Miller–Dieker syndrome
| Miller–Dieker syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Miller–Dieker lissencephaly syndrome | |
 | |
| Miller–Dieker syndrome is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner | |
Miller–Dieker syndrome, Miller–Dieker lissencephaly syndrome (MDLS), and chromosome 17p13.3 deletion syndrome[1] is a micro deletion syndrome characterized by congenital malformations. Congenital malformations are physical defects detectable in an infant at birth which can involve many different parts of the body including the brain, hearts, lungs, liver, bones, or intestinal tract. MDS is a contiguous gene syndrome – a disorder due to the deletion of multiple gene loci adjacent to one another. The disorder arises from the deletion of part of the small arm of chromosome 17p (which includes both the LIS1 and 14-3-3 epsilon genes), leading to partial monosomy. There may be unbalanced translocations (i.e. 17q:17p or 12q:17p), or the presence of a ring chromosome 17.
This syndrome should not be confused with Miller syndrome, an unrelated rare genetic disorder, or Miller Fisher syndrome, a form of Guillain–Barré syndrome.
Signs and symptoms

The brain is abnormally smooth, with fewer folds and grooves. The face, especially in children, has distinct characteristics including a short nose with upturned nares, thickened upper lip with a thin vermilion upper border, frontal bossing, small jaw, low-set posteriorly rotated ears, sunken appearance in the middle of the face, widely spaced eyes, and hypertelorism. The forehead is prominent with bitemporal hollowing.[3]
Characteristics that are not visual include intellectual disabilities, pre- and postnatal growth retardation, epilepsy, and reduced lifespan. Failure to thrive, feeding difficulties, seizures and decreased spontaneous activity are often seen. Death usually occurs in infancy and childhood. Multiple abnormalities of the brain, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract (the stomach and intestines) may occur.[citation needed]
Cause
MDS is a microdeletion syndrome involving loss of the gene PAFAH1B1 on chromosome 17 which is responsible for the syndrome's characteristic sign of lissencephaly. The loss of another gene, YWHAE, in the same region of chromosome 17 increases the severity of the lissencephaly in patients with Miller–Dieker syndrome. Additional genes in the deleted region are likely to contribute to the varied features of Miller–Dieker syndrome.[4]
It may be a random event during the formation of reproductive cells or in early fetal development or due to familial chromosomal rearrangement called chromosomal translocation. In less than 20%, inheritance is through an autosomal dominant pattern. The parent is usually unaffected, but carries a particular chromosomal rearrangement called a balanced translocation, in which no genetic material is gained or lost. Increased rate of unexplained fetal loss may be observed in MDS carriers with balanced translocations although they may be otherwise asymptomatic.[5] However, they can become also unbalanced as they are passed to the next generation. Miller–Dieker syndrome is usually not inherited. The deletion event occurs randomly during gametogenesis (formation of eggs or sperm) or in early foetal development.[citation needed] Therefore, no history of the disorder is usually seen in their families.[citation needed]
Diagnosis
The disease may be diagnosed by cytogenetic techniques like fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), testing for a microdeletion at LIS1.[6]
Early detection
With the use of prenatal ultrasonographic imaging, early detection of abnormal brain development in the fetus with MDS can be seen. At birth, facial dysmorphism can be present in the infant. Young children, when affected, can have feeding difficulties, severe intellectual disability, developmental delay, and seizures. MRI facilitates early detection of this syndrome in children by revealing a "smooth brain" image, also called lissencephaly.[7] Children with this syndrome may remain underdiagnosed because of rarity and the prevalence of facial features that appear to be dysmorphic. The syndrome shares distinct external features (phenotype) similar to more common syndromes. Lack of relevant family history may delay diagnosis. FDNA provides a service that in turn increases the chances of detecting these distinct characteristics, which, when shown to a geneticist, can assist in reaching the right medical diagnosis. If a couple has had one child with MDS, they can be offered prenatal screening in future pregnancies. This option is particularly important for the 20% of MDS families where one parent carries a balanced chromosome rearrangement. The risk of these couples having another child with MDS depends on the exact type of chromosomal rearrangement present and may be as high as 25–33%. For families in which both parents' chromosomes are normal, the risk of having another child with MDS is low (1% or less). Either chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis can be used early in a pregnancy to obtain a small sample of cells from the developing embryo for chromosome studies. Early prenatal diagnosis by ultrasound is not reliable because the brain is normally smooth until later in pregnancy. Couples who are considering prenatal diagnosis should discuss the risks and benefits of this type of testing with a geneticist or genetic counselor.[citation needed]
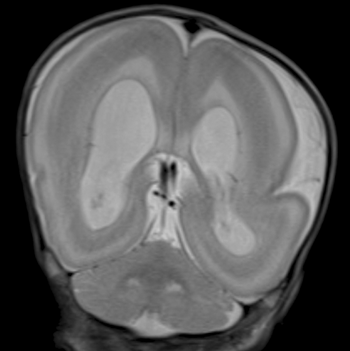
Visuals of the brain
The brain is usually grossly abnormal in outline when someone is diagnosed with Miller–Dieker syndrome. Only a few shallow sulci and shallow Sylvian fissures are seen; this takes on an hourglass or figure-8 appearance on the axial imaging. The thickness and measurement for a person without MDS is 3–4 mm. With MDS, a person's cortex is measured at 12–20 mm.[citation needed]
Treatment
While no cure for MDS is available yet, many complications associated with this condition can be treated, and a great deal can be done to support or compensate for functional disabilities. Because of the diversity of the symptoms, it can be necessary to see a number of different specialists and undergo various examinations, including:[citation needed]
- Developmental evaluation
- Cardiologists evaluation
- Otolaryngology
- Treatment of seizures
- Urologic evaluation
- Genetic counseling-balanced chromosomal translocation should be excluded if parents with an affected child are planning another pregnancy, so parents with affected children should visit a genetic counselor.
This disease is fairly uncommon, and treatment is scarce.
Prognosis
Most individuals with this condition do not survive beyond childhood. Individuals with MDS usually die in infancy and therefore do not live to the age where they can reproduce and transmit MDS to their offspring. Due to more accurate diagnosis by MRI and improved management of symptoms with medical treatments including gastrostomy(feeding tubes), suction machines, seizure medications, tracheostomy, and management of secretions, more children are surviving into adulthood and have a better quality of life. Development of skills and core strength may be improved with physical therapy, but improvement is limited by the severity of the condition. Some children may be able to sit up, crawl, or say a few basic words, but most are severely developmentally delayed and remain at the level of infants for their lifetime. At all ages the most common cause of death is pneumonia, often after multiple cases have weakened the respiratory function.[4]
Epidemiology
Miller-Dieker occurs in less than one in 100,000 people and can occur in all races.[citation needed] Given this statistic, it is conclusive that roughly 75000 people worldwide are affected by MDS.[citation needed]
History
MDS was named for the two physicians, James Q. Miller[8] and H. Dieker.,[9] who independently described the condition in the 1960s. The hallmark of MDS is lissencephaly, a condition in which the outer layer of the brain, the cerebral cortex, is abnormally thick and lacks the normal convolutions (gyri). In some areas of the brain, gyri are fewer in number but wider than normal (pachygyri). Other areas lack gyri entirely (agyri). Normally, during the third and fourth months of pregnancy, the brain cells in the baby multiply and move to the surface of the brain to form the cortex. Lissencephaly is caused by a failure of this nerve cell migration. MDS is often called Miller-Dieker lissencephaly syndrome.[citation needed]
JQ Miller described the disease and in 1969 H Dieker emphasized that it should also take the name lissencephaly syndrome because several malformations occur beyond the brain itself. When MDS was initially described, geneticists assumed it followed an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance. In the early 1990s, several patients with Miller–Dieker syndrome were found to be missing a small portion of chromosome 17. (17p13.3) (a partial deletion).[citation needed]
References
- ↑ Huang, HC; Bautista, SL; Chen, BS; Chang, KP; Chen, YJ; Wuu, SW (1996). "Miller-Dieker syndrome with microdeletion of chromosome 17p13.3: report of one case". Zhonghua Minguo Xiao Er Ke Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi [Journal]. Zhonghua Minguo Xiao Er Ke Yi Xue Hui. 38 (6): 472–6. PMID 9473821.
- ↑ "Miller-Dieker syndrome: MedlinePlus Genetics". medlineplus.gov. Retrieved 2 March 2024.
- ↑ Herman, T E; Siegel, M J (April 2008). "Miller–Dieker syndrome, type 1 lissencephaly". Journal of Perinatology. 28 (4): 313–315. doi:10.1038/sj.jp.7211920. PMID 18379572.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Dobyns, WB; Das, S; Pagon, RA; Adam, MP; Ardinger, HH; Wallace, SE; Amemiya, A; Bean, LJH; Bird, TD; Dolan, CR; Fong, CT; Smith, RJH; Stephens, K (1993). "PAFAH1B1-Related Lissencephaly/Subcortical Band Heterotopia". PAFAH1B1-Associated Lissencephaly/Subcortical Band Heterotopia. University of Washington, Seattle. PMID 20301752. Archived from the original on 2021-02-26. Retrieved 2022-05-17.
- ↑ Pollin, TI; Dobyns, WB; Crowe, CA; Ledbetter, DH; Bailey-Wilson, JE; Smith, AC (6 August 1999). "Risk of abnormal pregnancy outcome in carriers of balanced reciprocal translocations involving the Miller-Dieker syndrome (MDS) critical region in chromosome 17p13.3". American Journal of Medical Genetics. 85 (4): 369–75. doi:10.1002/(sici)1096-8628(19990806)85:4<369::aid-ajmg13>3.0.co;2-l. PMID 10398263.
- ↑ Izumi K, Kuratsuji G, Ikeda K, Takahashi T, Kosaki K (2007). "Partial deletion of LIS1: a pitfall in molecular diagnosis of Miller-Dieker syndrome". Pediatr. Neurol. 36 (4): 258–60. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2006.11.015. PMID 17437911.
- ↑ Chong, SS; Pack, SD; Roschke, AV; Tanigami, A; Carrozzo, R; Smith, AC; Dobyns, WB; Ledbetter, DH (February 1997). "A revision of the lissencephaly and Miller-Dieker syndrome critical regions in chromosome 17p13.3". Human Molecular Genetics. 6 (2): 147–55. doi:10.1093/hmg/6.2.147. PMID 9063734.
- ↑ Miller JQ (1963). "Lissencephaly in 2 siblings". Neurology. 13 (10): 841–50. doi:10.1212/wnl.13.10.841. PMID 14066999. S2CID 42698337.
- ↑ Dieker, H.; Edwards, R. H.; ZuRhein, G. et al. The lissencephaly syndrome. In: Bergsma, D. : The Clinical Delineation of Birth Defects: Malformation Syndromes. New York: National Foundation-March of Dimes (pub.) II 1969. Pp. 53–64.
External links
- Miller–Dieker NIH Archived 2010-05-28 at the Wayback Machine
- Miller-Dieker syndrome NIH Archived 2020-09-18 at the Wayback Machine
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
- Pages with script errors
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from September 2021
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- Articles with unsourced statements from April 2015
- Articles with unsourced statements from September 2020
- Webarchive template wayback links
- Autosomal dominant disorders
- Congenital disorders
- Rare diseases
- Syndromes
- Autosomal monosomies and deletions