Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
| Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia | |
|---|---|
 | |
| A schematic drawing of platelet factor 4, which when bound to heparin leads to an immune response in HIT | |
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is the development of thrombocytopenia (a low platelet count), due to the administration of various forms of heparin, an anticoagulant. HIT predisposes to thrombosis (the abnormal formation of blood clots inside a blood vessel) because platelets release microparticles that activate thrombin, thereby leading to thrombosis. When thrombosis is identified the condition is called heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and thrombosis (HITT). HIT is caused by the formation of abnormal antibodies that activate platelets. If someone receiving heparin develops new or worsening thrombosis, or if the platelet count falls, HIT can be confirmed with specific blood tests.[1]
The treatment of HIT requires stopping heparin treatment, and both protection from thrombosis and choice of an agent that will not reduce the platelet count any further. Several alternatives are available for this purpose; mainly used are danaparoid, fondaparinux, argatroban, and bivalirudin.[2][3]
While heparin was discovered in the 1930s, HIT was not reported until the 1960s.[4]
Signs and symptoms
Heparin may be used for both prevention and the treatment of thrombosis. It exists in two main forms: an "unfractionated" form that can be injected under the skin (subcutaneously) or through an intravenous infusion, and a "low molecular weight" form that is generally given subcutaneously. Commonly used low molecular weight heparins are enoxaparin, dalteparin, nadroparin and tinzaparin.[5][6]
In HIT, the platelet count in the blood falls below the normal range, a condition called thrombocytopenia. However, it is generally not low enough to lead to an increased risk of bleeding. Most people with HIT, therefore, do not experience any symptoms. Typically, the platelet count falls 5–14 days after heparin is first given; if someone has received heparin in the previous three months, the fall in platelet count may occur sooner, sometimes within a day.[1]
The most common symptom of HIT is enlargement or extension of a previously diagnosed blood clot, or the development of a new blood clot elsewhere in the body. This may take the form of clots either in arteries or veins, causing arterial or venous thrombosis, respectively. Examples of arterial thrombosis are stroke, myocardial infarction ("heart attack"), and acute leg ischemia. Venous thrombosis may occur in the leg or arm in the form of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and in the lung in the form of a pulmonary embolism (PE); the latter usually originates in the leg, but migrates to the lung.[1][7]
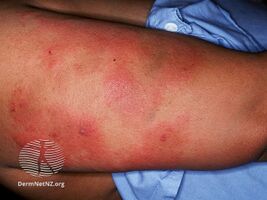
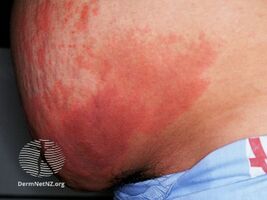
In those receiving heparin through an intravenous infusion, a complex of symptoms ("systemic reaction") may occur when the infusion is started. These include fever, chills, high blood pressure, a fast heart rate, shortness of breath, and chest pain. This happens in about a quarter of people with HIT. Others may develop a skin rash consisting of red spots.[1][7]
-
Heparin induced thrombocytopenia
-
Heparin induced thrombocytopenia
Mechanism
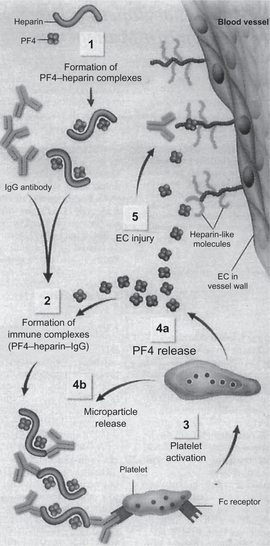
The administration of heparin can cause the development of HIT antibodies, suggesting heparin may act as a hapten, thus may be targeted by the immune system. In HIT, the immune system forms antibodies against heparin when it is bound to a protein called platelet factor 4 (PF4). These antibodies are usually of the IgG class and their development usually takes about 5 days. However, those who have been exposed to heparin in the last few months may still have circulating IgG, as IgG-type antibodies generally continue to be produced even when their precipitant has been removed. This is similar to immunity against certain microorganisms, with the difference that the HIT antibody does not persist more than three months.[1][7] HIT antibodies have been found in individuals with thrombocytopenia and thrombosis who had no prior exposure to heparin, but the majority are found in people who are receiving heparin.[8]
The IgG antibodies form a complex with heparin and PF4 in the bloodstream. The tail of the antibody then binds to the FcγIIa receptor, a protein on the surface of the platelet. This results in platelet activation and the formation of platelet microparticles, which initiate the formation of blood clots; the platelet count falls as a result, leading to thrombocytopenia.[1][7] In addition, the reticuloendothelial system (mostly the spleen) removes the antibody-coated platelets, further contributing to the thrombocytopenia.
Formation of PF4-heparin antibodies is common in people receiving heparin, but only a proportion of these develop thrombocytopenia or thrombosis.[1] This has been referred to as an "iceberg phenomenon".[4]
Diagnosis
HIT may be suspected if blood tests show a falling platelet count in someone receiving heparin, even if the heparin has already been discontinued. Professional guidelines recommend that people receiving heparin have a complete blood count (which includes a platelet count) on a regular basis while receiving heparin.[5][9]
However, not all people with a falling platelet count while receiving heparin turn out to have HIT. The timing, severity of the thrombocytopenia, the occurrence of new thrombosis, and the presence of alternative explanations, all determine the likelihood that HIT is present. A commonly used score to predict the likelihood of HIT is the "4 Ts" score introduced in 2003.[10] A score of 0–8 points is generated; if the score is 0–3, HIT is unlikely. A score of 4–5 indicates intermediate probability, while a score of 6–8 makes it highly likely. Those with a high score may need to be treated with an alternative drug, while more sensitive and specific tests for HIT are performed, while those with a low score can safely continue receiving heparin, as the likelihood that they have HIT is extremely low.[1][7][11] In an analysis of the reliability of the 4T score, a low score had a negative predictive value of 0.998, while an intermediate score had a positive predictive value of 0.14 and a high score a positive predictive value of 0.64; intermediate and high scores, therefore, warrant further investigation.[12]
| Element | The 4T score for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia[9][10] |
|---|---|
| Thrombocytopenia | 2 points if the fall in platelet count is >50% of the previous value, AND the lowest count (nadir) is 20–100 × 109/liter 1 point if the fall is 30–50% or the nadir is 10–19 × 109/liter No points if the fall is less than 30% or the nadir is <10 × 109/liter. |
| Timing | 2 points if the fall is between days 5–10 after commencement of treatment 1 point if the fall is after day 10. If someone has been exposed to heparin within the last 30 days and then has a drop in platelet count within a day of reexposure, 2 points are given. If the previous exposure was 30–100 days ago, 1 point If the fall is early but there has been no previous heparin exposure, no points. |
| Thrombosis | 2 points in new proven thrombosis, skin necrosis (see below), or systemic reaction 1 point if progressive or recurrent thrombosis, silent thrombosis or red skin lesions No points if there are no symptoms. |
| Alternative cause possible | 2 points if no other cause 1 point if there is a possible alternative cause No points if there is a definite alternative cause. |
The first screening test in someone suspected of having HIT is aimed at detecting antibodies against heparin-PF4 complexes. This may be with a laboratory test of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay type. This ELISA test, however, detects all circulating antibodies that bind heparin-PF4 complexes, and may also falsely identify antibodies that do not cause HIT. Therefore, those with a positive ELISA are tested further with a functional assay. This test uses platelets and serum from the patient; the platelets are washed and mixed with serum and heparin. The sample is then tested for the release of serotonin, a marker of platelet activation. If this serotonin release assay (SRA) shows high serotonin release, the diagnosis of HIT is confirmed. The SRA test is difficult to perform and is usually only done in regional laboratories.[1][7]
If someone has been diagnosed with HIT, some recommend routine Doppler sonography of the leg veins to identify deep vein thromboses, as this is very common in HIT.[7][11]
Treatment
Given the fact that HIT predisposes strongly to new episodes of thrombosis, simply discontinuing the heparin administration is insufficient. Generally, an alternative anticoagulant is needed to suppress the thrombotic tendency while the generation of antibodies stops and the platelet count recovers. To make matters more complicated, the other most commonly used anticoagulant, warfarin, should not be used in HIT until the platelet count is at least 150 x 109/L because a very high risk of warfarin necrosis exists in people with HIT who have low platelet counts. Warfarin necrosis is the development of skin gangrene in those receiving warfarin or a similar vitamin K inhibitor. If the patient was receiving warfarin at the time when HIT is diagnosed, the activity of warfarin is reversed with vitamin K.[1][9] Transfusing platelets is discouraged, as a theoretical risk indicates that this may worsen the risk of thrombosis; the platelet count is rarely low enough to be the principal cause of significant hemorrhage.[9]
