Tenapanor
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Ibsrela |
| Other names | Tenapanor hydrochloride |
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | NHE3 inhibitors |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | By mouth |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Legal | |
| License data | |
| Legal status |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
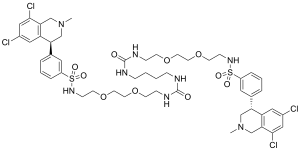
| Formula | C50H66Cl4N8O10S2 |
| Molar mass | 1145.04 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Tenapanor, sold under the brand name Ibsrela, is a medication used to treat irritable bowel syndrome with constipation (IBS-C).[1] It is taken by mouth.[1]
Common side effects include diarrhea, abdominal swelling, and lightheadedness.[1] Use in pregnancy and breastfeeding is believed to be safe.[1] It acts by blocking the sodium-proton exchanger NHE3 there by decreasing the uptake of sodium by the intestines.[1]
Tenapanor was approved for medical use in the United States in 2019.[1] As of 2021; however, it is not yet in pharmacies.[2] As of 2021 it is not approved in Europe or the United Kingdom.[3]
Medical uses
It is used for irritable bowel syndrome with constipation (IBS-C).[4]
Dosage
It is usually taken at a dose of 50 mg two times per day.[1]
History
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication.[5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 "Tenapanor Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 27 January 2021. Retrieved 25 September 2021.
- ↑ "Ibsrela Prices and Ibsrela Coupons - GoodRx". GoodRx. Retrieved 25 September 2021.
- ↑ "Tenapanor". SPS - Specialist Pharmacy Service. 26 May 2017. Archived from the original on 23 July 2017. Retrieved 25 September 2021.
- ↑ "Drug Trials Snapshots: Ibsrela". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 27 September 2019. Archived from the original on 19 November 2019. Retrieved 18 November 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ "New Drug Therapy Approvals 2019". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 31 December 2019. Archived from the original on 16 September 2020. Retrieved 15 September 2020.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|
|---|
- "Tenapanor". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM). Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 1 July 2021.
- Pages using duplicate arguments in template calls
- Wikipedia articles incorporating the PD-notice template
- Use dmy dates from November 2019
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Chemical articles without CAS registry number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs missing an ATC code
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Drugs acting on the gastrointestinal system and metabolism
- RTT
- All stub articles
- Gastrointestinal system drug stubs