Hydrochlorothiazide/triamterene
| Combination of | |
|---|---|
| Hydrochlorothiazide | Thiazide diuretic |
| Triamterene | Potassium-sparing diuretic |
| Names | |
| Trade names | Maxzide, Dyazide, others |
| Clinical data | |
| Routes of use | By mouth |
| Defined daily dose | not established[1] |
| Legal | |
| Legal status |
|
Hydrochlorothiazide/triamterene, also known as co-triamterzide, is a combination medication of hydrochlorothiazide and triamterene.[2] It is used to treat high blood pressure and swelling.[2] Specifically it is used in those who develop low blood potassium when on only hydrochlorothiazide.[3] It is taken by mouth.[2]
Side effects may include nausea, trouble sleeping, dizziness, feeling light headed with standing, kidney problems, allergies, and muscle cramps.[3] Other serious side effects may include high blood potassium.[3] Use in pregnancy and breastfeeding is not generally recommended.[3] Use in those with significant kidney problems is not recommended.[3] It decreases blood pressure mainly by hydrochlorothiazide while triamterene decreases the amount of potassium lost.[3]
The combination was approved for medical use in the United States in 1965.[3] A month supply in the United Kingdom costs the NHS about 0.95 £ per month as of 2019.[4] In the United States the wholesale cost of this amount is about 3.90 USD.[5] In 2017, it was the 101st most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than seven million prescriptions.[6][7]
Dosage
The defined daily dose is not established[1]
Society and culture
Cost
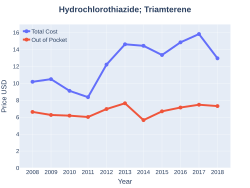
A month supply in the United Kingdom costs the NHS about 0.95 £ per month as of 2019.[4] In the United States the wholesale cost of this amount is about 3.90 USD.[5] In 2017, it was the 101st most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than seven million prescriptions.[6][7]
-
Hydrochlorothiazide/triamterene costs (US)
-
Hydrochlorothiazide/triamterene prescriptions (US)
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "WHOCC - ATC/DDD Index". www.whocc.no. Archived from the original on 1 July 2021. Retrieved 10 September 2020.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "2.9. Cardiovascular system: oedema". BNF 86: September 2023 - March 2024. BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. 2023. p. 254. ISBN 978-0857114617.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 "Triamterene and Hydrochlorothiazide - FDA prescribing information, side effects and uses". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 22 April 2019. Retrieved 5 March 2019.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. p. 76. ISBN 9780857113382.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "NADAC as of 2019-02-27". Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Archived from the original on 2019-03-06. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "The Top 300 of 2020". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 12 February 2021. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Hydrochlorothiazide; Triamterene - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 11 April 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
External links
- Pages using duplicate arguments in template calls
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Chemical articles without CAS registry number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs missing an ATC code
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Drugs that are a combination of chemicals
- Articles using infobox templates with no data rows
- RTT
- Drugs