Talk:Cortisol/Archive 1
| This is an archive of past discussions. Do not edit the contents of this page. If you wish to start a new discussion or revive an old one, please do so on the current talk page. |
| Archive 1 |
Untitled
This sentence needs a rewrite. I'm not sure what it's supposed to say
- Since swelling is caused by the immune system, Cortisol can help to decrease the swell and severe allergy reaction. --LeeHunter 23:32, 12 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- It was obviously written by an ESL kid.01:51, 24 October 2015 (UTC)01:51, 24 October 2015 (UTC)01:51, 24 October 2015 (UTC)01:51, 24 October 2015 (UTC)01:51, 24 October 2015 (UTC)01:51, 24 October 2015 (UTC)~~ — Preceding unsigned comment added by 2604:6000:E641:5300:83F:15CF:5536:A31 (talk)
Come aqain?
"Oral contraceptives increase cortisol levels in young women which perform whole-body resistance exercise training. ". The contraceptives increase excerise? young women who exercise? the oral contraceptives perform the resistance exercise? This sentance made me lose respect for Wikipedia. —Preceding unsigned comment added by 89.145.198.172 (talk) 17:45, 30 June 2009 (UTC)
The language on this page is so extremely unclear that it makes the whole article useless. It contradicts itself internally and with relation to references because of the unclear language, overuse of scientific terms and frequent use of double negatives. It will be highly appreciated if someone with knowledge of the subject will simplify the wording. I came to this page seeking clarification of Cortisol and it's relationship to Stress and Inflammation and left more confused than before.Jpvosloo (talk) 19:38, 2 August 2009 (UTC) hola que hace Yes, please. I, the Sun Rotarmie Soldier, you rush to the aid. Cortisol (possibly prednisolone, Hidrokortizon, dexamethasone) Kontrazeptieva are well suited for younger US- Amerikanere. We land, take these Kontrazeptieva regularly, with breakfast - Kafe, in Maison de Accuel. When training in French language obviously he did not mind. When marketing with local aborigines, on tram Stayshen * ... * may. But only a little. After about 5 months could these younger subject, in still good condition, take off back to USA.Moshe Vitalievitch (talk) 14:50, 31 March 2016 (UTC)
Should merge with hydrocortisone?
There is another less developed page entitled hydrocortisone. Obviously it deals with the same substance. Perhaps that entry should be merged with this one? KBi 03:25, 3 May 2005 (UTC)
I suppose they could be merged, as hydrocortisone is the synthetic cousin of cortisol (as far as I know)...
- According to Guyton, Hall: Textbook of Medical Physiology (p.875), these are just two names for the same substance. --Eleassar777 21:59, 29 May 2005 (UTC)
- I looked up online sources such as the NIH and they say that hydrocortisone is the synthetic version of cortisone and that is is similar, but apparently not exactly, the same. Also, some people are allergic to hydrocortisone, though that article is about the skin and perhaps you can be allergic to natural cortisone on the skin or elsewhere. I would keep the article together, as they've apparently been merged now, and simply make sure that the distinction between them is made. Kjkolb 16:46, Jun 14, 2005 (UTC)
- Cortisol and Hydrocortisone are absolutely the exact same molecule. The only distinction is the sphere of usage of the term. Cortisol is uniformly used in biochemistry. Hydrocortisone is the term used in pharmacology.
- If you search the PubMed Substance database, you'll find 56 entries (because this is a meta-database from different sources), all for the same compound, all listing cortisol and hydrocortisone among the MANY, MANY synonyms. (A historically important synonym is Kendall's Compound F).
- However, you are correct that hydrocortisone and cortisone are similar, but not the same! But this is not about cortisone, it's about cortisol/hydrocortisone!
- Cortisol/hydrocortisone and cortisone both occur in the body. Cortisone itself is not particularly active, if at all, but they are interconverted by the enzyme 11-beta deoxysteroid dehydrogenase, types 1 and 2 (for each direction). See the Metabolism section of this article. Historically, cortisone was used theraputically, but this has largely been replaced with hydrocortisone or the synthetics.
- The article for Hydrocortisone now redirects to Cortisol, as it should. The Cortisone article is separate, and should remain so.
- This article incorrectly indicates that "Hydrocortisone is the chemical form of cortisol used for oral administration or intravenous injection". I'll correct this to:
- Hydrocortisone is the pharmaceutical term for cortisol used for oral administration, intravenous injection, or topical application.
- Bob Kerns (talk) 16:36, 6 December 2008 (UTC)
- I realise I risk challenging a huge body of respected expertise here, in addition to which I'm no biochemist and this question comes from personal experience, but I think it's important enough an issue to raise in the hope that someone more educated in these matters can comment. If hydrocortisone, produced outside the body, and naturally occurring cortisol, produced in the body, are indeed interchangeable, why should someone (i.e. me in this case) suffer fairly serious, very characteristic, allergic symptoms to the former - administered transdermally and at a physiological dose - and have no such reactions to animal-derived cortisol extracts? To clarify; when I say very characteristic, I mean that it is a set of symptoms which ONLY occur on exposure to synthetic steroid medications; when I say animal-derived cortisol extracts, I am not talking about a weak supplement formulation not worthy of the name, but one which restores my very low cortisol levels to normal. Could it not be that the chemical (hydrocortisone) in isolation from its biological context is not treated by the body in the same way as that which is naturally produced [by a body]? Glaciare (talk) 11:00, 1 August 2010 (UTC)
- (I'd forgotten about writing the previous comment...) To answer your question:
- I cannot quite fathom the concentration of hydrocortisone and area of application that would be required to restore very low cortisol levels to normal. I'm sure it would be substantial, as we are talking about transdermal adsorption of perhaps 10-15 mg of material. For reference, a Androderm patch has of area, with of testosterone in an alcohol-based gel. The total patch is in area. Furthermore, this is a higly non-physiologic mechanism for delivery of hydrocortisone, as it is far too slow to mimic the diurnal variation in blood levels. Instead, you are subjecting the skin, locally, to concentrations far beyond physiological levels, which over the long run, may be quite damaging to the skin, due to collagen loss, even if you rotate it among different sites. This is why over-the-counter hydrocortisone preparations are limited to 1% concentration. So you would need a very large amount of preparation, over a very large surface area, rotated from site to site, to successfully treat the condition and avoid serious problems with the skin.
- So concentrating it at the skin as you are doing is indeed going to be treated by the body in a very different way, than the much more dilute and uniform distribution resulting from normal adrenal adsorption.
