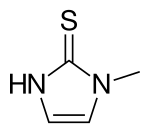
Thiamazole
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Tapazole, others |
| Other names | thiamazole (INN, BAN); methimazole (USAN); MMI |
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Thioamide[1] |
| Main uses | Hyperthyroidism[1] |
| Side effects | Itchiness, hair loss, nausea, muscle pain, swelling, abdominal pain[1] |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | By mouth |
| Defined daily dose | 10 mg[2] |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682464 |
| Legal | |
| License data |
|
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Bioavailability | 93% |
| Protein binding | None |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 5-6 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C4H6N2S |
| Molar mass | 114.17 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 146 °C (295 °F) |
| Solubility in water | 275[3] mg/mL (20 °C) |
| |
| |
Thiamazole, also known as methimazole, is a medication used to treat hyperthyroidism.[1] This includes Graves disease, toxic multinodular goiter, and thyrotoxic crisis.[1] It is taken by mouth.[1] Full effects may take a few weeks to occur.[4]
Common side effects include itchiness, hair loss, nausea, muscle pain, swelling, and abdominal pain.[1] Severe side effects may include low blood cell counts, liver failure, and vasculitis.[1] Use is not recommended during the first trimester of pregnancy but may be used in the second trimester or third trimester.[5] It may be used during breastfeeding.[5] Those who developed significant side effects may also have problems with propylthiouracil.[1] Thiamazole is a thioamide and works by decreasing the production of thyroid hormones.[1]
Thiamazole was approved for medical use in the United States in 1950.[1] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[6] It is available as a generic medication.[1] A month supply in the United States has a wholesale cost of about US$6.80.[7] It is also available in Europe and Asia.[8] In 2017, it was the 244th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than one million prescriptions.[9][10]
Medical uses
Thiamazole is a drug used to treat hyperthyroidism such as in Graves' disease, a condition that occurs when the thyroid gland begins to produce an excess of thyroid hormone. The drug may also be taken before thyroid surgery to lower thyroid hormone levels and minimize the effects of thyroid manipulation. Additionally, thiamazole is used in the veterinary setting to treat hyperthyroidism in cats.
Dosage
The defined daily dose is 10 mg by mouth.[2]
Side effects
It is important to monitor any symptoms of fever or sore throat while taking thiamazole; this could indicate the development of agranulocytosis, an uncommon but severe side effect resulting from a drop in the white blood cell count (to be specific, neutropenia, a deficiency of neutrophils). A complete blood count (CBC) with differential is performed to confirm the suspicion, in which case the drug is discontinued.[11] Administration of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (rhG-CSF) may increase recovery.
Other known side effects include:
- skin rash
- itching
- abnormal hair loss
- upset stomach
- vomiting
- loss of taste
- abnormal sensations (tingling, prickling, burning, tightness, and pulling)
- swelling
- joint and muscle pain
- drowsiness
- dizziness
- decreased platelet count (thrombocytopenia)
- aplasia cutis congenita (prenatal exposure)
- thyroid gland enlargement (prenatal exposure)
- choanal atresia (prenatal exposure during the first trimester of pregnancy)
Interactions
Side effects may occur for individuals who:
- Take anticoagulants ('blood thinners') such as warfarin (Coumadin), diabetes medications, digoxin (Lanoxin), theophylline (Theobid, Theo-Dur), and vitamins
- Have ever had any blood disease, such as decreased white blood cells (leukopenia), decreased platelets (thrombocytopenia) or aplastic anemia, or liver disease (hepatitis, jaundice)
Mechanism of action
Thiamazole inhibits the enzyme thyroperoxidase, which normally acts in thyroid hormone synthesis by oxidizing the anion iodide (I−) to iodine (I2), hypoiodous acid (HOI), enzyme linked hypoiodate (EOI) facilitating iodine's addition to tyrosine residues on the hormone precursor thyroglobulin, a necessary step in the synthesis of triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4).
It does not inhibit the action of the sodium-dependent iodide transporter located on follicular cells' basolateral membranes. Inhibition of this step requires competitive inhibitors such as perchlorate and thiocyanate.
Chemical properties
The imidazole derivative thiamazole is a white to matte brown crystalline powder with a characteristic odour. The boiling point is 280 °C (decomposition). Thiamazole is soluble in water, ethanol and chloroform, but hardly soluble in ether.[13] Galenic preparations are injectable solutions and tablets.
Thiamazole acts as a free radical scavenger for radicals such as the hydroxyl radical (•OH) radical.[14] It is used as free radical scavenger in organic chemistry.[15]
Society and culture
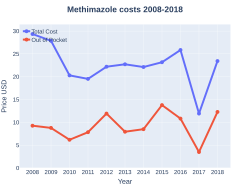
Cost
A month supply in the United States has a wholesale cost of about US$6.80.[7] In 2017, it was the 244th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than one million prescriptions.[9][10]
-
Methimazole costs (US)
-
Methimazole prescriptions (US)
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 "Methimazole Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 17 July 2019. Retrieved 8 April 2019.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "WHOCC - ATC/DDD Index". www.whocc.no. Archived from the original on 3 December 2020. Retrieved 8 September 2020.
- ↑ "DrugBank: Methimazole (DB00763)". drugbank.ca. Archived from the original on 15 January 2017. Retrieved 21 July 2015.
- ↑ Spina, Domenico (2008). The Flesh and Bones of Medical Pharmacology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 74. ISBN 9780723437161. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 8 April 2019.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Methimazole Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 8 April 2019. Retrieved 8 April 2019.
- ↑ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "NADAC as of 2019-02-27". Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Archived from the original on 6 March 2019. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ↑ Jastrzębska, Helena (2015). "Antithyroid drugs". Thyroid Research. 8 (Suppl 1): A12. doi:10.1186/1756-6614-8-S1-A12. PMC 4480840.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "The Top 300 of 2020". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 18 March 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "Methimazole - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 8 July 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ↑ Fumarola, A; Di Fiore, A; Dainelli, M; Grani, G; Calvanese, A (November 2010). "Medical treatment of hyperthyroidism: state of the art". Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes. 118 (10): 678–84. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1253420. PMID 20496313.
- ↑ Crescioli C, Cosmi L, Borgogni E, et al. (October 2007). "Methimazole inhibits CXC chemokine ligand 10 secretion in human thyrocytes". J. Endocrinol. 195 (1): 145–55. doi:10.1677/JOE-07-0240. PMID 17911406.
- ↑ Entry on Thiamazol. at: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, retrieved 10. November 2014.
- ↑ Taylor, J.J.; Willson, R.L.; Kendall-Taylor, P. (29 October 1984). "Evidence for direct interactions between methimazole and free radicals". FEBS Letters. 176 (2): 337–340. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(84)81192-8.
- ↑ Inhibition of amine oxide, 30 December 2010, archived from the original on 14 April 2019, retrieved 14 April 2019
External links
| Identifiers: |
|
|---|
- "Methimazole". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 27 October 2020. Retrieved 16 May 2020.
- Pages using duplicate arguments in template calls
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Use dmy dates from September 2019
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Chemical articles without CAS registry number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs missing an ATC code
- Antithyroid drugs
- Imidazoles
- RTT
- Thioureas
- Pfizer brands
- World Health Organization essential medicines