No higher resolution available.
This file is from a shared repository and may be used by other projects.
The description on its file description page there is shown below.
License
Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-SA 3.0)
Summary
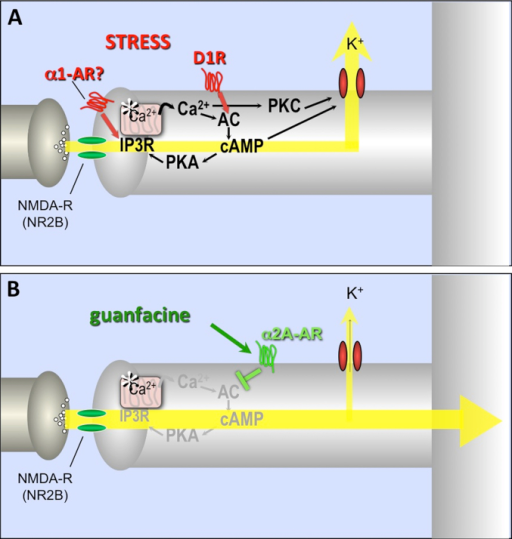
Author:Arnsten AF, Raskind MA, Taylor FB, Connor DF, Dept. Neurobiology, Yale University School of Medicine(Openi/National Library of Medicine) Source:https://openi.nlm.nih.gov/detailedresult?img=PMC4244027_gr3&query=&req=4 Description:fig3: The strength of dlPFC glutamate NMDA receptor connections on spines is dynamically modulated by arousal state. A. During stress, high levels of DA D1 receptor stimulation activate feedforward, cAMP- calcium (Ca2+) signaling, which opens nearby potassium (K+) channels to rapidly weaken connections and reduce PFC neuronal firing. NE stimulation of alpha-1 receptors also reduces PFC neuronal firing through IP3- Ca2+-protein kinase C (PKC) mechanisms (the ultrastructural localization of alpha-1 receptors in primate PFC is not yet known). Calcium is stored in the spine apparatus (indicated by asterisk), the endoplasmic reticulum in the spine. B. Guanfacine stimulation of post-synaptic alpha-2A receptors on PFC spines strengthens network connections, increases PFC neuronal firing and improves working memory by inhibiting feedforward cAMP- Ca2+ signaling and closing K+ channels on spines near the synapse. These actions likely contribute to guanfacine's therapeutic effects in patients. Additional abbreviations: AC = adenylyl cyclase; IP3R = inositol triphosphate receptors; PKA = protein kinase A.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment |
|---|
| current | 22:48, 6 February 2022 |  | 512 × 539 (168 KB) | Ozzie10aaaa | Author:Arnsten AF, Raskind MA, Taylor FB, Connor DF, Dept. Neurobiology, Yale University School of Medicine(Openi/National Library of Medicine) Source:https://openi.nlm.nih.gov/detailedresult?img=PMC4244027_gr3&query=&req=4 Description:fig3: The strength of dlPFC glutamate NMDA receptor connections on spines is dynamically modulated by arousal state. A. During stress, high levels of DA D1 receptor stimulation activate feedforward, cAMP- calcium (Ca2+) signaling, which opens nearby potassium (... |
File usage
The following page uses this file:

