Besifloxacin
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Besivance |
| Other names | Besifloxacin hydrochloride |
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Antibiotic (fluoroquinolone)[1] |
| Main uses | Bacterial conjunctivitis[2] |
| Side effects | Redness of the eye[2] |
| Routes of use | Ophthalmic |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a610011 |
| Legal | |
| License data |
|
| Legal status |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H21ClFN3O3 |
| Molar mass | 393.84 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Besifloxacin, sold under the brand name Besivance, is an antibiotic used to treat bacterial conjunctivitis.[2] It is used as an eye drop.[2]
Common side effects include redness of the eye.[2] Other side effects may include allergic reactions.[1] Safety in pregnancy is unclear.[1] It is a fluoroquinolone and works by blocking DNA topoisomerases.[1]
Besifloxacin was approved for medical use in the United States in 2009.[2] In the United States a 5 ml bottle costs about 210 USD as of 2022.[3]
Medical use
Besifloxacin is indicated in the treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis caused by sensitive germs,[4] as well as in the prevention of infectious complications in patients undergoing laser therapy for the treatment of cataracts.[5][6]
Dosage
It is used as one drop three times per day for 7 days.[2] It comes as a 0.6% solution.[1]
Side effects
During the treatment, the most frequently reported ocular adverse reaction was the appearance of conjunctival redness (approximately 2% of patients). Other possible adverse reactions, reported in subjects treated with besifloxacin were: eye pain, itching of the eye, blurred vision, swelling of the eye or eyelid.
Pharmacodynamics
Besifloxacin is a fluoroquinolone that has a broad spectrum in vitro activity against a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative ocular pathogens: e.g., Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum, Moraxella lacunata, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus hominis, Streptococcus mitis, Streptococcus oralis, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Streptococcus salivarius. Besifloxacin has been found to inhibit production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in vitro.[8]
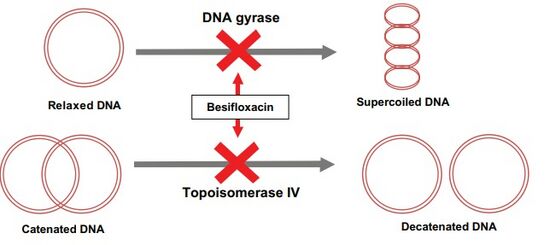
The mechanism of action of besifloxacin involves inhibition of two enzymes which are essential for the synthesis and replication of bacterial DNA: the bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 "Besifloxacin Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 24 January 2021. Retrieved 10 January 2022.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 "DailyMed - BESIVANCE- besifloxacin suspension". dailymed.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 24 March 2021. Retrieved 10 January 2022.
- ↑ "Besivance Prices, Coupons & Savings Tips - GoodRx". GoodRx. Archived from the original on 16 August 2021. Retrieved 10 January 2022.
- ↑ Malhotra R, Ackerman S, Gearinger LS, Morris TW, Allaire C (December 2013). "The safety of besifloxacin ophthalmic suspension 0.6 % used three times daily for 7 days in the treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis". Drugs in R&D. 13 (4): 243–52. doi:10.1007/s40268-013-0029-1. PMC 3851703. PMID 24142473.
- ↑ Majmudar PA, Clinch TE (May 2014). "Safety of besifloxacin ophthalmic suspension 0.6% in cataract and LASIK surgery patients". Cornea. 33 (5): 457–62. doi:10.1097/ICO.0000000000000098. PMC 4195578. PMID 24637269.
- ↑ Nielsen SA, McDonald MB, Majmudar PA (2013). "Safety of besifloxacin ophthalmic suspension 0.6% in refractive surgery: a retrospective chart review of post-LASIK patients". Clinical Ophthalmology. 7: 149–56. doi:10.2147/OPTH.S38279. PMC 3552478. PMID 23355771.
- ↑ Comstock, Timothy L.; Karpecki, Paul M.; Morris, Timothy W.; Zhang, Jin-Zhong (29 March 2010). "Besifloxacin: a novel anti-infective for the treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis". Clinical Ophthalmology. 4: 215–225. doi:10.2147/OPTH.S9604.
- ↑ Zhang JZ, Ward KW (January 2008). "Besifloxacin, a novel fluoroquinolone antimicrobial agent, exhibits potent inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines in human THP-1 monocytes". J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 61 (1): 111–6. doi:10.1093/jac/dkm398. PMID 17965029.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|
|---|
- Pages using duplicate arguments in template calls
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Chemical articles without CAS registry number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs missing an ATC code
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Chloroarenes
- Azepanes
- Fluoroquinolone antibiotics
- Cyclopropanes
- RTT
- All stub articles
- Antibiotic stubs