Trigeminal autonomic cephalgia
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Trigeminal autonomic cephalgia | |
|---|---|
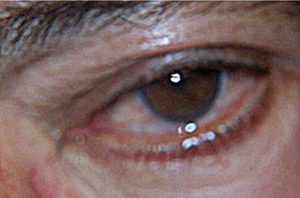 | |
| Short-lasting unilateral neuralgiform headache with conjunctival injection and tearing | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
| Types | Cluster headache, chronic paroxysmal hemicrania, short-lasting unilateral neuralgiform headache with conjunctival injection and tearing, hemicrania[1] |
Trigeminal autonomic cephalalgia (TAC) refers to a group of headaches that present with pain on one side of the head in the trigeminal nerve area, with associated autonomic symptoms on the same side, such as eye watering and redness or drooping eyelids.[1][2]
Types
TACs include
- Cluster headache
- Paroxysmal hemicrania (chronic or episodic)
- Short-lasting unilateral neuralgiform headache attacks with conjunctival injection and tearing (SUNCT)
- Short-lasting unilateral neuralgiform headache attacks with cranial autonomic symptoms (SUNA)
- Long-lasting autonomic symptoms with hemicrania (LASH)
Treatment
Treatment for TACs varies depending on the exact type, but can include medication such as Indomethacin (in the case of chronic paroxysmal hemicrania) or acute and prophylactic therapy (in the case of cluster headache).[3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Swanson, Jerry W.; Bartleson, J. D. (2022). "20. Cranial and facial pain". In Jankovic, Joseph; Mazziotta, John C.; Pomeroy, Scott L. (eds.). Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. Vol. I. Principles of diagnosis (8th ed.). Edinburgh: Elsevier. p. 249. ISBN 978-0-323-64261-3. Archived from the original on 2023-07-02. Retrieved 2023-06-10.
- ↑ Diener, Hans Christoph; Tassorelli, Cristina; Dodick, David W. (1 March 2023). "Management of Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Including Chronic Cluster: A Review". JAMA Neurology. 80 (3): 308–319. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2022.4804. ISSN 2168-6149. Archived from the original on 10 June 2023. Retrieved 10 June 2023.
- ↑ Graff-Radford, Steven. "Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias" (slides). Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 January 2017. Retrieved 12 January 2017.