NBPF10
| NBPF20 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | NBPF20, NBPF member 20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 614007; HomoloGene: 41035; GeneCards: NBPF20; OMA:NBPF20 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Neuroblastoma breakpoint family member 10 is a protein that in Homo sapiens is encoded by the NBPF10 gene.[3][4]
The full gene is 75,313 bp, with the major isoform of mRNA being 10,697 bp long. The gene is located at 1q21.1. NBPF contains what is known as the DUF1220 repeats. The highly conserved, repeated region is believed to be originated from MGC8902. The NBPF family has been linked to primate evolution.[4] It is assumed to be related to the 1q21.1 deletion syndrome and 1q21.1 duplication syndrome.[5]
Homology
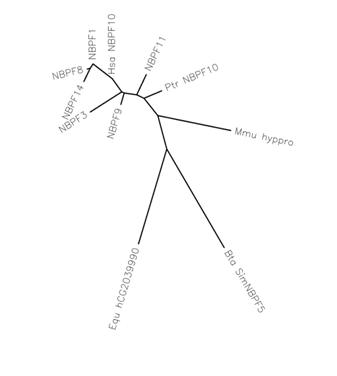
Paralogs of NBPF10 includes other NBPF family members. Orthologs of NBPF10 are found in other primates; distant orthologs are found in bovine, equine, and canine
Functional role
Although NBPF10's function is unknown, there is reason to believe that NBPF10 is an important biomarker for the Odontoblast Phenotype[6]
Gene Neighborhood
NOTCH2NL, SEC22B, HFE2, TXNIP are close neighbors of NBPF10. All of these neighboring genes are well studied in their own right.
Post-translational modification
NBPF10 has extremely low threonine content which may make the protein less susceptible to post-translational modification.[citation needed]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000162825 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: NBPF10 neuroblastoma breakpoint family, member 10". Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ^ a b Vandepoele K, Van Roy N, Staes K, Speleman F, van Roy F (November 2005). "A novel gene family NBPF: intricate structure generated by gene duplications during primate evolution". Mol. Biol. Evol. 22 (11): 2265–74. doi:10.1093/molbev/msi222. PMID 16079250.
- ^ Dumas, L.; Sikela, J. M. (2009-01-01). "DUF1220 Domains, Cognitive Disease, and Human Brain Evolution". Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology. 74. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory: 375–382. doi:10.1101/sqb.2009.74.025. ISSN 0091-7451. PMC 2902282. PMID 19850849.
- ^ Butler W.T.; Ritchie H. (February 1995). "The nature and functional significance of dentin extracellular matrix proteins". Int J Dev Biol. 39 (1): 169–79. PMID 7626404.