] It is provided in the form of 1 mL ampoules containing 2.5 mg estradiol benzoate and 25 mg testosterone isobutyrate in a microcrystalline aqueous suspension and is administered by intramuscular injection once every 4 to 6 weeks.[6][8] EB/TiB reportedly has a duration of about 14 to 21 days.[9]
The medication is available only in the Czech Republic and Slovakia.[10][11][12][13] EB/TiB was originally developed and marketed by the Swiss pharmaceutical company Ciba and was introduced for medical use by 1953,[6] following the development of testosterone isobutyrate in 1952.[14] It was intermittently manufactured by Spofa[15] and then Biotika[3] and is now manufactured by BB Pharma.[10][11][16]
The effect of EB/TiB on gonadotropin levels in postmenopausal women have been studied.[17]
An oral tablet product with the same brand name of Femandren, containing ethinylestradiol and methyltestosterone, was marketed around the same time as Femandren M, and should not be confused with the injectable formulation.[18][4][5]
| Route | Medication | Major brand names | Form | Dosage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oral | Testosterone undecanoate | Andriol, Jatenzo | Capsule | 40–80 mg 1x/1–2 days |
| Methyltestosterone | Metandren, Estratest | Tablet | 0.5–10 mg/day | |
| Fluoxymesterone | Halotestin | Tablet | 1–2.5 mg 1x/1–2 days | |
| Normethandronea | Ginecoside | Tablet | 5 mg/day | |
| Tibolone | Livial | Tablet | 1.25–2.5 mg/day | |
| Prasterone (DHEA)b | – | Tablet | 10–100 mg/day | |
| Sublingual | Methyltestosterone | Metandren | Tablet | 0.25 mg/day |
| Transdermal | Testosterone | Intrinsa | Patch | 150–300 μg/day |
| AndroGel | Gel, cream | 1–10 mg/day | ||
| Vaginal | Prasterone (DHEA) | Intrarosa | Insert | 6.5 mg/day |
| Injection | Testosterone propionatea | Testoviron | Oil solution | 25 mg 1x/1–2 weeks |
| Testosterone enanthate | Delatestryl, Primodian Depot | Oil solution | 25–100 mg 1x/4–6 weeks | |
| Testosterone cypionate | Depo-Testosterone, Depo-Testadiol | Oil solution | 25–100 mg 1x/4–6 weeks | |
| Testosterone isobutyratea | Femandren M, Folivirin | Aqueous suspension | 25–50 mg 1x/4–6 weeks | |
| Mixed testosterone esters | Climacterona | Oil solution | 150 mg 1x/4–8 weeks | |
| Omnadren, Sustanon | Oil solution | 50–100 mg 1x/4–6 weeks | ||
| Nandrolone decanoate | Deca-Durabolin | Oil solution | 25–50 mg 1x/6–12 weeks | |
| Prasterone enanthatea | Gynodian Depot | Oil solution | 200 mg 1x/4–6 weeks | |
| Implant | Testosterone | Testopel | Pellet | 50–100 mg 1x/3–6 months |
| Notes: Premenopausal women produce about 230 ± 70 μg testosterone per day (6.4 ± 2.0 mg testosterone per 4 weeks), with a range of 130 to 330 μg per day (3.6–9.2 mg per 4 weeks). Footnotes: a = Mostly discontinued or unavailable. b = Over-the-counter. Sources: See template. | ||||
See also
- Estradiol benzoate/progesterone
- List of combined sex-hormonal preparations
- List of sex-hormonal aqueous suspensions
References
- ^ "FOLIVIRIN Injekční suspenze, Příbalová Informace - Informace Pro Uživatele" [FOLIVIRIN Suspension for injection, Package Information - Information For Users] (PDF). Biotika A.S. (in Czech). Czech Republic: State Institute for Drug Control. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2019-05-20. Retrieved 2019-05-20.
- ^ Kubíková D (2014). "Menopauzální symptomy a hormonální substituční terapie" [Menopausal symptoms and hormone replacement therapy]. Praktické Lékárenství (in Czech). 10 (2): 68–73. ISSN 1801-2434.
- ^ a b Josef M (14 May 2010). "Farmakoterapie endokrinních onemocnění a léčba kortikosteroidy" [Pharmacotherapy of endocrine diseases and treatment with corticosteroids]. Farmakoterapie vnitřních nemocí [Pharmacotherapy of internal diseases] (4th ed.). Grada Publishing a.s. pp. 380–. ISBN 978-80-247-9524-9.
In addition, testosterone isobutyrate in FOLIVIRIN, Biotika, an injection containing 25 mg testosterone isobutyrate and 2.5 mg estradiol benzoate is available. It is applied every 4-6 weeks depending on the effect.
