Viltolarsen
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Viltepso |
| Other names | NS-065/NCNP-01 |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Antisense oligonucleotide |
| Main uses | Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD)[1] |
| Side effects | upper respiratory tract infection, injection site reaction, cough, fever[1] |
| Routes of use | Intravenous |
| Typical dose | 80 ug/kg[1] |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Legal | |
| License data |
|
| Legal status | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C244H381N113O88P20 |
| Molar mass | 6924.910 g·mol−1 |
Viltolarsen, sold under the brand name Viltepso, is a medication used to treat certain cases of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD).[1] Specifically it is used for the approximately 8% of people with DMD who have a mutation that is amenable to exon 53 skipping.[3] As of 2020 it was unclear if it results in improvements.[3] It is given by injection into a vein over an hour.[1]
Common side effects include upper respiratory tract infection, injection site reaction, cough, and fever.[1] Other potential concerns include kidney problems.[1] It is a morpholino antisense oligonucleotide.[1]
Viltolarsen was approved for medical use in the United States in 2020.[1] It is not approved in Europe, as of 2020, though has orphan designation.[4] In the United States it costs about 1,500 USD per 250 mg as of 2021.[5] This is about 730,000 USD for a person who is 30 kg.[6]
Medical uses
Viltolarsen is used to treat Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) in people who have a confirmed mutation of the DMD gene that is amenable to exon 53 skipping.[3][2]
While it results in improvements in biochemical markers evidence as of 2020 does not support improved outcomes for the people affected.[3]
Dosage
The typical dose is 80 ug/kg once per week.[1]
Side effects
The most common side effects include upper respiratory tract infection, injection site reaction, cough, and pyrexia (fever).[3][7][2]
Although kidney toxicity was not observed in the clinical studies, the clinical experience is limited, and kidney toxicity, including potentially fatal glomerulonephritis, has been observed after administration of some antisense oligonucleotides.[3]
Mechanism of action
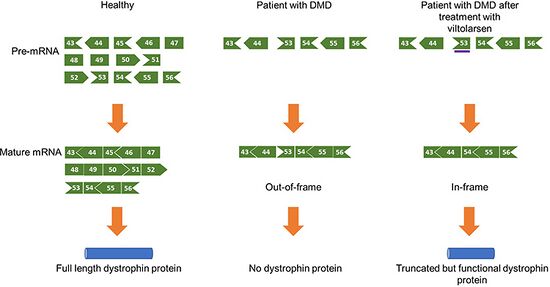
In terms of the mechanism of action of this PMO we find that it binds to exon 53. As a consequence the exon is skipped and truncated however a functional dystrophin protein is created[8]
History
Viltolarsen was evaluated in two clinical studies with a total of 32 participants, all of whom were male and had genetically confirmed DMD.[3] The increase in dystrophin production was established in one of those two studies, a study that included sixteen DMD participants, with eight participants receiving viltolarsen at the recommended dose.[3] In the study, dystrophin levels increased, on average, from 0.6% of normal at baseline to 5.9% of normal at week 25.[3] Trial 1 provided data for evaluation of the benefits of viltolarsen.[7] The combined populations from both trials provided data for evaluation of the side effects of viltolarsen.[7] Trial 1 was conducted at six sites in the United States and Canada and Trial 2 was conducted at five sites in Japan.[7] All participants in both trials were on a stable dose of corticosteroids for at least three months before entering the trials.[7]
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) concluded that the applicant's data demonstrated an increase in dystrophin production that is reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit in people with DMD who have a confirmed mutation of the dystrophin gene amenable to exon 53 skipping.[3] A clinical benefit of the drug has not been established.[3] In making this decision, the FDA considered the potential risks associated with the drug, the life-threatening and debilitating nature of the disease, and the lack of available therapies.[3]
The application for viltolarsen was granted priority review designation and the FDA granted the approval to NS Pharma, Inc.[3]
After golodirsen was approved in December 2019, viltolarsen is the second approved targeted treatment for people with this type of mutation in the United States.[3][9]
Society and culture
Cost
Viltepso is over $733,000 a year for a 30 kilogram (66 pound) patient.[6]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 "Viltolarsen Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Retrieved 15 September 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Viltepso- viltolarsen injection, solution". DailyMed. 12 August 2020. Archived from the original on 27 August 2021. Retrieved 18 August 2020.
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 3.13 "FDA Approves Targeted Treatment for Rare Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Mutation". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 12 August 2020. Archived from the original on 20 August 2020. Retrieved 12 August 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ "EU/3/20/2282: Viltolarsen". Archived from the original on 9 January 2021. Retrieved 15 September 2021.
- ↑ "Viltepso Prices, Coupons & Patient Assistance Programs". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 14 April 2021. Retrieved 15 September 2021.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "FDA gives speedy approval to another Duchenne drug". BioPharma Dive. Archived from the original on 2021-06-27. Retrieved 2021-08-03.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 "Drug Trials Snapshots: Viltepso". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 12 August 2020. Archived from the original on 19 August 2020. Retrieved 18 August 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Roshmi, Rohini Roy; Yokota, Toshifumi (16 December 2021). "Pharmacological Profile of Viltolarsen for the Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: A Japanese Experience". Clinical Pharmacology: Advances and Applications. 13: 235–242. doi:10.2147/CPAA.S288842. Archived from the original on 3 April 2023. Retrieved 3 April 2024.
- ↑ Anwar S, Yokota T (August 2020). "Golodirsen for Duchenne muscular dystrophy". Drugs of Today. 56 (8): 491–504. doi:10.1358/dot.2020.56.8.3159186. PMID 33025945.
Further reading
- Dhillon S (July 2020). "Viltolarsen: First Approval". Drugs. 80 (10): 1027–1031. doi:10.1007/s40265-020-01339-3. PMID 32519222. S2CID 219542850.
- Dzierlega K, Yokota T (June 2020). "Optimization of antisense-mediated exon skipping for Duchenne muscular dystrophy". Gene Ther. 27 (9): 407–416. doi:10.1038/s41434-020-0156-6. PMID 32483212. S2CID 219157034.
- Hwang J, Yokota T (October 2019). "Recent advancements in exon-skipping therapies using antisense oligonucleotides and genome editing for the treatment of various muscular dystrophies". Expert Rev Mol Med. 21: e5. doi:10.1017/erm.2019.5. PMID 31576784. S2CID 203641010.
- Roshmi RR, Yokota T (October 2019). "Viltolarsen for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy". Drugs Today. 55 (10): 627–639. doi:10.1358/dot.2019.55.10.3045038. PMID 31720560.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|
|---|
- "Viltolarsen". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM). Archived from the original on 2021-08-27. Retrieved 2021-08-03.
- Pages using duplicate arguments in template calls
- Wikipedia articles incorporating the PD-notice template
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Infobox drug articles without a structure image
- Chemical articles without CAS registry number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs missing an ATC code
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Drugs not assigned an ATC code
- Antisense RNA
- Muscular dystrophy
- Therapeutic gene modulation
- Orphan drugs
- RTT