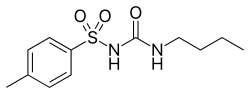
Tolbutamide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Orinase, others |
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Sulfonylurea[1] |
| Main uses | Type 2 diabetes[1] |
| Side effects | Nausea, itchiness, rash, low blood sugar[1] |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | By mouth (tablet) |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682481 |
| Legal | |
| License data |
|
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Protein binding | 96% |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP2C19-mediated) |
| Elimination half-life | 4.5 to 6.5 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H18N2O3S |
| Molar mass | 270.35 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 128.5 to 129.5 °C (263.3 to 265.1 °F) |
| |
| |
Tolbutamide is a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes.[1] It is a second line treatment after metformin.[1] It is taken by mouth.[1] Effects may last for up to 24 hrs.[1]
Common side effects include nausea, itchiness, and rash.[1] Other side effect may include low blood sugar.[1] Those with liver or kidney problems have more frequent side effects.[1] Use in pregnancy is not generally recommended.[2] It is a sulfonylurea.[1] It works by stimulating the release of insulin by the pancreas.[1]
Tolbutamide was discovered in 1956 and approved for medical use in 1957.[3][1] It is available as a generic medication.[2] In the United States 100 tablets of 500 mg costs about 92 USD as of 2021.[4] This amount in the United Kingdom costs the NHS about £73.[2]
Medical uses
Dosage
It is generally used at a dose of 1 to 2 grams per day.[1]
Side effects
- Hypoglycemia
- Weight gain
- Hypersensitivity: cross-allergicity with sulfonamides
- Drug interactions (especially first-generation drugs): Increased hypoglycemia with cimetidine, insulin, salicylates, and sulfonamides
Salicylates displace tolbutamide from its binding site on plasma binding proteins which lead to increase in free tolbutamide concentration, thus hypoglycemic shock.
History
Orinase was developed by Upjohn Co. at a time when the primary medical treatment for diabetes was insulin injections. Eli Lilly had a lock on the market for insulin production at the time. Orinase, like other treatments for drugs detected by so-called paraclinical signs rather than clinically observable signs or patient-reported symptoms, benefitted from an increased sensitivity and availability of blood glucose testing. Milton Moskowitz (editor in 1961 of Drug and Cosmetic Industry) claimed the introduction of Orinase, "expanded the total market by bringing under medical care diabetics who were formerly not treated."[5] It did this by changing the mindset about diabetes even more than insulin had. Treatment of this chronic disease was no longer seen as a mere slowing of "inexorable degeneration", but instead viewed through "a model of surveillance and early detection."[5]: 84
Orinase and other sulfonylureas emerged from European pharmaceutical research into antibiotics, specifically from attempts to develop sulfa compounds. One of the contenders for a new sulfa antibiotic had serious side effects during clinical trials at the University of Montpellier including blackouts, convulsions, and coma, side effects not observed with any other drugs in the sulfa cohort. An insulin researcher at the same university heard of these side effects and recognized them as common results of hypoglycemia. The resulting class of drugs for lowering blood sugar came to be known as the sulfonylureas, starting with Orinase and still in use today in other forms.
Unfortunately for diabetics dependent on insulin as a treatment for their condition, this research at Montpellier occurred in the early 1940s and was significantly disrupted by the German occupation of France during World War II. Development of these compounds was taken over by German pharmaceutical companies, which were obviously disinclined to share their bounty with nations upon which they were waging war. The German research was, in turn, disrupted by Germany's defeat in 1945 and the partition of Germany into East and West Germany. The sulfonylureas were trapped in East Germany. In 1952, someone smuggled a sample to a West German pharmaceutical company and research resumed. Clinical trials in diabetics began in 1954 in Berlin. In 1956, two different sulfonylureas were brought to market in Germany under the trade names Nadisan and Rastinon. American pharmaceutical companies in the postwar period had been seeking to establish business relations with the remnants of German pharmaceutical giants weakened by the war and partition of Germany. Upjohn (based in Kalamazoo until its purchase by Pharmacia in the 1990s) made deals with Hoechst, maker of Rastinon. The result was a cross-licensing agreement which produced Orinase.
Upjohn stood to open up a whole new arena of treatment for diabetes, one with a built-in and sustainable market, i.e. patient population. Just as two German companies brought sulfonylureas to market within the same year, Upjohn discovered Eli Lilly had begun clinical trials for carbutamide, another oral hypoglycemic. Upjohn pushed for large-scale clinical trials from 1955–1957, enrolling over 5,000 patients at multiple sites.
Upjohn's formulation was preferred when the Lilly formulation demonstrated evidence of toxicity in parallel trials at the Joslin Clinic. Lilly pulled carbutamide and halted development, leaving the field open for Upjohn to market its new treatment. In 1956, Upjohn filed for approval from the Food and Drug Administration. Jeremy A. Greene found the application's size – 10,580 pages in 23 volumes with 5,786 cases reports – was necessary to "render visible the relatively small improvements provided in less severe forms of diabetes." Indeed, Orinase was marketed by Upjohn not as a cure-all for all diabetics, but specifically as a treatment that was "not an oral insulin" and "did not work in all diabetics". Those were the instructions for marketing given to Upjohn's salespeople. As indicated by the FDA application, Orinase had been demonstrated "not to be effective in severe diabetes, but only in milder cases of the disease."[5]: 93 Orinase was one of a new class of drugs (including treatments for hypertension and hypercholesterolemia) aimed at providing marginal benefits over existing treatments for patients who had not previously been a target market for pharmaceuticals. As blood sugar testing for diagnosis of diabetes became more widespread, a curious side effect occurred: because blood sugar testing is not absolutely definitive in diagnoses of diabetes, more people were receiving borderline tests regarding their glycemic status. These borderline persons could be considered as being at risk for diabetes – prediabetic. Prediabetic patients have elevated blood sugar, but normal levels of sugar in their urine (glycosuria). Upjohn saw an opportunity to benefit and definitely market to a yet-greater expansion of the diabetic population, beyond even the "hidden diabetics" revealed by earlier public health campaigns. Upjohn also found a new use for Orinase: as a diagnostic. Orinase Diagnostic was added to the Orinase product line and, by 1962, was being sold as means of detecting prediabetes in that an abnormal response to Orinase following administration of cortisone in a "stress test" could be taken to indicate prediabetes. Orinase thus not only served to detect a previously hidden patient population, but also detected a patient population most likely to be interested in Orinase as a treatment for their newly diagnosed prediabetes. By the late 1960s, Orinase Diagnostic was withdrawn and the drug reverted to its therapeutic purpose. By that point, prediabetes had become a diagnosable and treatable condition which had dramatically increased the market for Orinase.
Orinase began to fall out of favor in May 1970 when asymptomatic prediabetics on long-term regimens of Orinase began to see news reports (beginning with the Washington Post) that Orinase may have serious side effects including death from cardiovascular problems, according to a long-term study. In many cases, patients learned of this before their physicians, and also before FDA could advise relabeling the medication or suggesting alterations in appropriate usage. The question of whether Orinase did or did not increase cardiovascular problems has not been conclusively settled. The result was that Orinase and other medical treatments for prediabetes were "rolled back" by the FDA and practitioners in an attempt to focus on symptomatic patients for whom the risks of treatment might be balanced by the symptoms of the disease.
Pharmacia and Upjohn (now merged) stopped making Orinase in 2000, though a generic is still available and occasionally used.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 "Tolbutamide Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 17 August 2019. Retrieved 5 October 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 BNF (80 ed.). BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. September 2020 – March 2021. p. 749. ISBN 978-0-85711-369-6.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: date format (link) - ↑ Walker SR (2012). Trends and Changes in Drug Research and Development. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 109. ISBN 9789400926592. Archived from the original on 2017-09-10. Retrieved 2020-11-29.
- ↑ "Tolbutamide Prices, Coupons & Patient Assistance Programs". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 17 April 2021. Retrieved 5 October 2021.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Greene JA (2007). Prescribing by Numbers: Drugs and the Definition of Disease. Baltimore, MD.: Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-8477-1.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|
|---|
- Pages using duplicate arguments in template calls
- CS1 maint: date format
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Chemical articles without CAS registry number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs missing an ATC code
- Drugboxes which contain changes to watched fields
- Disulfiram-like drugs
- Potassium channel blockers
- Benzenesulfonylureas
- P-Tosyl compounds
- RTT