- ^ a b Arends G, Zörnig H, Hager H, Frerichs G, Kern W (14 December 2013). Hagers Handbuch der pharmazeutischen Praxis: Für Apotheker, Arzneimittelhersteller, Drogisten, Ärzte u. Medizinalbeamte. Springer-Verlag. pp. 1163–. ISBN 978-3-662-36329-4.
- ^ a b Hager HH, Kern W, List PH, Roth HJ (29 July 2013). Hagers Handbuch der Pharmazeutischen Praxis: Für Apotheker, Arzneimittelhersteller, Ärzte und Medizinalbeamte: Wirkstoffgruppen II Chemikalien und Drogen (A-AL). Springer-Verlag. pp. 109, 141, 178, 185. ISBN 978-3-662-25655-8.
- ^ a b c Ciba Symposium: 1953/57:Index. Ciba. 1953. p. 197.
Femandren M. C'est le nom des nouvelles ampoules cristallines destinées au traitement associé œs- trogène-androgène. Elles renferment, sous forme de microcristaux, 2,5 mg de mono- benzoate d'œstradiol et 50 mg d'isobutyra- te de testostérone ; elles sont indiquées pour traiter les cas où il convient d'administrer simultanément de l'hormone femelle et de l'hormone mâle et où il importe aussi d'obtenir un effet prolongé, par exemple lors de symptômes d'insuffisance à la ménopause ou après castration. L'effet d'une injection se prolonge pendant 3-6 semaines.
- ^ Aeppli H, Herrmann FU (1953). "Kombinierte Androgen-Oestrogenbehandlung mit Kristallsuspensionen". Gynecologic and Obstetric Investigation. 136 (5): 290–295. doi:10.1159/000308340. ISSN 1423-002X.
- ^ Horsky J, Presl J (6 December 2012). "Climacteric and Menopause". Ovarian Function and its Disorders: Diagnosis and Therapy. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 146–. ISBN 978-94-009-8195-9.
- ^ Ufer J (1 January 1978). Hormontherapie in der Frauenheilkunde: Grundlagen und Praxis [Hormone Therapy in Gynecology: Principles and Practice] (in German) (5th ed.). de Gruyter. p. 276. ISBN 978-3110066647. OCLC 924728827.
- ^ a b "Estradiol: Uses, Dosage & Side Effects". Drugs.com.
- ^ a b "Testosterone Injections: Uses, Side Effects & Warnings". Drugs.com.
- ^ Sweetman SC, ed. (2009). "Sex hormones and their modulators". Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference (36th ed.). London: Pharmaceutical Press. pp. 2133–2134. ISBN 978-0-85369-840-1.
- ^ "Home". micromedexsolutions.com.
- ^ Drescher H (April 1952). "Unsere Erfahrungen mit einer neuartigen Testosteron-isobutyrat-Kristallsuspension" [Experiences with a New Testosterone Isobutyrate Crystal Suspension]. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. (in German). 77 (14): 431–2. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1115985. PMID 12988767. S2CID 260092180.
- ^ Schreiber V (6 December 2012). "Thyroxine Binding to Anterior Pituitary Proteins in Vitro: Correlation with Anterior Pituitary Growth". In Lissak K (ed.). Hormones and Brain Function. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 145–. doi:10.1007/978-1-4684-2007-4_14. ISBN 978-1-4684-2007-4.
- ^ "Folivirin Injection". bbpharma.sk.
- ^ Talas M, Gazárak F, Stehliková J, Lubuský D, Fingerová H (1975). "FSH- und LH-Spiegel im Serum von Frauen nach chirurgischer Kastration und bei hormonaler Behandlung von Ausfallsbeschwerden" [Serum FSH and LH levels in women following surgical castration and during hormonal management of menopause symptoms]. Zentralbl Gynakol (in German). 97 (25): 1580–7. ISSN 0044-4197. PMID 1227215.
- ^ Kahr H, Müller HA (1956). "Behandlung der Menstruationsstörungen". Konservative Therapie der Frauenkrankheiten. Springer. pp. 1–85. doi:10.1007/978-3-7091-5694-0_1. ISBN 978-3-7091-5696-4.
- CS1 Czech-language sources (cs)
- CS1 German-language sources (de)
- Articles with short description
- Short description matches Wikidata
- Infobox drug articles with non-default infobox title
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs missing an ATC code
- Drugs with no legal status
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Drugs that are a combination of chemicals
- Combined estrogen–androgen formulations
- All stub articles
- Genito-urinary system drug stubs