Separated shoulder
| Separated shoulder | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Acromioclavicular joint injury, acromioclavicular separation, AC joint separation, AC separation | |
 | |
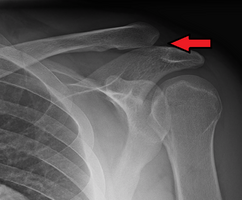
| An Xray showing a separated shoulder. Notice the separation between the end of the collarbone and the scapula. | |
| Specialty | Orthopedics, emergency medicine |
| Symptoms | Pain, deformity, decreased range of motion[1][2] |
| Types | Type I, II, III, IV, V, VI[2] |
| Causes | Trauma such as a fall[2] |
| Risk factors | Contact sports[3] |
| Diagnostic method | Examination, X-rays[2] |
| Differential diagnosis | Dislocated shoulder, clavicle fracture[4] |
| Treatment | Type I and II: Sling and pain medication[2] Type III: Conservative management and surgery if still symptoms[2] Type IV, V, VI: Surgery[2] |
| Frequency | Relatively common[3] |
A separated shoulder, also known as acromioclavicular joint injury, is a common injury to the acromioclavicular joint.[2] The AC joint is located at the outer end of the clavicle where it attaches to the acromion of the scapula.[2] Symptoms include pain which may make it difficult to move the shoulder and often a deformity.[2][1]
It is most commonly due to a fall onto the front and upper part of the shoulder when the arm is by the side.[2] They are classified as type I, II, III, IV, V, or VI with the higher the number the more severe the injury.[2] Diagnosis is typically based on physical examination and X-rays.[2] In type I and II injuries there is minimal deformity while in a type III injury the deformity resolves upon lifting the arm upwards.[2] In type IV, V, and VI the deformity does not resolve with lifting the arm.[2]
Generally types I and II are treated without surgery, while type III may be treated with or without surgery, and types IV, V, and VI are treated with surgery.[3] For type I and II treatment is usually with a sling and pain medications for a week or two.[2] In type III injuries surgery is generally only done if symptoms remain following treatment without surgery.[2]
A separated shoulder is a common injury among those involved in sports, especially contact sports.[3] It makes up about half of shoulder injuries among those who play hockey, football, and rugby.[1] Those affected are typically 20 to 30 years old.[3] Males are more often affected than females.[3] The injury was initially classified in 1967 with the current classification from 1984.[1]
Cause

Separated shoulders often occur in people who participate in sports[5]. The separation is classified into 6 types, with 1 through 3 increasing in severity, and 4 through 6 being the most severe[6]. The most common manner of injury is a fall on the tip of the shoulder. In falls where the force is transmitted indirectly, often only the acromioclavicular ligament is affected, and the coracoclavicular ligaments remain unharmed.[7]
Mechanism

The acromion of the scapula is connected to the clavicle by the superior acromioclavicular ligament. The coracoclavicular ligaments connect the clavicle to the coracoid process. The two ligaments that form the coracoclavicular ligaments are the trapezoid and conoid ligaments. These three ligaments add support to the shoulder joint.[8]There are several types of soft tissue disruptions that may cause acromioclavicular separation:[9][10]
- The conoid and trapezoid ligaments may tear at any location
- The lateral clavicle may ride upward after being avulsed from its periosteum
- The acromioclavicular ligaments may be torn
- The conoid-trapezoid ligament origin may avulse from the coracoid
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is based on physical examination and an x-ray. A physical examination can identify point tenderness, pain at the AC joint with cross-arm adduction, and pain relief with an injection of a local anesthetic. The cross-arm adduction will produce pain specifically at the AC joint and will be done by elevating the arm to a 90° angle, flexing the elbow to a 90° angle, and adducting the arm across the chest. The pain in the shoulder is hard to pinpoint due to the shared innervation of the AC joint and the glenohumeral joint. An injury to the AC joint will result in pain over the AC joint, in the anterolateral neck and in the region in the anterolateral deltoid.[7][9]
X-ray indicates a separated shoulder when the acromioclavicular joint space is widened (it is normally 5 to 8 mm),[11]it can be classified into 6 types.
Type (grade) I

A Type I AC separation involves direct trauma to the shoulder causing the injury to ligaments that form the joint, but no severe tearing or fracture. [12]
Type (grade) II

A Type II AC separation involves complete tearing of the acromioclavicular ligament, as well as a partial tear of the coracoclavicular ligaments. This often causes a noticeable bump on the shoulder.[13] The clavicle is unstable to direct stress examination. On radiographs, the lateral end of the clavicle may be slightly elevated by pressing on the sternal aspect of the clavicle forcing the acromial end down, additionally loss of movement are common.[14]
Type (grade) III
In a Type III AC separation both acromioclavicular and coracoclavicular ligaments are torn without significant disruption of the deltoid or trapezial fascia.[13] A significant bump, resulting in some shoulder deformity, is formed by the lateral end of the clavicle, this bump, caused by the clavicle's dislocation, is permanent.[15] The clavicle can be moved in and out of place on the shoulder. [16]
-
Type 3
-
Type 3 AC joint separation on plain X ray
Type (grade) IV

This is a type III injury with avulsion of the coracoclavicular ligament from the clavicle, with the distal clavicle displaced posteriorly into or through the trapezius and may tent the posterior skin.[13] A displaced clavicle is easily seen on a radiograph. It is important to evaluate the sternoclavicular joint also, because there can be an anterior dislocation of the sternoclavicular joint and posterior dislocation of the AC joint. This injury may require surgery, but the risks and benefits must be weighed.[17][18]
Type (grade) V

This is a more severe form of a type III injury, with the trapezial and deltoid fascia stripped off of the acromion as well as the clavicle. This is type III but with exaggeration of the vertical displacement of the clavicle from the scapula. Distinguishing between Type III and Type V separations based on radiographs is difficult and often unreliable between surgeons.[19] Type V is manifested by a 2- to 3-fold increase in the coracoclavicular distance.[13] The shoulder manifests as a severe droop, secondary to downward displacement of the scapula and humerus due to loss of the clavicular strut.[13]
Type (grade) VI

This is type III with inferior dislocation of the distal end of the clavicle below the coracoid. This injury is associated with severe trauma and frequently accompanied by multiple other injuries.[13] The mechanism is thought to be severe hyperabduction and external rotation of the arm, combined with retraction of the scapula. The distal clavicle is found in 2 orientations, either subacromial or subcoracoid. With the subcoracoid dislocation, the clavicle becomes lodged behind the intact conjoined tendon. The posterior superior AC ligaments, which often remain attached to the acromion, get displaced into the AC interval, making anatomic reduction difficult. The tissue needs to be surgically cleared and then reattached after reduction. Most patients with type VI injuries have paresthesia that resolves after relocation of the clavicle [13]
Treatment
Treatment of a separated shoulder depends on the severity of the injury. When beginning treatment, the first steps should be to control inflammation, and to rest and ice the joint. Anti-inflammatories such as ibuprofen may also relieve pain and inflammation. One can wear a sling until the pain subsides; then simple exercises can be started.[20]
Non-surgical
Type I and type II shoulder separation are the most common types of separated and rarely need surgery.[15] However, the risk of arthritis with type II separations is greatly increased, if it becomes severe, the Mumford procedure or distal clavicle excision can be performed.[21]
Most non-surgical treatment options include physical therapy to build up the muscles and help stabilize the joint. Literature regarding long-term follow-up after surgical repair of type III injuries is scarce, and those treated nonoperatively generally do quite well.[22]
Non-surgical treatment is as good as or better than surgical treatment, or anything attained because of surgery is quite limited.[23] It appears that after a while, the body "remodels" the joint, either expanding the distal clavicle or causing it to atrophy.[24]
Those who do have a separated shoulder will most often return to having full function, although some may have continued pain in the area of the AC joint. With the continued pain there are some things that maybe causing it. It may be due to an abnormal contact between the bone ends when the joint is in motion, the development of arthritis, or an injury to a piece of the cushioning cartilage that is found between the bone ends of this joint.[7]
Surgical
Type IV, V, and VI shoulder separations are very uncommon but always require surgery.[25] There is some debate among orthopedic surgeons, however, about the treatment of type III shoulder separation; many with type III shoulder separation who do not undergo surgical treatment recover as well without any risks that surgery may present.[26][27] Those who opt out of surgery also have faster recovery times and are able to return to work or sports sooner[27]
There have been many surgeries described for complete acromioclavicular separations, including arthroscopic surgery. There is no consensus on which is best. There has been a focus on attempting to restore horizontal, as well as vertical, instability. A review found that although horizontal stability can be more reliably restored with additional acromioclavicular joint reconstruction (in addition to coracoclavicular ligament reconstruction), there is no clear advantage with respect to outcomes.[28]
A common surgery is some form of modified Weaver-Dunn procedure, which involves cutting off the end of the clavicle portion, partially sacrificing the coracoacromial ligament and suturing the displaced acromial end to the lateral aspect of the clavicle for stabilization, then often some form of additional support is introduced to replace the coracoclavicular ligament(s). Variations of this support includes grafting of tendons from the leg[29] or the use of synthetic sutures or suture anchors.[30]
After one does have surgery, a sling should be worn to support and protect the shoulder for a few days, the treatment will focus on controlling the pain[31]. A shoulder immobilizer is worn for 4 - 6 weeks after surgery to help decrease strain on CC ligament, after about four weeks range of motion exercises can be started[32]. After about three months, more active strengthening will be incorporated which focus on improving the strength and control of muscles, in other words non-contact sports can begin; and after six months contact sports can begin[33]
Physical therapy
Some physical therapy exercises that can be performed to help rehab the shoulder[8] such as, internal shoulder rotation amd external shoulder rotation[34] While lying on your side you can perform internal rotation and external rotation with a light weight. The light weight can be any type of object such as a 1-5 lb dumbbell weight[35][34]
-
Strengthening the shoulder joint.
-
Passively moving the shoulder joint
-
Side-lying external rotation start
-
Side-lying external rotation end
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Willimon SC, Gaskill TR, Millett PJ (February 2011). "Acromioclavicular joint injuries: anatomy, diagnosis, and treatment". The Physician and Sportsmedicine. 39 (1): 116–22. doi:10.3810/psm.2011.02.1869. PMID 21378494.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 2.15 2.16 Stucken C, Cohen SB (January 2015). "Management of acromioclavicular joint injuries". Orthopedic Clinics of North America. 46 (1): 57–66. doi:10.1016/j.ocl.2014.09.003. PMID 25435035.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 Bishop JY, Kaeding C (December 2006). "Treatment of the acute traumatic acromioclavicular separation". Sports Medicine and Arthroscopy Review. 14 (4): 237–45. doi:10.1097/01.jsa.0000212330.32969.6e. PMID 17135974. Archived from the original on 2021-08-29. Retrieved 2019-11-30.
- ↑ Heckman J, Agarwal A, Schenck RC (2013). Current Orthopedic diagnosis & treatment. Current Medicine Group. p. 4. ISBN 9781461311072. Archived from the original on 2017-10-12.
- ↑ "Shoulder separation - aftercare: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". medlineplus.gov. Archived from the original on 1 November 2020. Retrieved 20 November 2020.
- ↑ MD, Stephan Anderson. Trauma and Emergency Radiology, an Issue of Radiologic Clinics of North America, EBook. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 814. ISBN 978-0-323-67834-6. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 "Shoulder Separation - OrthoInfo - AAOS". www.orthoinfo.org. Archived from the original on 25 November 2020. Retrieved 20 November 2020.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Kiel, John; Kaiser, Kimberly (2020). "Acromioclavicular Joint Injury". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Archived from the original on 18 January 2021. Retrieved 20 November 2020.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 SACCOMANNO, MARISTELLA F.; DE IESO, CARMINE; MILANO, GIUSEPPE (8 July 2014). "Acromioclavicular joint instability: anatomy, biomechanics and evaluation". Joints. 2 (2): 87–92. ISSN 2512-9090. Archived from the original on 6 March 2021. Retrieved 2 December 2020.
- ↑ Marchese, Richard M.; Bordoni, Bruno (2020). "Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Coracoclavicular Joint (Coracoclavicular Ligament)". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 2 December 2020.
- ↑ Marincek, Borut; Dondelinger, Robert F. (2007). Emergency Radiology: Imaging and Intervention. 255: Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9783540689089. Archived from the original on 2020-02-17. Retrieved 2019-08-19.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ↑ Goodman, Jeremy; Veeramachaneni, Nirmal; Winslow, Emily. The Washington Manual Surgery Survival Guide. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 220. ISBN 978-0-7817-4368-6. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 8 November 2020.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 13.4 13.5 13.6 Mazzocca AD, Arciero RA, Bicos J (February 2007). "Evaluation and treatment of acromioclavicular joint injuries". American Journal of Sports Medicine. 35 (2): 316–29. doi:10.1177/0363546506298022. PMID 17251175. Archived from the original on 2021-08-29. Retrieved 2019-11-30.
- ↑ Pappas, Michael D.; Yamamoto, Loren G.; Anene, Okechukwu. Pediatric Radiology Review. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 164. ISBN 978-1-59745-146-8. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 2 December 2020.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Shahady, Edward J. Primary Care of Musculoskeletal Problems in the Outpatient Setting. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 69. ISBN 978-0-387-36220-5. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 8 November 2020.
- ↑ Pfeiffer, Ronald P.; Mangus, Brent C.; Trowbridge, Cynthia. Concepts of Athletic Training. Jones & Bartlett Publishers. p. 186. ISBN 978-1-284-02215-5. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
- ↑ Miller, Mark D.; Hart, Jennifer Adele; MacKnight, John M. Essential Orthopaedics. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 175. ISBN 978-1-4160-5473-3. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
- ↑ Kiel, John; Ponnarasu, Subitchan; Kaiser, Kimberly (2020). "Sternoclavicular Joint Injury". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
- ↑ Kraeutler MJ, Williams GR Jr, Cohen SB, Ciccotti MG, Tucker BS, Dines JS, Altchek DW, Dodson CC (October 2012). "Inter- and intraobserver reliability of the radiographic diagnosis and treatment of acromioclavicular joint separations". Orthopedics. 35 (10): e1483-7. doi:10.3928/01477447-20120919-16. PMID 23027484. Archived from the original on 2021-08-29. Retrieved 2019-11-30.
- ↑ Diaz, Linda Gazzillo. Survey of Athletic Injuries for Exercise Science. Jones & Bartlett Publishers. p. 195. ISBN 978-1-4496-4844-2. Archived from the original on 2021-08-29. Retrieved 2020-11-08.
- ↑ Giacomo, Giovanni Di; Pouliart, Nicole; Costantini, Alberto; Vita, Andrea de. Atlas of Functional Shoulder Anatomy. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 44. ISBN 978-88-470-0759-8. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 2 December 2020.
- ↑ Prybyla D, Owens BD (2005-03-15). "Acromioclavicular Joint Separations". eMedicine.com. Archived from the original on 2007-02-27. Retrieved 2006-11-01.
- ↑ Schlegel TF, Burks RT, Marcus RL, Dunn HK (2001). "A Prospective Evaluation of Untreated Acute Grade III Acromioclavicular Separations". The American Journal of Sports Medicine. 29 (6): 699–703. doi:10.1177/03635465010290060401. PMID 11734479.
- ↑ Rawes ML, Dias JJ (1996). "Long-term results of conservative treatment for acromioclavicular dislocation" (PDF). The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. British Volume. 78 (B): 410–2. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.78B3.0780410. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-10-10.
- ↑ Jones (Prof.), Roger. Oxford Textbook of Primary Medical Care. Oxford University Press. p. 1117. ISBN 978-0-19-856782-0. Archived from the original on 2021-08-29. Retrieved 2020-12-03.
- ↑ Boffano, Michele; Mortera, Stefano; Wafa, Hazem; Piana, Raimondo (19 October 2017). "The surgical treatment of acromioclavicular joint injuries". EFORT Open Reviews. 2 (10): 432–437. doi:10.1302/2058-5241.2.160085. ISSN 2058-5241. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 3 December 2020.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Fritz, Sandy. Sports & Exercise Massage - E-Book: Comprehensive Care in Athletics, Fitness, & Rehabilitation. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 359. ISBN 978-0-323-08229-7. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 3 December 2020.
- ↑ Jordan, Robert W.; Malik, Shahbaz; Bentick, Kieran; Saithna, Adnan (2018-09-28). "Acromioclavicular joint augmentation at the time of coracoclavicular ligament reconstruction fails to improve functional outcomes despite significantly improved horizontal stability" (PDF). Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy. 27 (12): 3747–3763. doi:10.1007/s00167-018-5152-7. ISSN 0942-2056. PMID 30267185. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-02-12. Retrieved 2019-11-30.
- ↑ Mirzayan R (2005). "Acromioclavicular Injuries: New Management Options Emerge". eMedicine.com. Archived from the original on 2021-08-29. Retrieved 2006-11-11.
- ↑ Breslow MJ, Jazrawi LM, Bernstein AD, Kummer FJ, Rokito AS (2002). "Treatment of acromioclavicular joint separation: suture or suture anchors?". Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. 11 (3): 225–9. doi:10.1067/mse.2002.123904. PMID 12070493. Archived from the original on 2000-03-01.
- ↑ Ma, Richard; Smith, Patrick A.; Smith, Matthew J.; Sherman, Seth L.; Flood, David; Li, Xinning (8 February 2015). "Managing and recognizing complications after treatment of acromioclavicular joint repair or reconstruction". Current Reviews in Musculoskeletal Medicine. 8 (1): 75–82. doi:10.1007/s12178-014-9255-6. ISSN 1935-973X. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 3 December 2020.
- ↑ Warth, Ryan J.; Martetschläger, Frank; Gaskill, Trevor R.; Millett, Peter J. (16 December 2012). "Acromioclavicular joint separations". Current Reviews in Musculoskeletal Medicine. 6 (1): 71–78. doi:10.1007/s12178-012-9144-9. ISSN 1935-973X. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 3 December 2020.
- ↑ van Bergen, Christiaan J A; van Bemmel, Annelies F; Alta, Tjarco D W; van Noort, Arthur (18 December 2017). "New insights in the treatment of acromioclavicular separation". World Journal of Orthopedics. 8 (12): 861–873. doi:10.5312/wjo.v8.i12.861. ISSN 2218-5836. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 3 December 2020.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 "Shoulder Surgery Exercise Guide - OrthoInfo - AAOS". www.orthoinfo.org. Archived from the original on 30 November 2020. Retrieved 2 December 2020.
- ↑ Paz, Jaime C.; West, Michele P. Acute Care Handbook for Physical Therapists - E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 549. ISBN 978-1-4160-6948-5. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 2 December 2020.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
- Wheeless Online online orthopedic resource (for orthopedists) Archived 2006-11-09 at the Wayback Machine
- Rollo J, Raghunath J, Porter K (October 2005). "Injuries of the acromioclavicular joint and current treatment options". Trauma. 7 (4): 217–223. doi:10.1191/1460408605ta349oa. Archived from the original on 2006-10-17.