Renal oncocytoma
| Renal oncocytoma | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Micrograph of a renal oncocytoma. | |
| Specialty | Oncology |
A renal oncocytoma is a tumour of the kidney made up of oncocytes, epithelial cells with an excess amount of mitochondria.[1][2]
Signs and symptoms
Renal oncocytomas are often asymptomatic and are frequently discovered by chance on a CT or ultrasound of the abdomen. Possible signs and symptoms of a renal oncocytoma include blood in the urine, flank pain, and an abdominal mass.
Pathophysiology
Renal oncocytoma is thought to arise from the intercalated cells of collecting ducts of the kidney. It represent 5% to 15% of surgically resected renal neoplasms. Ultrastructurally, the eosinophilic cells have numerous mitochondria.
Histologic appearance
-
Micrograph of a renal oncocytoma. H&E stain.
-
Micrograph of a renal oncocytoma. H&E stain.
-
Micrograph of a renal oncocytoma. H&E stain.
-
Micrograph of a renal oncocytoma. H&E stain.
-
Micrograph of a renal oncocytoma. H&E stain.
-
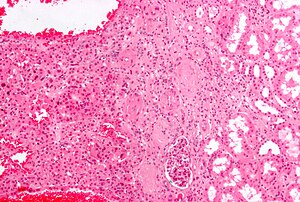
Micrograph of chromophobe RCC oncocytic variant, the main differential diagnosis of renal oncocytoma.
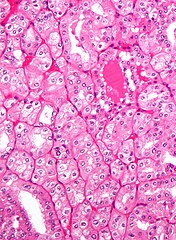
An oncocytoma is an epithelial tumor composed of oncocytes, large eosinophilic cells having small, round, benign-appearing nuclei with large nucleoli and excessive amounts of mitochondria.
Diagnosis
-
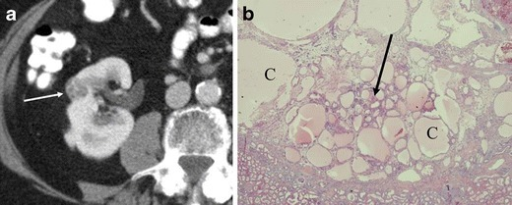
a,b)Renal oncocytoma with cystic change.
-
Renal oncocytoma of the right kidney at CT.
-
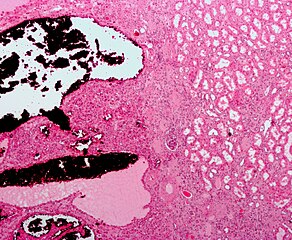
Gross appearance of a renal oncocytoma (left of image) and a slice of a normal kidney (right of image). Note the rounded contour, the mahogany colour and the central scar.
In gross appearance, the tumors are tan or mahogany brown, well circumscribed and contain a central scar. They may achieve a large size (up to 12 cm in diameter).
The main differential diagnosis of renal oncocytoma is chromophobe renal cell carcinoma oncocytic variant, which like the renal oncocytoma has eosinophilic cytoplasm, but has perinuclear clearing and, typically, some degree of nuclear atypia.
Immunohistochemical profile
- Cytokeratin AE1/AE3 +
- Vimentin -
- EMA +
- CD10+/-
- CK7 +/- parcellaire
- CK20 -
- CK19 -
- AMACR (Racemase) -
- S100 +
- c-kit (CD117) +
- Cadherin-E +
- TFE3 -
- CAM5.2 +
Treatment
Renal oncocytoma is considered benign, cured by nephrectomy. There are some familial cases in which these tumors are multicentric rather than solitary.[4] However, they may be resected to exclude a malignant tumor, e.g. renal cell carcinoma.
Prognosis
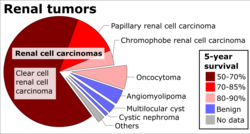
The overall five-year survival rate has been estimated to be 63%, with 100% disease-specific survival.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ Coburn V, Radfar A, Snook D, Mahalingam M (2007). "Cutaneous oncocytoma - a report of three cases and review of the literature". J. Cutan. Pathol. 34 (4): 355–9. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2006.00620.x. PMID 17381809. S2CID 19955625.
- ↑ "Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology - Thyroid:oncocytic tumors". Archived from the original on 2009-01-23. Retrieved 2009-02-01.
- ↑ [Renal Neoplasms: An Update on Immunohistochemical and Histochemical Features http://www.dako.com/08066_12may10_webchapter26.pdf Archived 2015-09-23 at the Wayback Machine]
- ↑ Robbins pathology, page 1015[full citation needed]
- ↑ Gudbjartsson, Tomas; Hardarson, Sverrir; Petursdottir, Vigdis; Thoroddsen, Asgeir; Magnusson, Jonas; Einarsson, Gudmundur V. (2005). "Renal oncocytoma: a clinicopathological analysis of 45 consecutive cases". BJU International. 96 (9): 1275–1279. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2005.05827.x. ISSN 1464-4096. PMID 16287444. S2CID 19390518.
External links
| Classification |
|---|