Tuberculous pericarditis
| Tuberculous pericarditis | |
|---|---|
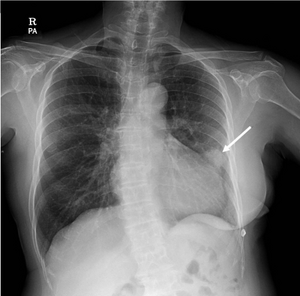 | |
| Rounded, bulging mass in the superior cardiac border and adjacent lung nodule arrow on chest X-ray. | |
Tuberculous pericarditis is a form of pericarditis.
Pericarditis caused by tuberculosis is difficult to diagnose, because definitive diagnosis requires culturing Mycobacterium tuberculosis from aspirated pericardial fluid or pericardial biopsy, which requires high technical skill and is often not diagnostic (the yield from culture is low even with optimum specimens). The Tygerberg scoring system helps the clinician to decide whether pericarditis is due to tuberculosis or whether it is due to another cause: night sweats (1 point), weight loss (1 point), fever (2 point), serum globulin > 40g/l (3 points), blood total leucocyte count <10 x 109/l (3 points); a total score of 6 or more is highly suggestive of tuberculous pericarditis.[1] Pericardial fluid with an interferon-γ level greater than 50pg/ml is highly specific for tuberculous pericarditis.[citation needed]
There are no randomized trials which evaluate the length of anti-tuberculosis treatment required for tuberculous pericarditis.[2] There is a small but not conclusive benefit for treatment with a schedule of steroids with anti-tuberculosis drugs. Open surgical drainage of fluid though effective in preventing cardiac tamponade was associated with more deaths.[3][needs update]
References
- ↑ Reuter H, Burgess L, van Vuuren W, Doubell A (2006). "Diagnosing tuberculous pericarditis". Q J Med. 99 (12): 827–39. doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcl123. PMID 17121764.
- ↑ Wiysonge, Charles S.; Ntsekhe, Mpiko; Thabane, Lehana; Volmink, Jimmy; Majombozi, Dumisani; Gumedze, Freedom; Pandie, Shaheen; Mayosi, Bongani M. (13 September 2017). "Interventions for treating tuberculous pericarditis". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 9: CD000526. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000526.pub2. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 5618454. PMID 28902412.
- ↑ Mayosi BM. (2002). Mayosi, Bongani M (ed.). "Interventions for treating tuberculous pericarditis". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (4): CD000526. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000526. PMC 5618454. PMID 12519546.
External links
| Classification |
|---|