Ethinylestradiol/levonorgestrel
 Rigevidon, an example of a combined ethinylestradiol/levonorgestrel birthcontrol pill | |
| Combination of | |
|---|---|
| Ethinylestradiol | Estrogen |
| Levonorgestrel | Progestogen |
| Names | |
| Trade names | Altavera, Alysena, Amethyst, Twirla, others[1] |
| Clinical data | |
| Main uses | Birth control[2] |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | By mouth, transdermal (patch) |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a601050 |
| Legal | |
| Legal status |
|
Ethinylestradiol/levonorgestrel (EE/LNG), also known as ethinyl estradiol/levonorgestrel, is a combined birth control pill or birth control patch made up of ethinylestradiol, an estrogen and levonorgestrel a progestin.[3][4] It is used for birth control, symptoms of menstruation, endometriosis, and as emergency contraception.[1][3] It is taken by mouth or applied to the skin.[1][4]
Side effects can include nausea, headache, blood clots, breast pain, depression, and liver problems.[3] Use is not recommended during pregnancy, the initial three weeks after childbirth, and in those at high risk of blood clots.[3] However, it may be started immediately after a miscarriage or abortion.[5] Smoking while using combined birth control pills is not recommended.[1] It works by stopping ovulation, making the mucus at the opening to the cervix thick, and making the uterus not suitable for implantation.[1]
Ethinylestradiol/levonorgestrel has been approved for medical use in the United States at least since 1982.[1] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[6] It is available as a generic medication.[7] In the United Kingdom three months of medication costs the NHS about 1.80 pounds.[8] In the United States it costs about $25–50 per month.[7] It is marketed under a large number of brand names.[1] In 2017, it was the 136th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than four million prescriptions.[9][10]
Medical uses
It is used as a form of birth control.[2]
Dosage
The defined daily dose is not established.[11] It is taken as 21 active pills of 30 micrograms ethinylestradiol / 150 micrograms levonorgestrel and 7 inactive pills.[2]
Side effects
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
It should not be used in the initial 6 weeks following delivery and is not recommended between 6 weeks and 6 months unless their is no other suitable option.[2]
Society and culture
Cost
In the United Kingdom three months of medication costs the NHS about 1.80 pounds.[8] In the United States it costs about $25–50 per month.[7] It is marketed under a large number of brand names.[1] In 2017, it was the 136th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than four million prescriptions.[9][10]
-
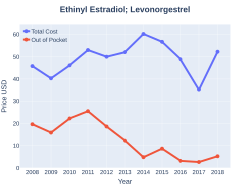
Ethinylestradiol/levonorgestrel costs (US)
-
Ethinylestradiol/levonorgestrel prescriptions (US)
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 "Ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel medical facts from Drugs.com". www.drugs.com. Archived from the original on 1 January 2017. Retrieved 1 January 2017.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "ETHINYLESTRADIOL/LEVONORGESTREL oral - Essential drugs". medicalguidelines.msf.org. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 30 August 2020.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 World Health Organization (2009). Stuart MC, Kouimtzi M, Hill SR (eds.). WHO Model Formulary 2008. World Health Organization. pp. 363–5. hdl:10665/44053. ISBN 9789241547659.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "DailyMed - TWIRLA- levonorgestrel/ethinyl estradiol patch". dailymed.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 25 October 2022. Retrieved 18 February 2024.
- ↑ "Erlibelle 30micrograms/150micrograms film-coated tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC) - (eMC)". www.medicines.org.uk. Archived from the original on 2 January 2017. Retrieved 1 January 2017.
- ↑ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Hamilton, Richart (2015). Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2015 Deluxe Lab-Coat Edition. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 349. ISBN 9781284057560.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 British national formulary : BNF 69 (69 ed.). British Medical Association. 2015. p. 552. ISBN 9780857111562.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "The Top 300 of 2020". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 12 February 2021. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "Ethinyl Estradiol; Levonorgestrel - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 5 March 2018. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedwho
External links
| Identifiers: |
|---|
- Pages using duplicate arguments in template calls
- Pages with reference errors
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Chemical articles without CAS registry number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs missing an ATC code
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Drugs that are a combination of chemicals
- Combined oral contraceptives
- World Health Organization essential medicines
- RTT
- WHRTT