Portal:Energy
| Main page | New articles & Tasks |
 The Energy Portal Welcome to Wikipedia's Energy portal, your gateway to energy. This portal is aimed at giving you access to all energy related topics in all of its forms.
|
Page contents: Selected article • Selected image • Selected biography • Did you know? • General images • Quotations • Related portals • Wikiprojects • Major topics • Categories • Help • Associated Wikimedia |
Introduction
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek ἐνέργεια (enérgeia) 'activity') is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed; matter and energy may also be converted to one another. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J).
Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy.
Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass when stationary (called rest mass) also has an equivalent amount of energy whose form is called rest energy, and any additional energy (of any form) acquired by the object above that rest energy will increase the object's total mass just as it increases its total energy.
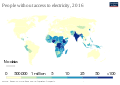
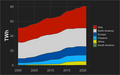
Human civilization requires energy to function, which it gets from energy resources such as fossil fuels, nuclear fuel, or renewable energy. The Earth's climate and ecosystems processes are driven by the energy the planet receives from the Sun (although a small amount is also contributed by geothermal energy). (Full article...)
Selected article
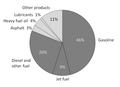
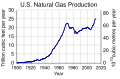
Natural gas, often referred to as simply 'gas', is a gaseous fossil fuel consisting primarily of methane. Natural gas is found in oil fields, natural gas fields, and in coal beds (as coalbed methane). Before use as a fuel, natural gas undergoes extensive processing to remove almost all materials other than methane.
Natural gas is a major source of electricity generation, and particularly high efficiencies can be achieved through combining gas turbines with a steam turbine in combined cycle mode. Natural gas burns cleaner than other fossil fuels, producing about 30% less carbon dioxide than oil and about 45% less than coal, per unit of energy released. It is also expected that natural gas reserves will peak around 2030, some 20 years after peak oil production. Compressed natural gas is also used as a cleaner alternative to other automobile fuels such as gasoline (petrol) and diesel. Natural gas is also used domestically for cooking and for central heating.
The major difficulty in the use of natural gas is transportation and storage because of its low density. Pipeline transport is economical, but is impractical across oceans. Liquefied natural gas can be shipped in LNG carriers, however the required liquefaction facilities add to the cost. The practice of flaring gas released in the course of recovering petroleum, so adding to greenhouse gas emissions, is now illegal in many countries.
Selected image

Photo credit: From an image by Arnold Paul
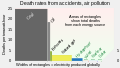
Coal-fired power stations transform chemical energy into 36%-48% electricity and 52%-64% waste heat.
Did you know?

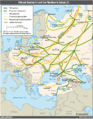
- The 1,222 km long Nordstream pipeline between Russia and the Germany is the world's longest underwater pipeline?
- Due to the vast quantity of coal burnt in fossil fuel power plants, they cause more radioactive contamination than nuclear power plants?
- Chinese energy policy includes using renewable energy for the rural electrification of 3.5 million households by 2010?
- The 354 MW SEGS solar power plant (pictured) in the Mojave Desert is the world's largest?
- Known reserves of petroleum are typically estimated at around 1.2 trillion barrels, or at 3.74 trillion barrels if oil sands are included?
- The concentration of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide has increased from about 280 parts per million to about 380 ppm since the start of the Industrial Revolution. That's an increase of 35.71%. The estimated population of the world in 1750 was 791 Million people. The estimated population of the world on June 30th, 2007 was 6.6 Billion people. That's an increase of 734.39%.?
- In the 1990s Bougainville conflict, islanders cut off from oil supplies due to a blockade used coconut oil to fuel their vehicles?
- The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) is considered a cartel by many observers?
Selected biography
Hansen studied at the University of Iowa, obtaining a B.A. in Physics and Mathematics, an M.S. in Astronomy and a Ph.D. in Physics. He was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 1996 and received the Heinz Environment Award for his research on global warming in 2001.
Hansen is a vocal critic of the Bush Administration's ideology on climate change. In 2005 and 2006, he claimed that NASA administrators have tried to influence his public statements about the causes of climate change. He has also claimed that the White House edited climate-related press releases from federal agencies to make global warming seem less threatening, and that he is unable to speak 'freely', without the backlash of other government officials.
Hansen has said that a global tipping point will be reached by 2016 if levels of greenhouse gases are not reduced. After this point global warming becomes unstoppable. As a result he claims that there may be a rise in sea levels by as much as 10 feet (3 metres) by 2100.
In the news
- 22 June 2024 – Russian invasion of Ukraine
- Russia launches missile and drone strikes across Ukraine, injuring two people and damaging energy infrastructure. Ukraine says that it shot down 12 of 16 missiles and all 13 drones. (Reuters)
- 16 June 2024 – Russian invasion of Ukraine
- Norway announces that it will give Ukraine 1.1 billion kroner (US$103 million) to help repair its energy infrastructure and secure the country's electricity supply before the winter. (Le Monde)
- 15 June 2024 – Russian invasion of Ukraine
- The United States announces a $1.5 billion aid package to Ukraine, focused primarily on the country's energy industry and humanitarian assistance. (Politico)
General images
Quotations
- "Breaking the dependence on oil is, in my view, a matter of political will. A consistent policy will turn obstacles into opportunities. To hide behind excuses of ignorance or economic considerations is not leading us to a sustainable future." – Mona Sahlin, 2006
- "America is addicted to oil, which is often imported from unstable parts of the world. The best way to break this addiction is through technology." – George W. Bush, 2006
- "Energy independence [for India] has to be our nation's first and highest priority. We must be determined to achieve this within the next 25 years i.e. by the year 2030." – Abdul Kalam, 2005
- "Energy security is assuming a strategic significance once reserved for territorial security, and the global environmental challenges from energy production and use are amongst our most pressing." – John Howard, 2006
Related portals
WikiProjects
WikiProjects connected with energy:
Other WikiProjects that may be of interest:
Major topics
Major categories
National energy supply, use & conservation
National electricity sector
Politics, economics, environment
- Climate change
- Energy conservation
- Energy economics
- Energy crises
- Energy development
- Energy policy
- Peak oil
Energy sources
- Fuels
- Biofuels
- Fossil fuels
- Fusion power
- Nuclear technology
- Renewable energy
- Energy conversion
- Electric power
- Energy storage
Energy-related design
Scientific usage
Help

Puzzled by energy?
Can't answer your question?
Don't understand the answer?
- Ask at the reference desk
- Read the Wikipedia help pages
For further ideas, to leave a comment, or to learn how you can help improve and update this portal, see the talk page.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
- Portals with triaged subpages from June 2018
- All portals with triaged subpages
- All portals
- Portals with no named maintainer
- Random portal component with 41–50 available subpages
- Random portal component with 11–15 available image subpages
- Random portal component with 6–10 available subpages
- Energy portal
- Science portals
- Technology portals
- Energy