Arsthinol
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
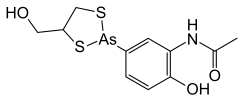
N-{2-Hydroxy-5-[4-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3,2-dithiarsolan-2-yl]phenyl}acetamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.965 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H14AsNO3S2 | |
| Molar mass | 347.28 g·mol−1 |
| Pharmacology | |
| P01AR01 (WHO) QP51AD01 (WHO) | |
| Oral | |
| Pharmacokinetics: | |
| 89 % Hepatic[1] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Arsthinol (INN) is an antiprotozoal agent. It was synthesized for the first time in 1949 by Ernst A.H. Friedheim by complexation of acetarsol with 2,3-dimercaptopropanol (British anti-Lewisite)[2] and has been demonstrated to be effective against amoebiasis and yaws. It was marketed few years later by Endo Products (Balarsen, Tablets, 0.1 g).[3] Among trivalent organoarsenicals, arsthinol was considered as very well tolerated.[4] Recently, it was studied for its anticancer activity.[5][6]
References
- ^ Cristau, B; Chabas, ME; Placidi, M (1975). "Voies et cinétiques d'excrétion de l'arsenic chez le Cobaye après injection de divers médicaments organo-arséniés". Ann Pharm Fr. 33: 577–89.
- ^ Friedheim, Ernst AH (1949). "A Five Day Peroral Treatment of Yaws with STB, a New Trivalent Arsenical". Am J Trop Med Hyg. s1-29 (2): 185–188. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.1949.s1-29.185. PMID 18116845.
- ^ Anonyme (1953). "New and nonofficial remedies; arsthinol". J Am Med Assoc. 152: 531.
- ^ Brown, CH; Gebhart, WF; Reich, A (1956). "Intestinal amebiasis: incidence, symptoms, and treatment with arsthinol (Balarsen)". JAMA. 160 (5): 360–363. doi:10.1001/jama.1956.02960400018005. PMID 13278204.
- ^ Gibaud, S; Alfonsi, R; Mutzenhardt, P; et al. (2006). "(2-Phenyl-[1, 3, 2] dithiarsolan-4-yl)-methanol derivatives show in vitro antileukemic activity". J Organomet Chem. 691 (5): 1081–1084. doi:10.1016/j.jorganchem.2005.11.007.
- ^ Becherirat, S.; Lanhers, M.-C.; Socha, M.; Yemloul, M.; Astier, A.; Loboda, C.; Aniceto, N.; Gibaud, S. (2013). "The antitumor effects of an arsthinol-cyclodextrin complex in an heterotopic mouse model of glioma" (PDF). Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 85 (3): 560–568. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2013.06.021. PMID 23831266.
Categories:
- CS1: long volume value
- Chemical articles with multiple compound IDs
- Multiple chemicals in an infobox that need indexing
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Chembox image size set
- Articles with short description
- Short description matches Wikidata
- Antiprotozoal agents
- Acetanilides
- Primary alcohols
- Phenols
- Organoarsenic dithiolates
- Arsenic heterocycles
- Arsenic(III) compounds
- Sulfur heterocycles
- Heterocyclic compounds with 1 ring
- All stub articles
- Antiinfective agent stubs