7p22.1 microduplication syndrome
| 7p22.1 microduplication syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Trisomy 7p22.1 | |
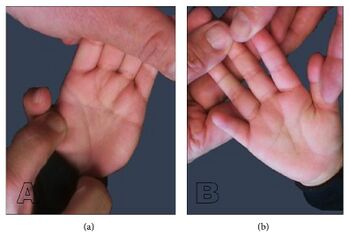 | |
| a) Left palmar creases bridged to form one and distal extends to 2-3 interspace b) right distal palmar crease extends to the 2-3 interspace. | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
| Symptoms | intellectual disabilities, speech and motor delay, facial dysmorphisms |
| Usual onset | Birth |
| Duration | Life-long |
| Causes | Duplication of the p22.1 region in chromosome 7 |
7p22.1 microduplication syndrome (also called Trisomy 7p22.1) is a genetic disorder which is characterized by cranial and facial dysmorphisms, intellectual disability, and motor-speech delays.[1] It is caused by a duplication of the p22.1 region of chromosome 7.
Signs and symptoms
The symptoms of this syndrome are (but are not limited to) cranio-facial dysmorphisms such as macrocephaly, frontal bossing, low-set ears, hypertelorism, etc., intellectual disabilities, speech and motor delays, and heart, ocular, renal and skeletal defects (such as patent foramen ovale or brachydactyly type D ).[2]
Causes
This condition (as the name implies) is caused by a 430 kB duplication of the p22.1 region of chromosome 7.[1]This mutation is autosomal recessive, meaning that a baby would need 1 copy of a mutated gene from both parents in order to show symptoms of the disorder.
Diagnosis
The evaluation of 7p22.1 microduplication syndrome is based on clinical features and molecular test.[1]
Treatment
The management of 7p22.1 microduplication depend on the presentation (i.e. generalized seizures are treated with antiepileptic drugs)[1]
Epidemiology
Only 60 cases of 7q22.1 microduplication syndrome have been recorded in medical literature.[3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Caselli, Rossella; Ballarati, Lucia; Vignoli, Aglaia; Peron, Angela; Recalcati, Maria Paola; Catusi, Ilaria; Larizza, Lidia; Giardino, Daniela (November 2015). "7p22.1 microduplication syndrome: Clinical and molecular characterization of an adult case and review of the literature". European Journal of Medical Genetics. 58 (11): 578–583. doi:10.1016/j.ejmg.2015.08.003. ISSN 1878-0849. Archived from the original on 20 May 2023. Retrieved 20 September 2023.
- ↑ RESERVED, INSERM US14-- ALL RIGHTS. "Orphanet: 7p22.1 microduplication syndrome". www.orpha.net. Archived from the original on 2023-07-22. Retrieved 2022-04-30.
- ↑ Goitia, Veronica; Oquendo, Marcial; Stratton, Robert (2015-03-29). "Case of 7p22.1 Microduplication Detected by Whole Genome Microarray (REVEAL) in Workup of Child Diagnosed with Autism". Case Reports in Genetics. 2015: e212436. doi:10.1155/2015/212436. ISSN 2090-6544. PMC 4393924. PMID 25893121.