Wellcome Trust
 | |
| Founded | 1936 |
|---|---|
| Founder | Sir Henry Wellcome |
| Registration no. | 210183 |
| Focus | Biomedical Research |
| Headquarters | London, NW1 United Kingdom |
| Location | |
Area served | United Kingdom and overseas |
| Disbursements | £11 billion (1936–2015)[1] |
| Endowment | £25.9 billion[2] |
Employees | 2,057[3] |
| Website | www |
The Wellcome Trust is a charitable foundation focused on health research based in London, in the United Kingdom. It was established in 1936 with legacies from the pharmaceutical magnate Henry Wellcome (founder of one of the predecessors of GlaxoSmithKline) to fund research to improve human and animal health. The aim of the Trust is to "support science to solve the urgent health challenges facing everyone." It had a financial endowment of £29.1 billion in 2020,[2] making it the fourth wealthiest charitable foundation in the world. In 2012, the Wellcome Trust was described by the Financial Times as the United Kingdom's largest provider of non-governmental funding for scientific research, and one of the largest providers in the world.[4] According to their annual report, the Wellcome Trust spent GBP £1.1Bn on charitable activities across their 2019/2020 financial year.[5] According to the OECD, the Wellcome Trust's financing for 2019 development increased by 22% to US$327 million.[6]
Headquarters

The Wellcome Trust's operations are run from two buildings on Euston Road in London. The Wellcome Building, at 183 Euston Road, built in 1932 in Portland stone houses the Wellcome Collection and the adjoining glass and steel building at 215 Euston Road is the Gibbs Building, by Hopkins Architects, which opened in 2004 as the administrative headquarters of the Wellcome Trust. In 2019, the Wellcome Trust also opened an office in Berlin.[7]
History
The trust was established to administer the fortune of the American-born British pharmaceutical magnate Sir Henry Wellcome.[8] Its income was derived from what was originally called Burroughs Wellcome, later renamed in the UK as the Wellcome Foundation Ltd.[9] In 1986, the trust sold 25% of Wellcome plc stock to the public. Overseen by incoming Director of Finance Ian Macgregor, this marked the beginning of a period of financial growth that saw the trust's value increase by almost £14bn in 14 years, as their interests moved beyond the bounds of the pharmaceutical industry.[10]
In 1995, the trust divested itself of any interest in pharmaceuticals by selling all remaining stock to Glaxo plc, the company's historic British rival, creating GlaxoWellcome plc. In 2000, the Wellcome name disappeared from the drug business altogether when GlaxoWellcome merged with SmithKline Beecham, to form GlaxoSmithKline plc.[11]
Activities
Biomedical research
Major investments
The Trust funds or co-funds a number of major biomedical research initiatives:[12]
- Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC), a cohort study of children born in England during 1991 and 1992.
- The Cancer Genome Project at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute.
- The Diamond Light Source, the UK's national synchrotron science facility in Oxfordshire.
- Developing Excellence in Leadership, Training and Science Initiative (DELTAS), a collaboration with the Department for International Development (DFID) to establish cutting-edge research and training programmes across the African continent.
- The Ebola Emergency Initiative, a fast-tracked research programme with the goal of identifying clinical and public health interventions to counter the West African Ebola Epidemic.
- The Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation/ Wellcome Trust Diabetes and Inflammation Laboratory facilitates research into the genetic component of type 1 diabetes and is based in the Cambridge Institute for Medical Research.
- The Seeding Drug Discovery Initiative.
- The Structural Genomics Consortium, an international organisation focussing on three-dimensional structures of proteins of medical relevance with an emphasis on open data.
- The Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, a non-profit, British genomics and genetics research institute.[13]
- UK Biobank and the UK Biobank Ethics and Governance Council.
Asia and Africa Programmes
- The KEMRI-Wellcome Trust Research Programme, established in 1989 in partnership with the Kenya Medical Research Institute.[14]
- The Malawi-Liverpool-Wellcome Trust Clinical Research Programme, established in 1995.
- The Africa Centre for Health and Population Studies in South Africa, established in 1998 in partnership with the South African Medical Research Council.
- The Wellcome Trust-Mahidol University-Oxford Tropical Medicine Research Programme in partnership with the Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University, researching in Thailand and Laos and established in 1979.
- The Vietnam Research Programme and Oxford University Clinical Research Unit in Ho Chi Minh City and Hanoi.
Seeding Drug Discovery Initiative
Also known as SDDI, this five-year initiative started in October 2005 with the remit "to facilitate the development of drug-like small molecules that address unmet medical needs." SDDI was based in London and managed by Richard Davis.[15] Through early 2010, SDDI had provided more than £80 million across 30 projects split between academic institutions and companies.[15] To early 2010, all but one of the company recipients were either start-ups or spin-outs.[15] In May 2010, an additional £110 million was added to the SDDI fund with the intent to extend the initiative for an additional 5 years.[16]
Supporting global research and development in COVID-19
The Wellcome Trust announced the need for at least $8 billion of new funding for research, development, and supply of treatments related to COVID-19.[17]
Improving research culture
In September 2019, Wellcome launched an initiative to reimagine research and improve the culture in which research is conducted. Current incentive structures and, as a result, culture and practices, prioritise publication outputs above all else. This is damaging people's wellbeing and undermining the quality of research itself.[18]
Support for Open Access and Open Data
The Wellcome Trust plays an important role in encouraging publication of research in open access repositories[19] such as Europe PubMed Central (EuropePMC). The Wellcome Trust believes that maximising the distribution of these papers – by providing free, online access – is the most effective way of ensuring that the research can be accessed, read and built upon. In turn, this will foster a richer research culture.[citation needed]
In 2016, the Wellcome Trust partnered with the US National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute to launch the Open Science Prize[20] to "help develop services, tools and platforms that enable open content to be discovered, assessed and re-used in ways that will advance discovery and spark innovation."[20]
In 2016, Wellcome Trust announced that it would be launching Wellcome Open Research,[21] an open access publication system running on the F1000 Research platform.[22] Article processing charges will be covered directly by Wellcome Trust. Papers from the system are now indexed in PubMed Central.[23]
Membership in the Global Health Innovative Technology Fund (GHIT)
In the summer of 2015, the Wellcome Trust joined the Japanese government, 7 Japanese pharmaceutical and diagnostics companies, The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, and the United Nations Development Program as funding partner of the Global Health Innovative Technology Fund (GHIT), which funds scientific research and development for anti-infectives and diagnostics for diseases that primarily affect the developing world.[24][25]
Public engagement and the Wellcome Collection
In June 2007, the Wellcome Building reopened after refurbishment as a public venue, housing the Wellcome Collection, the Wellcome Trust Centre for the History of Medicine at University College London and the Wellcome Library.[26] The aim of the Wellcome Collection is to enhance public understanding of medical science and history. The building contains gallery spaces, conference facilities, space for debates, drama and workshops, a café and a bookshop. The galleries show a small sample of works from Sir Henry Wellcome's collection, and host a programme of events and exhibitions. The Wellcome Collection and exhibitions are open to the public free of charge six days a week.[27]
The Wellcome Collection and Wellcome Library are members of The London Museums of Health & Medicine.
Wellcome Photography Prize
The Wellcome Trust runs an annual photography prize which aims to explore "the human side of three urgent health challenges". Judges in 2021 include Dr Dixon Chabanda, Sir Jeremy Farrar, Dr Katerina Srahulkova and Azu Nwagbogu. Winners in each category receive a prize of £10,000.
Wellcome Book Prize
The Wellcome Trust sponsors an annual book prize, the Wellcome Book Prize, which "aims to excite public interest and encourage debate" around medicine and health.[28]
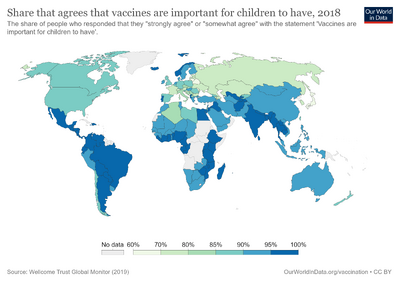
Wellcome Global Monitor
In June 2019, Wellcome released the results of the 2018 global survey on public attitudes toward science and health. Topics include trust of scientists, doctors, and nurses; religion and science, and vaccines, among others.[29] It was Wellcome's first Global Monitor and was intended to "provide robust evidence on how public attitudes vary across different demographic groups and countries."[30]
Investments
In August 2014, the Wellcome Trust bought the Co-operative Group's farm business (renamed Farmcare) for £249 million. This comprised "15,997 hectares (39,533 acres) of freehold and third party owned land, 15 farms, including three pack houses, over 100 residential properties, and 27 commercial properties."[31]
In 2015 the trust bought the Premier Marinas group.[32]
Criticisms
It has been reported that the Wellcome Trust has billions of investments on companies which contribute to the problems the philanthropy wants to solve.[33] Also in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, it has been revealed that the trust has investments with pharmaceutical companies, which means it should gain financially from the pandemic.[34]
See also
References
- ↑ "Wellcome Trust aims to increase spend to £5 billion over next 5 years". Archived from the original on 14 May 2016. Retrieved 29 June 2022.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Value of Wellcome's investments passes £25 billion". Wellcome Trust. 2018. Archived from the original on 8 September 2020. Retrieved 29 June 2022.
- ↑ "Charity Commission factsheet for the Wellcome Trust". Charity Commission for England and Wales. 17 December 2015. Archived from the original on 30 November 2018. Retrieved 29 June 2022.
- ↑ Andrew Jack (10 April 2012). "Wellcome challenges science journals". Financial Times. Archived from the original on 18 July 2012. Retrieved 16 April 2012.(registration required)
- ↑ "Wellcome's 2019/2020 Annual Report | Wellcome". wellcome.org. Archived from the original on 18 August 2022. Retrieved 29 January 2021.
- ↑ "Wellcome Trust | Development Co-operation Profiles – Wellcome Trust | OECD iLibrary". Archived from the original on 28 June 2021. Retrieved 16 August 2022.
- ↑ "Wellcome's Berlin office will focus on global health | Wellcome". wellcome.ac.uk. Archived from the original on 27 August 2020. Retrieved 4 January 2020.
- ↑ "History of Henry Wellcome". Archived from the original on 2 April 2016. Retrieved 29 June 2022.
- ↑ Hall, A. R. & Bembridge, B. A. Physic and philanthropy: a history of the Wellcome Trust 1936–1986. Cambridge (UK): Cambridge University Press, 1986. ISBN 0-521-32639-7
- ↑ briandeer.com Archived 22 April 2011 at the Wayback Machine Sunday Times investigation, February 1994]
- ↑ "Henry Wellcome's legacy". Wellcome.ac.uk. Archived from the original on 16 March 2016. Retrieved 21 May 2016.
- ↑ "Biomedical science funded projects". Archived from the original on 3 May 2016. Retrieved 29 June 2022.
- ↑ "MRC Centre United Kingdom: Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute". Medical Research Council. Archived from the original on 21 May 2012. Retrieved 22 December 2008.
- ↑ "Kenya and the KEMRI-Wellcome Trust Research Programme". Archived from the original on 5 April 2016. Retrieved 29 June 2022.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 "A Wellcome experiment in seeding drug discovery". Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 9 (3): 178–180. March 2010. doi:10.1038/nrd3130. PMID 20190777. S2CID 7960795.(subscription required)
- ↑ "Wellcome Trust extends Seeding Drug Discovery initiative". TMRM. AngelNews. 14 May 2010. Archived from the original on 14 January 2015. Retrieved 4 July 2013.
- ↑ "Coronavirus, COVID-19 research and development | Wellcome". wellcome.ac.uk. Archived from the original on 12 September 2020. Retrieved 29 June 2020.
- ↑ "Largest survey into research culture reveals high levels of stress and insecurity". January 2020. Archived from the original on 4 July 2020. Retrieved 29 June 2022.
- ↑ "Wellcome Trust position statement in support of open and unrestricted access to published research". Archived from the original on 31 August 2011. Retrieved 29 June 2022.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 "The Open Science Prize". Archived from the original on 31 August 2017. Retrieved 29 June 2022.
- ↑ "Wellcome Open Research provides all Wellcome researchers with a place to rapidly publish any results they think are worth sharing". wellcomeopenresearch.org. Archived from the original on 1 July 2022. Retrieved 8 November 2016.
- ↑ "Wellcome Open Research is now accepting submissions". Discussions – F1000 Research. 17 October 2016. Archived from the original on 9 November 2016. Retrieved 8 November 2016.
- ↑ "Archive of "Wellcome Open Research"". ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 2 June 2022. Retrieved 14 June 2017.
- ↑ "Japan in pioneering partnership to fund global health research", by Andrew Jack, Financial Times, 30 May 2013
- ↑ "Japanese Global Health Fund Welcomes the Wellcome Trust and Sysmex Corporation as New Funders and ANA, Morrison & Foerster, and Yahoo! Japan as New Sponsors", PR Newswire, 3 June 2015, <http://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/japanese-global-health-fund-welcomes-the-wellcome-trust-and-sysmex-corporation-as-new-funders-and-ana-morrison--foerster-and-yahoo-japan-as-new-sponsors-300093066.html Archived 1 November 2019 at the Wayback Machine>, accessed on 9/28/2015
- ↑ "The Wellcome Library". Archived from the original on 22 September 2013. Retrieved 29 June 2022.
- ↑ "Wellcome Collection opening hours". Archived from the original on 25 September 2014. Retrieved 29 June 2022.
- ↑ "About the Wellcome Book Prize | Wellcome Book Prize". wellcomebookprize.org. Archived from the original on 28 April 2022. Retrieved 15 March 2017.
- ↑ Branch, Glenn (2019). "Welcome News on Global Attitudes toward Science and Health from Wellcome". Skeptical Inquirer. 43 (5): 8–9.
- ↑ "Wellcome Global Monitor". Wellcome. Archived from the original on 3 September 2019. Retrieved 12 October 2019.
- ↑ "Wellcome Trust acquires the Co-operative Group's farms business". Wellcome.ac.uk. 4 August 2014. Archived from the original on 23 April 2016. Retrieved 21 May 2016.
- ↑ "Wellcome Trust acquires Premier Marinas Limited from BlackRock UK Property Fund | Wellcome". Archived from the original on 6 August 2020. Retrieved 29 June 2022.
- ↑ "Private research funders court controversy with billions in secretive investment". sciencemag.org. 6 December 2018. Archived from the original on 20 March 2021. Retrieved 19 March 2021.
The trust does not highlight, however, that some of the more than $1.2 billion it has handed out annually in recent years comes from investments in companies that contribute to the same problems the philanthropy wants to solve. Not long before the Hong Kong study was published, for example, the trust became an investor in Varo Energy, a company based in Cham, Switzerland, that sells fuel to shipping firms. One of Varo's main products is bunker fuel for marine engines: a cheap, sulfurous residue of oil refining that is a major source of soot pollution. Particulates billowing from ship stacks contribute to the premature deaths of 250,000 people annually, researchers estimate.
- ↑ Schwab, Tim (2021). "Covid-19, trust, and Wellcome: how charity's pharma investments overlap with its research efforts". The BMJ. 372: n556. doi:10.1136/bmj.n556. PMID 33658184. S2CID 232105541. Archived from the original on 20 March 2021. Retrieved 3 March 2021.
Wellcome’s financial interests have been published on the trust’s website and through financial regulatory filings but do not seem to have been disclosed as financial conflicts of interest in the context of Wellcome’s work on covid-19, even as they show that the trust is positioned to potentially gain from the pandemic financially.
External links
- Official website
- Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium (WTCCC) Archived 29 June 2022 at the Wayback Machine
- Other Wellcome Trust websites Archived 3 May 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- Scientific Conferences supported by the Wellcome Trust
- Ex Memoria – Wellcome Trust Awarded Film
- Surgery Live, a Wellcome Collection collaboration with Channel 4
- European Society for Clinical Microbioloy and Infectious Diseases Archived 10 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine
- Federation of European Biochemical Societies Archived 25 February 2021 at the Wayback Machine
- European Federation of Pharmaceutical Societies Archived 4 December 2019 at the Wayback Machine
- International Society for Infectious Diseases Archived 30 June 2022 at the Wayback Machine
- Pages with login required references or sources
- Webarchive template wayback links
- Pages containing links to subscription-only content
- Use dmy dates from January 2022
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- Use British English from February 2013
- Pages using infobox organization with unknown parameters
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from September 2011
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Official website not in Wikidata
- Wellcome Trust
- Organizations established in 1936
- Biomedical research foundations
- Foundations based in the United Kingdom
- Funding bodies in the United Kingdom
- Health charities in the United Kingdom
- Science and technology in the United Kingdom
- 1936 establishments in the United Kingdom
- British landowners