Various nonheparin agents are used as alternatives to heparin therapy to provide anticoagulation in those with strongly suspected or proven HIT: danaparoid, fondaparinux, bivalirudin, and argatroban.[2][3] Not all agents are available in all countries, and not all are approved for this specific use. For instance, argatroban is only recently licensed in the United Kingdom, and danaparoid is not available in the United States.[8] Fondaparinux, a factor Xa inhibitor, is commonly used off label for HIT treatment in the United States.[citation needed]
According to a systematic review, people with HIT treated with lepirudin showed a relative risk reduction of clinical outcome (death, amputation, etc.) to be 0.52 and 0.42 when compared to patient controls. In addition, people treated with argatroban for HIT showed a relative risk reduction of the above clinical outcomes to be 0.20 and 0.18.[13] Lepirudin production stopped on May 31, 2012.[14]
Epidemiology
Up to 8% of patients receiving heparin are at risk to develop HIT antibodies, but only 1–5% on heparin will progress to develop HIT with thrombocytopenia and subsequently one-third of them may suffer from arterial and/or venous thrombosis.[1] After vascular surgery, 34% of patients receiving heparin developed HIT antibodies without clinical symptoms.[15] The exact number of cases of HIT in the general population is unknown. What is known is that women receiving heparin after a recent surgical procedure, particularly cardiothoracic surgery, have a higher risk, while the risk is very low in women just before and after giving birth. Some studies have shown that HIT is less common in those receiving low molecular weight heparin.[7]
History
While heparin was introduced for clinical use in the late 1930s, new thrombosis in people treated with heparin was not described until 1957, when vascular surgeons reported the association.[4][16] The fact that this phenomenon occurred together with thrombocytopenia was reported in 1969;[17] prior to this time, platelet counts were not routinely performed.[4] A 1973 report established HIT as a diagnosis, as well as suggesting that its features were the result of an immune process.[4][18]
Initially, various theories existed about the exact cause of the low platelets in HIT. Gradually, evidence accumulated on the exact underlying mechanism.[4] In 1984–1986, John G. Kelton and colleagues at McMaster University Medical School developed the laboratory tests that could be used to confirm or exclude heparin-induced thrombocytopenia.[4][19]
Treatment was initially limited to aspirin and warfarin, but the 1990s saw the introduction of a number of agents that could provide anticoagulation without a risk of recurrent HIT.[4] Older terminology distinguishes between two forms of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: type 1 (mild, nonimmune mediated and self-limiting fall in platelet count) and type 2, the form described above. Currently, the term HIT is used without a modifier to describe the immune-mediated severe form.[4]
In 2021 a condition resembling HIT but without heparin exposure was described to explain unusual post-vaccination embolic and thrombotic events after the Oxford–AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine.[20][21][22] It is a rare adverse event (1:1 million to 1:100,000) resulting from COVID-19 vaccines (particularly adenoviral vector vaccines). This is also known as Thrombosis with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome or TTS.[23]
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 Ahmed I, Majeed A, Powell R (September 2007). "Heparin induced thrombocytopenia: diagnosis and management update". Postgrad Med J. 83 (983): 575–82. doi:10.1136/pgmj.2007.059188. PMC 2600013. PMID 17823223.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Watson, H (2012). "Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: second edition". British Journal of Haematology. 159 (5): 528–40. doi:10.1111/bjh.12059. PMID 23043677.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Bakchoul T, Greinacher A (2012). "Recent advances in the diagnosis and treatment of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia". Ther Adv Hematol. 3 (4): 237–51. doi:10.1177/2040620712443537. PMC 3627332. PMID 23606934.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 Kelton JG, Warkentin TE (October 2008). "Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: a historical perspective". Blood. 112 (7): 2607–16. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-02-078014. PMID 18809774.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Hirsh J, Bauer KA, Donati MB, Gould M, Samama MM, Weitz JI (June 2008). "Parenteral anticoagulants: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition)". Chest. 133 (6 Suppl): 141S–159S. doi:10.1378/chest.08-0689. PMID 18574264.
- ↑ Dooley C, Kaur R, Sobieraj DM (2014). "Comparison of the efficacy and safety of low molecular weight heparins for venous thromboembolism prophylaxis in medically ill patients". Curr Med Res Opin. 30 (3): 367–80. doi:10.1185/03007995.2013.837818. PMID 23971722.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 Warkentin TE (2006). "Think of HIT". Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2006: 408–14. doi:10.1182/asheducation-2006.1.408. PMID 17124091.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Warkentin TE, Makris M, Jay RM, Kelton JG (2008). "A spontaneous prothrombotic disorder resembling heparin-induced thrombocytopenia". Am J Med. 121 (7): 632–6. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2008.03.012. PMID 18589060.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 Keeling D, Davidson S, Watson H (May 2006). "The management of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia". Br. J. Haematol. 133 (3): 259–69. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2006.06018.x. PMID 16643427. Archived from the original on 2012-12-10.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Warkentin TE, Heddle NM (March 2003). "Laboratory diagnosis of immune heparin-induced thrombocytopenia". Curr Hematol Rep. 2 (2): 148–57. PMID 12901146.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Warkentin TE, Aird WC, Rand JH (2003). "Platelet-endothelial interactions: sepsis, HIT, and antiphospholipid syndrome". Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2003: 497–519. doi:10.1182/asheducation-2003.1.497. PMID 14633796.
- ↑ Cuker A, Gimotty PA, Crowther MA, Warkentin TE (September 2012). "Predictive value of the 4Ts scoring system for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Blood. 120 (20): 4160–4167. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-07-443051. PMC 3501714. PMID 22990018.
- ↑ Hirsh J, Heddle N, Kelton J (2004). "Treatment of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: a critical review". Arch Intern Med. 164 (4): 361–9. doi:10.1001/archinte.164.4.361. PMID 14980986.
- ↑ John G. Brock-Utne (2018-03-01). Clinical Anesthesia: Near Misses and Lessons Learned. Springer. pp. 156–. ISBN 978-3-319-71467-7. Archived from the original on 2020-09-22. Retrieved 2020-06-26.
- ↑ Lindhoff-Last E, Eichler P, Stein M, Plagemann J, Gerdsen F, Wagner R, Ehrly AM, Bauersachs R (March 2000). "A prospective study on the incidence and clinical relevance of heparin-induced antibodies in patients after vascular surgery". Thromb. Res. 97 (6): 387–93. doi:10.1016/s0049-3848(99)00198-x. PMID 10704647.
- ↑ Weismann RE, Tobin RW (February 1958). "Arterial embolism occurring during systemic heparin therapy". AMA Arch Surg. 76 (2): 219–25, discussion 225–7. doi:10.1001/archsurg.1958.01280200041005. PMID 13497418.
- ↑ Natelson EA, Lynch EC, Alfrey CP, Gross JB (December 1969). "Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. An unexpected response to treatment of consumption coagulopathy". Ann. Intern. Med. 71 (6): 1121–5. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-71-6-1121. PMID 5391254.
- ↑ Rhodes GR, Dixon RH, Silver D (March 1973). "Heparin induced thrombocytopenia with thrombotic and hemorrhagic manifestations". Surg Gynecol Obstet. 136 (3): 409–16. PMID 4688805.
- ↑ Kelton, John; Carter, C; Sheridan, D (1 January 1986). "A diagnostic test for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia". Blood. 67 (1): 27–30. doi:10.1182/blood.V67.1.27.27. PMID 3940551. Archived from the original on 23 December 2014. Retrieved 18 June 2015.
- ↑ Dyer, Owen (1 April 2021). "Covid-19: EMA defends AstraZeneca vaccine as Germany and Canada halt rollouts". The BMJ. doi:10.1136/bmj.n883. Archived from the original on 7 April 2021. Retrieved 7 April 2021.
- ↑ Greinacher, Andreas; Thiele, Thomas; Warkentin, Theodore E.; Weisser, Karin; Kyrle, Paul; Eichinger, Sabine (28 March 2021). "A Prothrombotic Thrombocytopenic Disorder Resembling Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia Following Coronavirus-19 Vaccination". Research Square. doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-362354/v1. Archived from the original on 7 April 2021. Retrieved 7 April 2021.
- ↑ "Updated ATAGI statement for healthcare providers on a specific clotting condition being reported after COVID-19 vaccination". Australian Government Department of Health. 2 April 2021. Archived from the original on 5 April 2021. Retrieved 7 April 2021.
- ↑ "Weighing up the potential benefits against risk of harm from COVID-19 Vaccine AstraZeneca" (PDF). Australian Government. 2021-04-13. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2021-04-16. Retrieved 2021-04-16.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |