Rickettsialpox
| Rickettsialpox | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Rickettsialpox lesion | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | Fever, scabby sore, rash[1] |
| Causes | Liponyssoides sanguineus[1] |
| Prognosis | Resolves in 2-3 weeks without treatment |
Rickettsialpox is a mite-borne infectious illness caused by Liponyssoides sanguineus, and presents with fever, scabby sore and a rash.[1]
It is caused by bacteria of the genus Rickettsia (Rickettsia akari).[2]Physician Robert Huebner and self-trained entomologist Charles Pomerantz played major roles in identifying the cause of the disease after an outbreak in 1946 in a New York City apartment complex, documented in "The Alerting of Mr. Pomerantz," an article by medical writer Berton Roueché.
Although it is not transmitted by a tick (a characteristic of spotted fever), the bacterium is a part of the spotted fever group of Rickettsia, and so this condition is often classified with that group.[3]
Signs and symptoms
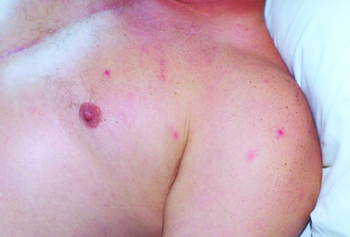
The first symptom is a bump formed by the bite, eventually resulting in a black, crusty scab. Many of the symptoms are flu-like including fever, chills, weakness and achy muscles but the most distinctive symptom is the rash that breaks out, spanning the infected person's entire body.[citation needed]
Transmission
The bacteria are originally found in mice and cause mites feeding on the mice (usually the house mouse) to become infected. Humans will get rickettsialpox when receiving a bite from an infected mite, not from the mice themselves.[citation needed]
The mite is Liponyssoides sanguineus, which was previously known as Allodermanyssus sanguineus.[4]
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of this infection is done via the following:[5]
- Physical examination
- Complete blood count
- Tests of blood serum
- Swabbing rash
Treatment
Rickettsialpox is treated with tetracyclines (doxycycline is the drug of choice). Chloramphenicol is a suitable alternative.[6]
Prognosis
Rickettsialpox is generally mild and resolves within 2–3 weeks if untreated. There are no known deaths resulting from the disease.[citation needed]
Epidemiology
Those dwelling in urban areas (which typically experience rodent problems) have a higher risk of contracting rickettsialpox.[citation needed]
History
The initial outbreak of the disease took place in the Regency Park complex which had 69 apartment units organized in three groups each three stories in height, located in Kew Gardens, in the New York City borough of Queens. Physicians who had seen patients starting in early 1946 had assumed that they were dealing with an atypical form of chickenpox, but the realization was made that they were dealing with a localized epidemic of unknown origins starting in the summer of that year. Physicians canvassed the residents of the building and found that there had been 124 cases of this disease from January through October among the 2,000 people living in the complex, reaching a peak of more than 20 cases reported in July. Individuals afflicted with the condition ranged in age from 3 months to 71, males and females were equally affected and the incidence among adults (6.5% of the 1,400 above age 15) exceeded that of children 14 and under (5.3%).[7]
Individuals would first have a small lesion at the site of the insect bite, which would eventually leave a small scar. Lymph nodes would become enlarged and about a week after the initial bite patients would start to experience chills, fever and headaches, accompanied by a maculopapular rash. The rash would last for about a week, with the full progress from the lesion being encountered until recovery typically being three weeks. Several characteristics were considered from an epidemiological perspective as being correlated with the condition. Men and women were equally affected and there was no apparent connection to occupation or school attended. The individuals obtained their meals at several different sources, and other individuals who lived elsewhere and purchased their food at these same places had not been affected. The water supply and milk consumed there were tested, with no unusual findings. There were dog kennels in the area and some tenants had dogs as pets, but an inspection of the animals found no ticks or insects.[7]
Many residents had reported the presence of mice in and around the apartments, especially in the basements of the buildings near the incinerators, where living and dead mice were found. Garbage disposed of through incinerator chutes was to be burned on a daily basis, with the ashes carted off by the New York City Department of Sanitation. Due to labor shortages, the material was not burned regularly, leaving ample food for the rodents. Mice were trapped in apartments and near the incinerators and antibodies to the rickettsialpox were found in their blood.[7] Visiting the complex with pest-control specialist and self-trained entomologist Charles Pomerantz, Huebner peeled back wallpaper to find the walls swarming with mites, so much so that tenants had said that "the walls had movement".[8] The mites were collected and rickettsial strains were isolated from some of them, with the name Rickettsia akari given to the organism.[7]
Public health officials took steps to prevent further outbreaks of the disease. The building operators were told to ensure that the incinerators were fired on a regular basis to ensure that food available to the mice that harbored the disease was eliminated as quickly and thoroughly as possible.[7] Pest control measures were undertaken through the New York City Department of Health and its commissioner Israel Weinstein to eliminate the mice in and around the buildings with the cooperation of property owners.[9]
Another 20 cases of rickettsialpox were discovered elsewhere in New York City during the investigation of the Queens outbreak, including 10 cases found in an apartment building in the Bronx that had originally been diagnosed as atypical chickenpox. Mice were found in the basement of this building, as well as mites belonging to the same class found in Queens.[7] In addition to the initial cases from the first outbreak in Queens, over 500 cases of the disease were diagnosed in New York City from 1947 to 1951.[10]
Society and culture
- House (TV Series), Season 7, Episode 7 ("A Pox On Our House") - a patient contracts rickettsialpox after breaking a glass jar found sealed in the bottom of a shipwreck[11][12][13]
See also
Reference3s
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Adem, Patricia V. (May 2019). "Emerging and re-emerging rickettsial infections". Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology. 36 (3): 146–151. doi:10.1053/j.semdp.2019.04.005. ISSN 0740-2570. PMID 31101391. Archived from the original on 2022-06-09. Retrieved 2022-06-06.
- ↑ "rickettsialpox" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ↑ "eMedicine - Rickettsialpox : Article by Julie A Ake". 2019-07-10. Archived from the original on 2008-09-24. Retrieved 2021-06-03.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ "Rickettsialpox: eMedicine Infectious Diseases". Archived from the original on 2010-11-29. Retrieved 2010-04-26.
- ↑ "Rickettsialpox: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". medlineplus.gov. Archived from the original on 29 July 2021. Retrieved 24 February 2022.
- ↑ Pedro-Pons, Agustín (1968). Patología y Clínica Médicas. Vol. 6 (3rd ed.). Barcelona: Salvat. p. 844. ISBN 84-345-1106-1.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 Greenberg, Morris; Pellitteri, Ottavio J.; and Jellison, William L. "Rickettsialpox - A Newly Recognized Rickettsial Disease", American Journal of Public Health, July 1947. Accessed July 25, 2009.
- ↑ Beeman, Edward A. "Robert J. Huebner, M.D.:A Virologist’s Odyssey" Archived 2015-02-13 at the Wayback Machine, National Institutes of Health, 2005. Accessed July 23, 2009.
- ↑ Staff. "NEW FEVER TRACED TO MITE ON MICE; U.S. Health Service Roots Out Cause of Spotted Ailment That Struck in Queens NO CURE IS FOUND AS YET Victim Made Ill by Bite of Insect--Weinstein Urges War on Rodents Some Removed to Hospitals Blood of Patients Sampled" Archived 2019-05-23 at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, October 4, 1946. Accessed July 23, 2009.
- ↑ Parola, Philippe. "Rickettsial Diseases", p. 63. CRC Press, 2007. ISBN 0-8493-7611-4. Accessed July 25, 2009.
- ↑ "Smallpox, Rickettsialpox Scare "House" Doctors: Is Threat Real?". www.cbsnews.com. Archived from the original on 2020-11-26. Retrieved 2021-06-03.
- ↑ "House MD Episodes: Season 7 #707 "A Pox On Our House"". www.housemd-guide.com. Archived from the original on 2019-09-09. Retrieved 2021-06-03.
- ↑ Bradley, Bill (17 November 2014). "8 Rare 'House, M.D.' Cases That Can Actually Happen". HuffPost. Archived from the original on 17 April 2021. Retrieved 3 June 2021.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |