Colestipol
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | koe les' ti pol[1] |
| Trade names | Colestid, Cholestabyl, others |
| Other names | Colestipol hydrochloride |
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Bile acid sequestrant[2] |
| Main uses | High cholesterol, biliary obstruction, liver disease[2][1] |
| Side effects | Constipation[2] |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | By mouth (suspension or tablets) |
| Typical dose | 5 to 30 gram/day[3] |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682157 |
| Legal | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Bioavailability | None |
| Excretion | Faeces, in complex with bile acids |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | (C4H10N3)m(C3H6O)n |
Colestipol, sold under the brand name Colestid among others, is a medication used to treat high cholesterol, biliary obstruction, and liver disease.[2][1] In liver disease it is used to decrease itchiness.[1] It is taken by mouth.[2]
Common side effects include constipation.[2] Other side effects may include fat soluble vitamin deficiency.[2] While there is no evidence of harm in pregnancy, such use has not been well studied.[4] It is a bile acid sequestrant.[2] It works by binding bile acids in the intestines and preventing them from being reabsorbed.[1] This decreases in bile results in less cholesterol being made by the liver.[1]
Colestipol was approved for medical use in the United States in 1977.[2] It is available as a generic medication.[1] In the United Kingdom 30 doses of 5 grams costs the NHS about £15 as of 2021.[3] This amount in the United States costs about 31 USD.[5]
Medical use
It is also used to treat certain types of chronic diarrhea.[6]
Dosage
It may be taken at a dose of 5 to 30 grams per day.[3]
Side effects
The following notable side effects may occur:[7]
- gastrointestinal tract disturbances, especially (mild, occasionally severe) constipation
- sometimes increase in VLDL[citation needed] and triglyceride synthesis
Interactions
Colestipol can bind to a number of drugs and nutrients in the gut and inhibit or delay their absorption. Such substances include:[7]
- thiazide diuretics, furosemide
- gemfibrozil
- benzylpenicillin, tetracycline
- digoxin
- lipid-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K)
Contraindications
Colestipol is contraindicated in hypertriglyceridemia (high level of triglycerides in the blood).[citation needed]
Chemistry
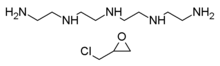
Colestipol is a copolymer of diethylenetriamine (DETA) —or tetraethylenepentamine according to some sources[8][9]— and epichlorohydrin.[10][11] The structure drawing (top right) shows the DETA moieties in blue and the epichlorohydrin moieties in red.
 |
  |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 "Colestipol". LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. 2012. Archived from the original on 6 May 2021. Retrieved 6 January 2022.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 "Colestipol Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 17 January 2021. Retrieved 6 January 2022.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 BNF 81: March-September 2021. BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. 2021. p. 212. ISBN 978-0857114105.
- ↑ "Colestipol Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 30 November 2020. Retrieved 6 January 2022.
- ↑ "Colestipol Prices, Coupons & Savings Tips - GoodRx". GoodRx. Archived from the original on 17 August 2021. Retrieved 6 January 2022.
- ↑ "colestipol (Colestid)". MedicineNet. Archived from the original on 2020-10-26. Retrieved 2020-10-19.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Drugs.com: Colestipol Hydrochloride Archived 2019-08-20 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Clinical Pharmacology: Colestipol structure Archived 2016-03-04 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center & Care Group: Colestipol structure Archived 2010-12-29 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Haberfeld H, ed. (2009). Austria-Codex (in German) (2009/2010 ed.). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag. ISBN 978-3-85200-196-8.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ↑ Steinhilber D, Schubert-Zsilavecz M, Roth HJ (2005). Medizinische Chemie (in German). Stuttgart: Deutscher Apotheker Verlag. p. 433. ISBN 3-7692-3483-9.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link)
External links
| Identifiers: |
|
|---|
- Pages using duplicate arguments in template calls
- Webarchive template wayback links
- CS1 maint: unrecognized language
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Chemical articles without CAS registry number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs missing an ATC code
- Drugboxes which contain changes to verified fields
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from January 2012
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- Articles with changed CASNo identifier
- Chemicals that do not have a ChemSpider ID assigned
- Bile acid sequestrants
- RTT