Congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma
Congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma (CIE), also known as Nonbullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma[1]: 484 is a rare type of the ichthyosis family of skin diseases which occurs in 1 in 200,000 to 300,000 births. CIE comes under the umbrella term autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis (ARCI), which include non-syndromic congenital ichthyoses such as harlequin ichthyosis and lamellar ichthyosis.[2]
Symptoms and signs
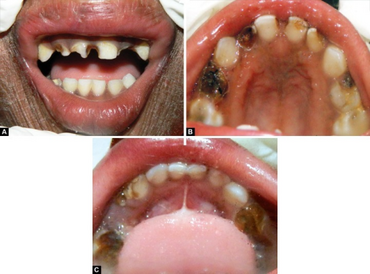
Infants are often born in a collodion membrane, a shiny, wax outer layer on the skin and usually with ectropion, a condition in which the eyelids turn outwards. When the membrane is shed, the skin is red with a generalized white scale. Palms, soles and areas on the joints are often affected with hyperkeratosis, a thickening of the layer of dead skin cells on the surface of the skin forming scales. Eclabium (eversion of the lips), ectropion and alopecia (hair loss) are more common in CIE than in Lamellar ichthyosis (LI).[3][non-primary source needed]
CIE can present very similarly to LI and they often share characteristics, though the two conditions can often be differentiated by the appearance of the scales. Scales on patients with CIE are fine and white on skin with erythema while appear larger and greyer on the limbs, compared to LI where scales appear large and dark.[4][non-primary source needed]
Genetics
CIE is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder. This means a child must inherit a defective pair of genes (one from each parent) to show the symptoms. Parents who are carriers of the defective genes show no symptoms but their children have a 25% chance of having CIE.[citation needed]
There are several genetic faults which can produce CIE. Known genes involved include TGM1, ALOX12B, ALOXE3, NIPAL4, ABCA12, CYP4F22, LIPN, CERS3, PNPLA1, ST14, and CASP14.[5][non-primary source needed]
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of this condition, Congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma, can be done via the following:[6]
- Medical history
- Symptoms
- Physical exam
- Laboratory test
Treatment
Currently there is no cure for nonbullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma . Management focuses on specific signs and symptoms each individual exhibits.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ Freedberg IM, Fitzpatrick TB (2003). Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-138076-0.
- ↑ Oji V, Tadini G, Akiyama M, Blanchet Bardon C, Bodemer C, Bourrat E, et al. (October 2010). "Revised nomenclature and classification of inherited ichthyoses: results of the First Ichthyosis Consensus Conference in Sorèze 2009". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 63 (4): 607–41. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2009.11.020. hdl:2263/15323. PMID 20643494.
- ↑ Fischer J, Faure A, Bouadjar B, Blanchet-Bardon C, Karaduman A, Thomas I, et al. (March 2000). "Two new loci for autosomal recessive ichthyosis on chromosomes 3p21 and 19p12-q12 and evidence for further genetic heterogeneity". American Journal of Human Genetics. 66 (3): 904–13. doi:10.1086/302814. PMC 1288171. PMID 10712205.
- ↑ Farasat S, Wei MH, Herman M, Liewehr DJ, Steinberg SM, Bale SJ, et al. (February 2009). "Novel transglutaminase-1 mutations and genotype-phenotype investigations of 104 patients with autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis in the USA". Journal of Medical Genetics. 46 (2): 103–11. doi:10.1136/jmg.2008.060905. PMC 3044481. PMID 18948357.
- ↑ Oji V, Preil ML, Kleinow B, Wehr G, Fischer J, Hennies HC, et al. (October 2017). "S1 guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of ichthyoses - update" (PDF). Journal of the German Society of Dermatology. 15 (10): 1053–1065. doi:10.1111/ddg.13340. PMID 28976107. S2CID 27585177. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2019-04-30. Retrieved 2020-12-28.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Nonbullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program". rarediseases.info.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 18 March 2021. Retrieved 3 September 2021.
External links
- GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Autosomal Recessive Congenital Ichthyosis Archived 2010-06-15 at the Wayback Machine
| Classification |
|---|
- Pages with script errors
- All pages needing factual verification
- Wikipedia articles needing factual verification from October 2020
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from March 2009
- Webarchive template wayback links
- Genodermatoses
- Rare diseases
- Autosomal recessive disorders