- As to why the difference: whatever you are applying to your skin is not the white crystalline powder that is pure hydrocortisone. I believe all current commercial hydrocortisone preparations are derived from plant sterols. Trace proteins from the plant origins or the chemicals used in the intermediate steps from this process could potentially be related to your symptoms. However, whatever your hydrocortisone is mixed with to make whatever creme or other formulation you are applying is a much more likely candidate, as there is a large quantity of material, compared to traces. Both your synthetic and animal-derived versions will have these "filler" materials, which are an important part of the drug delivery, but they will be different. Neither one is at all similar to the biological context in which cortisol is found in your body, where it is mostly circulating in the bloodstream, mostly bound to various proteins (Cortisol Binding Globulin and Albumin).
- If your preparation is being prepared by a compounding pharmacy, they may be starting with a preparation intended for oral use, rather than dermal.
- A much more natural way to get it into your system is orally, and this is what nearly every person with Addisons does in this day and age. This puts it into the bloodstream fairly quickly, which is important to match the high levels in the early morning. You can divide the dosage, with larger amounts in the AM, to more closely mimic the natural pulses produced by the body.
- I know of a couple cases where people used insulin pumps to deliver hydrocortisone succinate subcutaneously in a pattern throughout the day.
- But I hope your diagnosis of "very low cortisol" levels is based on actual stimulation testing, and not a single cortisol blood draw, which can be highly misleading, because the levels vary so much throughout the day. Use of hydrocortisone or similar steroids can actually suppress the body's cortisol production. Please do not change your therapy without competent medical advice, preferably from an endocrinologist, as the consequences of a lack of cortisol are quite serious, whether as a primary problem, or as a result of prior use of hydrocortisone. Also consider that if your body is not producing cortisol, it may not be producing aldosterone, which is also a serious problem.
- Finally, I want to note that asking medical advice on the talk pages of Wikipedia is not a very good approach. There are forums dedicated to the topic which will give you much better and broader feedback, but your best input is a doctor with some real expertise in this area -- an endocrinologist. I do not believe any competent endocrinologist would have you addressing low cortisol via transdermal treatment. Bob Kerns (talk) 08:54, 25 April 2011 (UTC)
- I realise I risk challenging a huge body of respected expertise here, in addition to which I'm no biochemist and this question comes from personal experience, but I think it's important enough an issue to raise in the hope that someone more educated in these matters can comment. If hydrocortisone, produced outside the body, and naturally occurring cortisol, produced in the body, are indeed interchangeable, why should someone (i.e. me in this case) suffer fairly serious, very characteristic, allergic symptoms to the former - administered transdermally and at a physiological dose - and have no such reactions to animal-derived cortisol extracts? To clarify; when I say very characteristic, I mean that it is a set of symptoms which ONLY occur on exposure to synthetic steroid medications; when I say animal-derived cortisol extracts, I am not talking about a weak supplement formulation not worthy of the name, but one which restores my very low cortisol levels to normal. Could it not be that the chemical (hydrocortisone) in isolation from its biological context is not treated by the body in the same way as that which is naturally produced [by a body]? Glaciare (talk) 11:00, 1 August 2010 (UTC)
- Hi Bob, and thanks for your reply. Firstly, my motive for posting this was a genuine curiosity about these two substances being regarded as interchangeable. I do have medical supervision (I do have clinically-low cortisol levels throughout the day) and - something I worded misleadingly in my first paragraph - I do take oral cortisol. My doctor did not try me with oral synthetic hydrocortisone because I have had such extreme reactions to all synthetic steroid medications - administered by any means - ranging from prolonged and 'mobile' grand urticaria with fever to systemic swelling. The hydrocortisone cream I used (once, some years ago, for eczema) produced the same grand urticaria - i.e. it moved all over my body for several weeks after cessation - so the chances of it being another excipient are minimal, I would say (nothing but synthetic steroid medication has ever caused this kind of reaction). I may be an odd case, but I wonder if any similar ones have been recorded in the literature...? Glaciare (talk) 14:47, 7 May 2011 (UTC)
Whoa
This article is a little scientifically intense to start off, it would be nice to have a more gentle intro. TitaniumDreads 6 July 2005 11:06 (UTC)
- Be bold. Also please source the cortisol/obesity comment with a serious reference. JFW | T@lk 6 July 2005 15:15 (UTC)
dans notre pays avec le cortisol / prednisolone aussi Knasti sont excités. Déportation - Insassere, et terroriste suspect Insassere. Le contrat ne les maladies non inflammatoires.Moshe Vitalievitch (talk) 15:11, 31 March 2016 (UTC) from 01.19.2016, in principle, everyone can come to us to try hormonisierende, healing, stem end, warming effect of cortisol / hydrocortisone (prednisolone). Prednisolone / cortisol which is a Vollks- drug. Also, and in particular, is well suited for low-paid, qualified or Worse About Skilled labor. Very well edited Wikipedia article. (63.087 bytes, they compare it with the Germany- 10,466 bytes or France - 18 387 octets.) Exciting / amusing entertainment. Highly professional user's to participate.Cort i sol (talk) 15:56, 15 June 2016 (UTC)
TV ads
what about the tv ads for fat people for otc meds that reduce cortisol. anyone know about info on how they do/dont work and why, & add it to the article - anonym420
- I live in a country without direct-to-consumer advertising, so we are spared this. Bottom line: they don't work. It's based on the premise that fat people have hypercortisolism, but this is not so, unless they have Cushing's disease (a rare condition compared to obesity). If these drugs worked, they'd be causing Addison's disease, which is more dangerous than Cushing's in the short term (hypotension and hypoglycemia being phenomena one would expect). JFW | T@lk 12:33, 5 September 2005 (UTC)
error ?
hello, i am not an expert, but after browsing several related topic on insulin, is there an error on the following paragraph (marked by asterisks), shouldn't the marked word be decreased instead of increased? :
"In normal release, cortisol has widespread actions which help restore homeostasis after stress. It acts as a physiological antagonist to insulin by promoting breakdown of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins and so mobilizing energy reserves. This leads to increased blood glucose concentrations and *increased* glycogen formation in the liver (Freeman, 2002)."
- Cortisol does indeed cause increased gluconeogenesis and increased glycogenesis at the liver. In other words, it stimulates the liver to make glucose, and make glycogen, which is the storage form of glucose. However, this is not counterproductive. The idea is to increase glucose now (primarily for neuron survival), and store some in case of continued or additional stresses. It also has an anti-insulin action at muscle, adipose, and other insulin-sensitive tissues where it prohibits glucose uptake. Just2seeusmile52 (talk) 00:44, 18 April 2010 (UTC)
- It sounds odd, but most of what I found on Google seems to support the present version. JFW | T@lk 16:41, 20 November 2005 (UTC)
You are right on the logic side but the fact is cortisol is not part of glycogen regulation. I was wondering the same thing until I saw how it goes: If there is increased blood glucose there would be increased glycogen formation. It goes well with the fact that it promotes after stress homeostasis(the epinephrine burst that decreased liver glycogen would be gone).
There are 4 major regulator of glycogen metabolism: insulin and then glucagon, epinephrine and norepinephrine; the first one resulting in increased stockage and the others in increased degradation. Stress normally induced degradation and cortisol is a stress hormone as is adrenaline(epinephrine) but it seems it is more post stress and so that could explain it.
cortisol does not increase glycogen formation and this statement needs to be removed.
- Cortisol promotes glycogen break down in muscle and glycogen synthesis in liver -- Kaplan physiology 2006. This is how it works: Cortisol stimulates processes such as glycogenolysis in muscles and gluconeogenesis, which increase blood sugar level. High blood sugar(=glucose) level causes beta cells of pancreas to release insulin. This insulin causes the liver to start synthesizing glycogen from the circulating glucose. Hope this helps. PS: Insulin also causes glycogen synthesis in muscles, but i guess this is offset by glycogen breakdown due to cortisol.Evox777 (talk) 03:22, 10 December 2009 (UTC)
Does Corticol cause Obesity?
is it true the hearing increased cortisol translates into obesity?
- Yes, see Cushing's syndrome. JFW | T@lk 10:24, 29 November 2005 (UTC)
pregnenolone
By my understanding, cortisol is synthesized from pregnenolone rather than progesterone. The steps in the cortisol synthetic pathway from cholesterol are: Cholesterol -> pregnenolone -> 17-OH pregnenolone -> 17-OH progesterone -> 11-deoxycortisol -> cortisol.
correction
I have found an alternatively described pathway that does show that cortisol can be synthesized via a progesterone intermediate. However, progesterone is first synthesized from pregnenolone, still making pregnenolone the original comitting precursor molecule for steroid hormone synthesis.
Side effects of topical application of cortisol cream
Are there any? I've found its immune-system repression is great for fighting psoriasis but I wonder if there are any long-term effects from repeated use on the same area of skin. 00:14, 5 August 2006 (UTC)
- Stretch marks (I developed some after a few uses of 0,1% Locoid only), thinning skin, permanent aged apprearance. With larger areas you also get large absorption and systemic effects. It's really just an emergency medication 82.131.63.11 (talk) 19:56, 6 June 2008 (UTC)
This is the tip of the iceberg. Of course, it depends on the dose and on your baseline levels of cortisol, but cushingoid symptoms (as described above) are certainly a risk. ACTH and endogenous cortisol suppression would also follow; after all, if you're putting it on your skin, why should your body make its own? Rapid discontinuation of topical hydrocortisone would then lead to Addison's Disease - like symptoms. Eventually one's pituitary gland would sense the change and correct the disruption in the feedback loop, but this would take some time.
Cleanup required
I think the Physiology section is awfully messy/noisy, and in the Pharmacology section, is it strictly necessary with all those ® signs? It's not like you'd write Microsoft® Windows® each time you refer to that family of OSes, e.g. DarkPhoenix 15:01, 8 January 2007 (UTC)
- Okay, why not replace that template with a section specific one. PhoenixTwo 17:13, 6 March 2007 (UTC)
Diseases vs Disorders
Perhaps the section named "Diseases" should be changed to "Disorders," since Metabolic syndrome is not a disease, though Cushing's is. (Also, the wording of the two descriptions, as it now stands, lacks consistency.) D021317c 09:10, 8 February 2007 (UTC)
more on topical application of cortisol cream
After 50 years I am finally able to self diagnose why my procedural memory is fine, but my declarative memory has always been a disaster. Cortisol!!
Throughout my childhood, I suffered from eczema and treated it by applying hydrocortisone cream directly to large open wounds (scratched areas behind knees and inside elbows). It appears the cortisol was absorbed directly into my bloodstream and severely damaged my hippocampus. This explains why I became a Professional Engineer (considered one of the best in my field), yet I have virtually no episodic or semantic memory. 159.221.32.10 13:29, 18 April 2007 (UTC)
Effect paragraph
hi, In the effects paragraph, one needs to change "gluconeogenesis" to gluconeolysis. Insulin who is the anti-glucose hormone will act on everything that lowers circulating glucose, ie by producing glycogen in the liver. Cortisol brakes down this glycogen to produce circulating glucose, glucagon has the same effect 159.221.32.10 08:07, 23 May 2007 (UTC)
- Welcome. One of the beautiful things about Wikipedia is that you do not need to ask anyone to change the article; you can be bold and update it yourself. --Selket Talk 09:19, 23 May 2007 (UTC)
- It's a good idea to do your homework first, and get the facts straight, though, especially on topics that relate to medicine. A side benefit is you learn so much more when you're careful about your fact checking! Cortisol works to increase glucose levels via gluconeogenesis (making new glucose, by breaking down fats and proteins), not glycolysis (breaking down glycogen). Bob Kerns (talk) 09:04, 25 April 2011 (UTC)
According to Human Anatomy and Physiology, 5th Ed. by E. Marieb (2001), "cortisol's prime metabolic effect is to provoke nucleogenesis, that is, the formation of glucose from noncarbohydrate molecules..." So, under stress cortisol acts to increase blood glucose levels to prepare for increased metabolic demands.Neuroninja (talk) 08:49, 24 November 2007 (UTC)
Effect on liver glycogen formation
Hi, According to the Columbia Encyclopedia on Google, according to Meisenberg & Simmons: Principles of Medical Biochemistry, 2. edition, and according to Boron & Boulpaep: Medical Physiology, cortisol increases glycogen synthesis in the liver, contrary to what the article says.
This makes sense: Cortisol is a chronic stress hormone which prepares the body for the action of epinephrine, a stress hormone working within seconds. In order to enhance the effects of epinephrine, cortisol stimulates glycogen synthesis so that, in times of need, more glycogen is available to be broken down when epinephrine levels rise. Epinephrine and glucagon are the hormones that promote glycogenolysis in the liver.
Cortisol raises the blood glucose level by stimulating gluconeogenesis in the liver, not by stimulating glycogenolysis.
User JFW quotes Freeman (2002) for saying that cortisol leads to increased glycogen formation in the liver, while in the current article, the book is used as a reference saying the opposite.
Are there any sources supporting the statement that cortisol decreases glycogen formation in the liver? Otherwise I'm going to change it. Nelly4 21:21, 12 June 2007 (UTC)Nelly4
Cortisol production site
Cortisol is not only produced in zona fasciculata but in zona reticularis as well? http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/89/Corticosteroid-biosynthetic-pathway-rat.png —Preceding unsigned comment added by Eslotter (talk • contribs) 01:22, 4 March 2008 (UTC)
Zona Reticularis produces Androgens, not Cortisol. The pathway in the above picture is a condensed version. Fasciculata and Reticularis have been combined because both of them are controlled by ACTH.http://themedicalbiochemistrypage.org/images/adrenalsteroidsynthesis.jpgEvox777 (talk) 08:13, 29 November 2009 (UTC)
Glycogen-issue edited
Decided to edit the controversial glycogen formation promoting-statement. Cortisol is a catabolic-agent, and therefore has no anabolic effects e.g. glycogenesis.
Sources of information:
Sjaastad ØV; Hove, K & Sand O, 2003. Physiology of Domestic Animals, Scandinavian Veterinary Press, Oslo, (755 pp)
Harvey RA; Champe PC, Ferrier DR, 2005. Biochemistry 3rd Edition,Lippincott's Illustrated Reviews, Baltimore —Preceding unsigned comment added by Little T85 (talk • contribs) 17:09, 11 October 2007 (UTC)
Hydrocortisone
"Hydrocortisone" redirects to "Cortisol". However "hydrocortisone" is the name used for exogenous (artificial therapeutic) cortisol, while "cortisol" is endogenous (produced by the body). The "Hydrocortisone" redirect should be changed to show this. Axl (talk) 10:04, 8 March 2008 (UTC)
Standards/quality note should be moved to the top of the article
From a readability and clarity standpoint, this entire article is a mess. There are numerous text references to highly esoteric items with no contextual information; there is no (clear) explanation of the varied usage of chemical names to refer to cortisol; there is little information on the relationship between cortisol and cortisone; and the references to various experimentation and research are vague and in some cases appear, at least superficially, to be self-contradictory (e.g., the cortisol/insulin relationship).
Although I could help in cleaning up the comprehensibility and formatting of the text, I'm not comfortable doing so without advanced knowledge of the subject matter. Therefore, I'll just put in my recommendation, and offer to help if it would be useful.
Blckclbrtn (talk) 00:47, 8 June 2008 (UTC)
Relationship to thyroid hormone (T3) and hypothyroidism
Does anyone have a journal (or endo textbook) reference for the fact that cortisol is required for T3 to bind to cellular receptors and enter cells? This is often repeated on various thyroid/adrenal lists and website, but I haven't been able to find a journal article to source it. (I can't find anything about whether rT3 actually binds to T3 receptors as an inactive 'decoy' either, or that matter..)
The article might also want to say something about the fact that thyroid treatment shouldn't be odne without first dealing with adrenal insufficiency - except I can't find any articles backing that up either. —Preceding unsigned comment added by 216.9.142.151 (talk) 05:35, 11 July 2008 (UTC)
- I had never heard of this requirement. I checked Guyton just to make sure. There is no mention of cortisol for synthesis/function/binding of T3 in the entire thyroid chapter. The process, as far as I am aware, follows something like this: T4 is avidly bound by thyroid hormone binding proteins from the liver (TBG, TTR, and albumin). Same for T3. T4 stays bound by the plasma proteins on average about six days, whereas T3 is released in about a day. When absorbed into the cell (no mention of mechanism or cortisol) they are bound by other binding proteins in the cell. T4 is converted to T3 by iodinase. When released from the cellular binding proteins, T3 binds to the thyroid hormone receptor in the nucleus. That complex also complexes with RXR and kicks off transcription. If you have references that point to the contrary, I'd like to see them. However, there is plenty of literature out there that shows the converse. T3 appears to be necessary for cortisol expression (e.g. here). Chaldor (talk) 06:29, 11 July 2008 (UTC)
- There's a fair bit of confusion floating around here; you address part of it; let me see if I can address the rest.
- The big issue with cortisol/Thyroid interaction is that increasing T3 levels increases overall metabolic rate, including the rate of metabolizing cortisol, which, if in short supply, can trigger an adrenal crisis. So indeed, one should treat adrenal insufficiency before beginning treatment for hypothyroidism -- but then, one should treat adrenal insufficiency promptly anyway, as it's far more life-threatening. (See for example, the emedicine.com articles on both adrenal crisis and hypothyroidism, each pointing out the dangers of neglecting the other condition). You can find references, both to the clinical concern, and the underlying physiology. As to rT3, cortisol required for binding, etc.. To the best of my knowledge (and without my usual fact checking, sorry -- it's hard to fact-check a negative), cortisol is not required for T3 to bind or enter. Actually, that's backwards -- the thyroid hormone receptors are nuclear receptors, and quite similar to the receptor for cortisol. So both molecules have to enter the cell before they bind to the receptors, which then bind to the DNA and affect transcription. As for T3 vs rT3 -- there is an interaction with cortisol there. What happens is that there are two pathways to get from T4 to T2, one via T3, one via rT3, depending on which iodine is removed first. Each iodine is removed by a different deiodinase enzyme, and cortisol affects the relative concentrations. Google for "deiodinase cortisol" for a slew of references. rT3 doesn't bind to the nuclear T3 receptors; that's a confusion. They're produced in competition, rather than bind in competition. (There do appear to possibly be nuclear binding sites for rT3: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7075548 -- the things you learn from fact-checking!) The article from Nature that you cite doesn't say what you say it says -- but probably what you meant to say it says. In the case of production of growth hormone, it appears that both cortisol and T3 are necessary. This has nothing to do with cortisol expression, but rather cortisol-triggered expression of genes involved in GH1 production. It's unclear how much we should generalize from that result -- but clinically, it's important to get both hormones right, and they do interact. Bob Kerns (talk) 09:39, 25 April 2011 (UTC)
Alphabet Soup
This is a nice description of cortisone, rather than cortisol (17-OH-cortisone, also known as compound F). Before the structures were known, the adrenal steroids were identified as spots on thin layer chromatography. Kendall called them compounds and Reichstein called them substances, and their letters don't match between systems. There's a nice retrospective essay: Dallman MF, "Adrenocortical function, feedback, and alphabet soup." Am J. Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 289: E361-2 (2005); http://ajpendo.physiology.org/cgi/reprint/289/3/E361.pdf. Kjg321 (talk) 21:16, 6 August 2008 (UTC)
Merge of sections
Biosynthesis and Regulation seem to have the same kind of information.--Nutriveg (talk) 16:36, 1 March 2009 (UTC)
Cortisol and autism
I was interested to read, here - http://www.physorg.com/news157869665.html - of a recent study suggesting a link between the daily cortisol cycle and at least some forms of autism spectrum disorder. Obviously further studies are needed before we can say much, but I wonder if this should be briefly mentioned in the article. 125.168.127.32 (talk) 11:24, 6 April 2009 (UTC)
Really?
It has been proposed that its primary function is to inversely mobilize the immune system to fight potassium-depleting diarrhea diseases.
The following quote is from an article published in Medical Hypotheses which is a non peer-reviewed fringe journal (opinion on scienceblogs). I am not a wikipedian and I do not know if this is a place for such speculative, unverified claims but if you are okay with that perhaps it should be at least underlined that the source of that information is at best controversial. --83.8.209.253 (talk) 21:53, 14 August 2009 (UTC)
Where's the logic
Prolonged cortisol secretion causes hyperglycemia and diabetes mellitus. The reason why in vivo experiments seem to deny this is that cortisone (a cortisol metabolite) greatly inhibits insulin.
- cortisol increases glucose by opposing insulin. Cortisone inhibits insuling. What do the experiments "seem to deny"? --CopperKettle 15:22, 23 October 2009 (UTC)
it is my understanding that all those effects listed are effects of taking in too much cortisol, isn't that right? if that is so, why is this not stated? it's confusing to meet up with sentences like "it 'enables' hypotonic urination." because if you think about it, why would you want a hormone in your body to enable a malfunction? I would rather suppose it is the excess of a hormone that would cause your body to malfunction. iNsOmNiAcAnDrEw 24.19.34.86 (talk) 21:56, 9 June 2010 (UTC)
Material needing clean-up
The following material - which tends towards being way over-specific for a general interest user generated encyclopedia - has been flagged as needing clean-up to be understandable/relevant to the Cortisol article. Please do so here before re-integrating improved content into the latter:
Extended content
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Effects
In normal release, cortisol (like other glucocorticoid agents) has widespread actions which help restore homeostasis after stress. (These normal endogenous functions are the basis for the physiological consequences of chronic stress - prolonged cortisol secretion.)
Cortisol counteracts insulin, contributing to hyperglycemia by stimulus of hepatic gluconeogenesis[1] and inhibition of the peripheral utilization of glucose[1] by decreasing the translocation of glucose transporters to the cell membrane,[2] specially GLUT4[3]. However cortisol increases glycogen synthesis (glycogenesis) in the liver.[4] Permissive effect of cortisol on insulin action on liver glycogenesis is observed in hepatocyte culture in laboratory. However, the mechanism is unknown.
BindingMost serum cortisol, all but about 4%, is bound to proteins including corticosteroid binding globulin (CBG), and serum albumin. Only free cortisol is available to receptors. RegulationThe primary control of cortisol is the pituitary gland peptide, adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). ACTH probably controls cortisol by controlling movement of calcium into the cortisol secreting target cells.[34]. ACTH is in turn controlled by the hypothalamic peptide, corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH), which is under nervous control. CRH acts synergistically with arginine vasopressin, angiotensin II, and epinephrine [35]. When activated macrophages start to secrete interleukin-1 (IL-1), which synergistically with CRH increases ACTH,[26] T-cells also secrete glucosteroid response modifying factor (GRMF or GAF) as well as IL-1, both of which increase the amount of cortisol required to inhibit almost all the immune cells [27]. Thus immune cells take over their own regulation, but at a higher cortisol set point. Even so, the rise of cortisol in diarrheic calves is minimal over healthy calves and drops below with time.[36] The cells do not lose all of the fight or flight override because of interleukin-1's synergism with CRH. Cortisol even has a negative feedback effect on interleukin-1 [37] which must be especially useful for those diseases which gain an advantage by forcing the hypothalamus to secrete too much CRH, such as the endotoxin bacteria..The suppressor immune cells are not affected by GRMF,[27] so that the effective set point for the immune cells may be even higher than the set point for physiological processes. GRMF (called GAF in this reference) primarily affects the liver rather than the kidneys for some physiological processes [38]. A high potassium media, which stimulates aldosterone secretion in vitro, also stimulates cortisol secretion from the fasciculata zone of dog adrenals [39] unlike corticosterone, upon which potassium has no effect [40]. Potassium loading increases ACTH and cortisol in people also [41]. This is no doubt the reason why a potassium deficiency causes cortisol to decline (as just mentioned) and why a potassium deficiency causes a decrease in conversion of 11deoxycortisol to cortisol [42]. This probably contributes to the pain in rheumatoid arthritis since cell potassium is always low in that disease [43] Factors affecting cortisol levelsFactors generally reducing cortisol levels
Factors generally increasing cortisol levels
Wikiuser100 (talk) 10:12, 23 May 2010 (UTC) Hi, when making so drastic changes please do it incrementally so they can be individually reverted. Particularly I disagree with your removal of "Factors generally increasing cortisol levels" since that's important information for controlling and estimating cortisol but you changed so much that I need some time to analyse all those changes.--Nutriveg (talk) 18:23, 24 May 2010 (UTC) References
"One study by a Japanese cosmetics company has asserted that makeup reduces cortisol levels in a mental stress situation." |
You have got to be kidding. I'm removing this immediately. —Preceding unsigned comment added by 71.101.187.191 (talk) 07:54, 1 September 2010 (UTC)
I think someone should start over.
A lot of very knowledgeable people have written comments about this article. I'm afraid I'm not one of them, or I would tackle it. Perhaps someone could just scrap this article and start over. To me it reads as if it were originally written in another language and then translated by machine. This subject is really important to a lot of people, but this article isn't helpful at all.
Mschucker (talk) 03:56, 6 June 2010 (UTC)
Hi! In contrast, I found the article fully understandable because I am a medical graduate with postgraduate training in endocrinology and immunology. A simple introduction would certainly help those who find so many technical words which they refer to as jargon. I found this article whilst looking for data on the serum cortisol levels in the normal adult and the level in chronic stress. I have a reference which cites a fivefold increase in serum cortisol in both acute and chronic stress; the article I have in my office also points to the danger of adrenal failure due to chronic stress as occurs in patients in an intensive care unit. The article followed serum cortisol levels in two groups i)patients with multiple fractures & ii)patients with overwhelming infection. I will retrieve my article and come again to this page! But please, Prof Wiki, DON'T erase this page!! Dr Allen E Gale Consultant Physician(Allergy) Hindmarsh South Australia, June26 2010 —Preceding unsigned comment added by 219.90.135.176 (talk) 00:55, 26 June 2010 (UTC)
Dr. Gale: how's it going? I just came across this page and am equally fascinated/excited by it. I spent all morning with a patient in adrenal crisis and am somewhat bewildered by a lot of the current controversies in the literature. I need a page that I can print off for the family that expresses some of the key issues (although it looks like there's so much ongoing debate that this may simply be an impossible task!)doctorwolfie (talk) 19:22, 19 October 2010 (UTC)
I am in agreement with Mschucker. The article is a mess. It may be informative but there are some sentences that just don't make sense whether you understand the topic or not. Verging on word salad at points. Also the article lacks structure and there is a derth of citation. Perhaps someone with experience of the subject matter would care to straighten it up. DrSparticle (talk) 04:06, 13 June 2011 (UTC)
Content Level
I have no medical or chemistry background/schooling but I found the level of detail in the Cortisol Page (assuming it to be accurate) to be very useful and in general , understandable - in places where it goes into much more detail, and maybe not as understandable, at least I am aware of where I need to complete more background reading. I would hate for this page to loose the detail that has been added. —Preceding unsigned comment added by 194.73.122.203 (talk) 13:30, 8 December 2010 (UTC) Subject cortisol large, we can say global. Subject affect the legitimate interests CONTENT 7336000000 people living on the globe. Perhaps, therefore, someone had the idea to organize the online forum on the thema <hormone cortisol>.DocDjames2 (talk) 13:17, 24 May 2016 (UTC)
Replaced cortisol values
I replaced the serum cortisol values, because the previous ones (from addisons-network.co.uk/ad_tests) often gave only "basal levels", which is a rather misleading value, since it changes substantially during 24 hours (as seen in the new values). The only previous values of use were the ones attributed to "USA" or "Hospital #2", but when looking at it's primary sources, the source for USA was completely missing, and "Hospital #2" gave a list of 4 studies, which made it rather hard to find in which one the values were actually taken. Anyone, feel free to find which one it was, and complement with those values. Mikael Häggström (talk) 16:49, 1 April 2011 (UTC)
Cortisol Effect on PMNT
The cortisol effect on PMNT and epinephrine synthesis is not listed under the effects of cortisol.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phenylethanolamine_N-methyltransferase —Preceding unsigned comment added by 139.127.234.31 (talk) 16:38, 16 May 2011 (UTC)
anti-itch cream
Since cortisol is widely used in anti-itch creams, shouldn't the article mention that use? — Preceding unsigned comment added by 24.99.127.37 (talk) 13:42, 18 June 2011 (UTC)
Caffeine's effect on cortisol
I think it should be mentioned that regular caffeine users develop a tolerance to cortisol increases (which is known for its damaging effects at high levels). As someone considering using caffeine to improve my mental performance, I had to read the cited study only to find that it compared controls with those who took a 250mg dose of caffeine after a week of abstinence, then find this after a thorough reading of the cited study. For others' convenience, I think the study I linked to along with how the stress-induced cortisol increase diminishes with tolerance should be mentioned in the article. 129.97.214.143 (talk) 04:26, 19 June 2011 (UTC)Subrosian,
Expand on statement, please...
Other effects
[. . .] However, prolonged cortisol secretion (which may be due to chronic stress or the excessive secretion seen in Cushing's syndrome) results in significant physiological changes.[1]
I think that since these other significant changes can actually be quite debilitating, the author of the paragraph should list those changes, at least the major ones. Thanks for your time, Wordreader (talk) 00:39, 18 May 2013 (UTC)
Normal Serum and urinary cortisol levels are wrong.
The upper limit of normal for midnight serum cortisols is below 2, with 5 and 8 being diagnostic of Cushings, depending on the setting of the testing (sleeping in hospital vs. outpatient).
The upper limit of normal for urine cortisol depends on the assay used. The one used in the US through some labs is about 50, in other labs (eg. Esoterix) the uln is 34). This is a critical edit to make since endocrinology residents and fellows tend to base their knowledge on what is on Wikipedia and wrong limits can result in misdiagnosis. Canada, last I heard, still uses the older assay method and the uln for urines there is 100. Using an Esoterix assay, the listed figure would be a number diagnostic of Cushings, not normal.
See Evaluation of the effectiveness of midnight serum cortisol in the diagnostic procedures for Cushing’s syndrome Giuseppe Reimondo, Barbara Allasino, Silvia Bovio, Piero Paccotti, Alberto Angeli and Massimo Terzolo, European Journal of Endocrinology (2005) 153 803–809, for a good discussion on normals vs. pathological levels at the upper limit. Please have a competent endocrinologist address this problem.
- Cortisol results in serum, urine and saliva are heavily dependent on the assay method used and on assay manufacturer.
Many results on this page are misleading for that reasons.Test results should only ever be interpreted using ranges and advice from the laboratory that performed the test. Wikipedia is not a reliable source of medical information. Arripay (talk) 22:51, 26 August 2013 (UTC)- previous comment edited as I mistakenly thought I was commenting on a different talk page! I agree that the reference ranges are misleading (for the reasons given above) and so I don't think reference ranges should be in this article. I would propose to delete them. I'd also stress that no-one, least of all doctors, should be using information/ranges from Wikipedia to interpret medical tests! Arripay (talk) 23:27, 26 August 2013 (UTC)
Normal Serum and urinary cortisol levels are wrong.
The upper limit of normal for midnight serum cortisols is below 2, with 5 and 8 being diagnostic of Cushings, depending on the setting of the testing (sleeping in hospital vs. outpatient).
The upper limit of normal for urine cortisol depends on the assay used. The one used in the US through some labs is about 50, in other labs (eg. Esoterix) the uln is 34). This is a critical edit to make since endocrinology residents and fellows tend to base their knowledge on what is on Wikipedia and wrong limits can result in misdiagnosis. Canada, last I heard, still uses the older assay method and the uln for urines there is 100. Using an Esoterix assay, the listed figure would be a number diagnostic of Cushings, not normal.
See Evaluation of the effectiveness of midnight serum cortisol in the diagnostic procedures for Cushing’s syndrome Giuseppe Reimondo, Barbara Allasino, Silvia Bovio, Piero Paccotti, Alberto Angeli and Massimo Terzolo, European Journal of Endocrinology (2005) 153 803–809, for a good discussion on normals vs. pathological levels at the upper limit. Please have a competent endocrinologist address this problem. — Preceding unsigned comment added by 71.114.54.122 (talk) 23:13, 21 August 2013 (UTC)
Epifoam
Epifoam redirects to this page. This is incorrect. Epifoam is a foam rubber like product sold in thin sheets, used for craft projects. It's definitely not cortisol. Hope somebody can sort this. Anniepoo (talk) 07:42, 5 December 2013 (UTC)
- Epifoam is most definitely a drug (hydrocortisone acetate and pramoxine hydrochloride). It may also be a foam rubber product, but a Google search hits are mainly to the drug. There is also a product that is used after liposuction surgery. I cannot locate a single web site that talks about a foam rubber like product other than the previous liposuction related link. The drug is a mixed product containing both hydrocortisone acetate and pramoxine hydrochloride. Regardless, the redirect should not be to cortisol, but to hydrocortisone acetate and pramoxine hydrochloride. However we currently do not have a article on this product. In the meantime, I have changed the target of the redirect to hydrocortisone acetate. Boghog (talk) 08:09, 5 December 2013 (UTC)
This article is pretty bad
Holy crap, this article is really bad considering its importance. Bad references and dubious info, primary studies, wrong information (cortisol actually shifts the immune system to Th2 and not Th1 as the article implies). --sciencewatcher (talk) 14:59, 21 May 2014 (UTC)
- I've fixed the completely wrong info on Th1/Th2 balance. I think it would be a good idea for an expert to go through the entire article. --sciencewatcher (talk) 18:43, 21 May 2014 (UTC)
Suggestion for changing one word (to an adverbial phrase) and moving it to a different part of the sentence
The "Cortisol#Gastric_and_renal_secretion" section of the article, contains a sentence in which there is a word that IMHO should be (changed, and) moved to a different part of the sentence.
The sentence I have in mind -- at least, as of https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Cortisol&oldid=635216372 -- says:
Net chloride secretion in the intestines is inversely decreased by cortisol in vitro (methylprednisolone).[49]
IMHO the word "inversely" is positioned in the wrong part of that sentence. I think what the word was intended to mean, is that
the fact that a certain thing (net chloride secretion) is decreased by [the action of] (some kind of result "caused by") cortisol
is somehow "opposite" in sign or direction, and hence "different" in an important way, from
the fact that -- as stated nearby, a couple of sentences away -- a certain other thing (gastric-acid secretion) is increased by cortisol
. (right?) Therefore, I suggest that the wording of the above sentence, -- (the one that I have in mind) -- should be changed to [something more like]
On the other hand, net chloride secretion in the intestines is decreased by cortisol in vitro (methylprednisolone).[49]
NOTE that the only changes are:
- the word "inversely" has been replaced by the phrase "On the other hand" and
- that phrase "On the other hand" is placed at the beginning of the sentence, instead of right next to the word "decreased".
Any comments? For example, comments about:
- whether the word "inversely" was originally intended to mean [something like] "On the other hand"
OR
- whether all that is OK being placed at the beginning of the sentence
Ordinarily, I would be more inclined to be bold, and to just make the [above mentioned] change to the article now. However, I do not have time to read this entire (long!) "Talk:" page, and the portion of it that I have read "so far", suggests to me that there might be a lot of complexity here, that I do not have the time (nor the inclination) to read about right now. (Also, ["!"] I do not know very much about cortisol.)
If there are no objections (with some reasonable amount of time), -- or, maybe even if there are some objections, but if they are able to be resolved (see "Wikipedia:Consensus"), or if [for some reason, e.g., "not serious", or "misguided", ...etc.] I am not persuaded [to change my mind] by those objections -- then I might decide to be bold, after all, and to make the above mentioned change to the article. --Mike Schwartz (talk) 23:00, 24 November 2014 (UTC)
Too Heavy on Primary Sources?
I am uncomfortable with some sections of the article that rely almost exclusively on primary sources (See: "Factors generally increasing cortisol levels" and "Factors generally reducing cortisol levels"). Wikipedia isn't a secondary source, and getting rid of (primary-sourced) trivia could go a long way in cleaning up this very important article. I imagine that these sections also leave the page vulnerable to self promotion (individuals inputing stand-alone facts that they/their lab discovered).
Thoughts? When is it appropriate to get rid of miscellaneous information on Wikipedia?
Czeer (talk) 16:32, 3 March 2015 (UTC)
- Thanks for your spot on comments and edits. Per WP:MEDRS, if you see primary sources supporting medical claims and animals studies mixed up with human clinical data, be WP:BOLD and get rid of it. I have made an initial attempt to further cleanup and reorganize the article. More work remains. Boghog (talk) 22:02, 3 March 2015 (UTC)
I agree with Czeer. There seems to be an over-reliance on singular studies to support certain positions in those two sections. Most of those studies seem to be preliminary or inadequately designed. Independent and better designed studies replicating the results should be cited in addition/corroboration, one feels. I wonder if these should be tagged with templates like [additional citation(s) needed] Knaveknight (talk) 07:22, 13 May 2016 (UTC)
Marijuana Associated with elevated cortisol?
"Smoking marijuana has been shown to increase cortisol levels."[1]
The study which the linked article refers to consisted of "10 marijuana addicts". 10 is not very many and it does not mention a control group or provide link to the study. Also ripe for reverse inference, these 10 marijuana addicts could have particularly stressful lives or naturally have a higher level of cortisol and use marijuana to "balance out" their stress.
If anybody has anything more on this I'd love to hear it, if there's real evidence then that would significant, until then I think this should be deleted. — Preceding unsigned comment added by Craigloverbutstr8 (talk • contribs) 03:08, 28 September 2015 (UTC)
This suggests kidney impairments can be a cause, not listed in the article: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24752431 108.48.94.155 (talk) 15:51, 30 October 2015 (UTC)
Taste in the mouth, overdose. Would be useful. Although, only for ringed Kontent. Describe the taste of hydrocortisone. Just as the simptom's of overdose (urine is transparent as the water, gluttony, warming sensation, as if they have suddenly 5 0000000 USD on [bank] account).Maybe, there also other specific symptoms which would be possible to identify themselves?109.128.245.208 (talk) 12:01, 9 April 2016 (UTC)== Causes of High Cortisol Levels ==
This suggests kidney impairments can be a cause, not listed in the article: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24752431 108.48.94.155 (talk) 15:51, 30 October 2015 (UTC)
adverse effects in long-term poisoning.
Übersetzung für Mund-Geschmack, Überdosierung. Wäre , vielleicht nützlich . Obwohl, nur für geringte Kontent. Beschreiben des Geschmack von Hydrokortison . So wie die Simptom's von Überdosierung ( Urin wird transparent als der Wasser, Gefrässigkeit, aufwärmendes Gefühl , als ob sie plotzlich 5 0000000 USD auf Beutsche Bank Konto haben). Stattdessen übersetzen mit Mung-Geschmak, Überdosierung. Wäre , vielleicht nutzlich . Obwohl, nur für geringte Kontent. Beschreiben des Geschmack von Hydrokortison . So wie die Simptom's von Überdosierung ( Urin wird transparent als der Wasser, Gefrässigkeit, aufwärmendes Gefühl , als ob sie plotzlich 5 0000000 USD auf [Bank] Konto haben). Taste in the mouth, overdose. Would be useful. Although, only for ringed Kontent. Describe the taste of hydrocortisone. Just as the simptom's of overdose (urine is transparent as the water, gluttony, warming sensation, as if they have suddenly 5 0000000 USD on Beutsche bank account). Maybe, there also other specific symptoms which would be possible to identify themselves?5milliards (talk) 12:12, 9 April 2016 (UTC)
Cortisol and state - politics.
is meant health policy, economic policy, Foreign policy, defense policy, social security policy. The price and the effectiveness of hormone hydrocortisone allow this issue. Yes, as only for the Politikere (Ministre) and deputies the Parlament. Thereafter, for the press, the police and the judiciary.Cortisol( prednisolone) hydrocortisone make voracious. Promotes bad kontrolierte appetite etc .Club Wikipedia Users (talk) 16:47, 6 April 2016 (UTC)I unravel an unnecessarily emotional post user <Unhöfliche BAMF>. We need examples of cortisol / hydrocortisone application in politics.Something big. Pointing. Doctor generalist (talk) 17:56, 16 January 2017 (UTC) Well . For example. secret (secret or not?) mixing of corticosteroid medication in the tea and soup. For revolutionaries in the Maidan area. In Kiev. It dostatochno a good example? Danach reichte es eine kleine Kortikosteroïda Dose für der Dicke President . Und ... kamm zum die Psycho - Effekte .OffersWhiskey (talk) 17:34, 24 January 2017 (UTC)
Abstinence Syndrome.
Is Abstinence Syndrome by immediate Deposition of one or more overdoses of hydrocortisone / cortisol comparable Abstinence Syndrome of other drugs? Come the pain, a Psyhose, a collapse of the circulatory system or not?5milliards (talk) 12:26, 9 April 2016 (UTC)
Normal levels:
Why not 538 nmo/L ? We all Anglophone accept this level 24 hours free cortisol.Italienne missionnaire manchot (talk) 11:58, 3 June 2016 (UTC)
What's the point in diurnal variation?
doi:10.1210/er.2015-1080 JFW | T@lk 14:23, 23 October 2016 (UTC) Cortisol / hydrocortisone has long been in Arsenal. Now. Bid. Article. Because of political provocative content.2A02:A03F:1616:E600:48B4:1D2B:8CAF:C98E (talk) 16:23, 13 February 2017 (UTC) I have some difficulty interpreating what is meant by the point above. Leopardtail (talk) 18:35, 23 May 2017 (UTC)
Binding Globulins
I note this article lacks reference to CBG and SHBG (and the other relevant binding globulin that slips my mind). Any special reason for this? Leopardtail (talk) 18:35, 23 May 2017 (UTC)
External links modified
Hello fellow Wikipedians,
I have just modified one external link on Cortisol. Please take a moment to review my edit. If you have any questions, or need the bot to ignore the links, or the page altogether, please visit this simple FaQ for additional information. I made the following changes:
- Added archive https://web.archive.org/web/20121113144240/http://www.acb.org.uk/docs/NHLM/Cortisol.pdf to http://www.acb.org.uk/docs/NHLM/Cortisol.pdf
When you have finished reviewing my changes, you may follow the instructions on the template below to fix any issues with the URLs.
This message was posted before February 2018. After February 2018, "External links modified" talk page sections are no longer generated or monitored by InternetArchiveBot. No special action is required regarding these talk page notices, other than regular verification using the archive tool instructions below. Editors have permission to delete these "External links modified" talk page sections if they want to de-clutter talk pages, but see the RfC before doing mass systematic removals. This message is updated dynamically through the template {{source check}} (last update: 18 January 2022).
- If you have discovered URLs which were erroneously considered dead by the bot, you can report them with this tool.
- If you found an error with any archives or the URLs themselves, you can fix them with this tool.
Cheers.—InternetArchiveBot (Report bug) 11:21, 13 August 2017 (UTC)
Talks
Hello, I am editing Wikipedia for a class assignment! I think that the chemistry and animals sections could use a bit more information. Daniypink (talk) 01:02, 13 September 2019 (UTC)
Cortisol/long term exposure
Is it possible that a child subjected to trauma and stress, such as physical abuse, insults, bullying resulting in fighting, constant verbal abuse from parents and siblings, cause a continuous high level of cortisol and other fear-based hormones' so as to have an addictive effect on a human? What about children who are uprooted from their homes and moved every few months for many years till young adulthood? Would this cause a rise in cortisol and associated physiological and psychological responses? Geezer550 (talk) 22:06, 23 February 2020 (UTC)
Factors decreasing cortisol levels
Why were factors decreasing cortisol levels removed from the article? § 79.106.215.67 (talk) 20:46, 19 April 2020 (UTC)
"Lifestyle" edits
This revert was justified because it is unscientific advice and misinformation based on non-WP:MEDRS sources. Coffeeking123, please stop. Zefr (talk) 14:08, 12 September 2021 (UTC)
Wiki Education Foundation-supported course assignment
![]() This article was the subject of a Wiki Education Foundation-supported course assignment, between 12 August 2020 and 25 November 2020. Further details are available on the course page. Peer reviewers: Esm23.
This article was the subject of a Wiki Education Foundation-supported course assignment, between 12 August 2020 and 25 November 2020. Further details are available on the course page. Peer reviewers: Esm23.
Above undated message substituted from Template:Dashboard.wikiedu.org assignment by PrimeBOT (talk) 18:31, 16 January 2022 (UTC)
Somebody reverted my edit
Can you please explain why my newly added citation for this article [2] was removed?202.169.23.60 (talk) 01:23, 12 May 2022 (UTC)
Untitled
Why is the  not have the angled display for the C2H2OH but the Hydrocortisone article has the
not have the angled display for the C2H2OH but the Hydrocortisone article has the 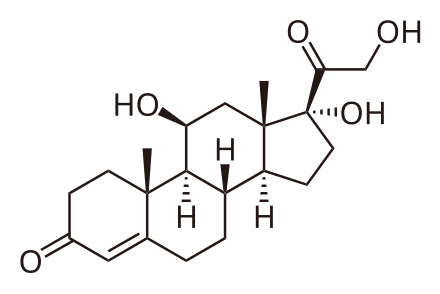 , which does? — Preceding unsigned comment added by Wparad (talk • contribs) 21:50, 3 March 2022 (UTC)
, which does? — Preceding unsigned comment added by Wparad (talk • contribs) 21:50, 3 March 2022 (UTC)
- ^ http://www.alphagalileo.org/ViewItem.aspx?ItemId=152795&CultureCode=en
- ^ |title=Hormones – cortisol and corticosteroids - Better Health Channel |url=https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/Hormones-cortisol-and-corticosteroids |access-date=2022-05-06 |website=www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au}}



