Tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis
| Tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis syndrome | |
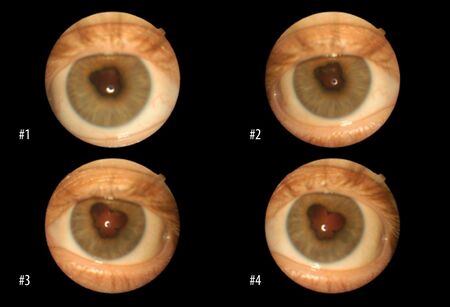 | |
| Posterior synechiae are visible; there is 2+ anterior chamber cell and flare | |
| Specialty | Ophthalmology |
Tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis (TINU) is a rare medical condition in which there is uveitis (inflammation of the uvea in the eye) together with tubulointerstitial nephritis (inflammation of the tubules inside the kidney).
Symptoms and signs
Uveitis may cause pain of the affected eye together with changes in vision. It may be accompanied by nonspecific systemic symptoms such as fever, involuntary weight loss, fatigue, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, and joint pains.[1]
Cause
The etiology of Tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis is not clear, however it may be of autoimmune origin. There seems to be a risk of the condition in relation to certain HLA haplotypes[2]
Diagnosis
We can see increased eosinophils under microscope after biopsy.[citation needed]
Management
Treatment for Tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis is based on oral corticosteroid[2]
History
It was first described in 1975.[1][3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Mackensen, F; Billing, H (November 2009). "Tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis syndrome". Current Opinion in Ophthalmology. 20 (6): 525–31. doi:10.1097/ICU.0b013e3283318f9a. PMID 19752730. S2CID 11461472.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 RESERVED, INSERM US14-- ALL RIGHTS. "Orphanet: Tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis syndrome". www.orpha.net. Archived from the original on 31 March 2023. Retrieved 11 November 2023.
- ↑ Dobrin, RS; Vernier, RL; Fish, AL (September 1975). "Acute eosinophilic interstitial nephritis and renal failure with bone marrow-lymph node granulomas and anterior uveitis. A new syndrome". The American Journal of Medicine. 59 (3): 325–33. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(75)90390-3. PMID 1163543.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |