Pure red cell aplasia
| Pure red cell aplasia | |
|---|---|
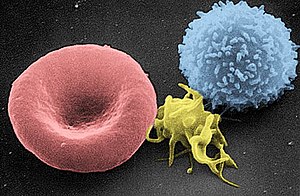 | |
| Scanning electron micrograph of blood cells. From left to right: human red blood cell, thrombocyte (platelet), leukocyte. Pure red cell aplasia affects the red blood cells in particular. | |
Pure red cell aplasia (PRCA) or erythroblastopenia refers to a type of aplastic anemia affecting the precursors to red blood cells but usually not to white blood cells. In PRCA, the bone marrow ceases to produce red blood cells. There are multiple etiologies that can cause PRCA. The condition has been first described by Paul Kaznelson in 1922.[1]
Signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms may include:
- Pale appearance
- Rapid heart rate
- Fatigue
Causes
Causes of PRCA include:
- Autoimmune disease.
- Thymoma.[2]
- Viral infections such as HIV, herpes, parvovirus B19 (Fifth disease),[3] or hepatitis.[citation needed]
- Lymphoproliferative. Association of pure red cell aplasia with T-cell large granular lymphocyte leukemia is well recognized, especially in China.[4]
- Idiopathic. Many cases of PRCA are considered idiopathic in that there is no discernible cause detected.[5]
- Drugs such as mycophenolic acid[6] or erythropoietin.[7][citation needed]
- Congenital. The term "hereditary pure red cell aplasia" has been used to refer to Diamond–Blackfan anemia.[8]
Diagnosis
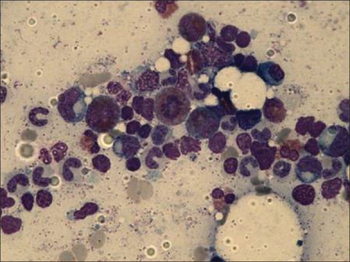
In terms of the evaluation of Pure red cell aplasia, a bone marrow exam is done[9]
Treatment
PRCA is considered an autoimmune disease as it will respond to immunosuppressant treatment such as cyclosporin in many patients,[10] though this approach is not without risk.[11]
It has also been shown to respond to treatments with rituximab and tacrolimus.[citation needed]
See also
- Diamond–Blackfan anemia (genetic red cell aplasia)
- Aplastic anemia (aplasia affecting other bone marrow cells as well)
References
- ↑ Kaznelson P (1922). "Zur Entstehung der Blutplättchen". Verh Dtsch Ges Inn Med. 34: 557–8.
- ↑ Hirokawa M, Sawada K, Fujishima N, et al. (January 2008). "Long-term response and outcome following immunosuppressive therapy in thymoma-associated pure red cell aplasia: a nationwide cohort study in Japan by the PRCA collaborative study group". Haematologica. 93 (1): 27–33. doi:10.3324/haematol.11655. PMID 18166782.
- ↑ Geetha D, Zachary JB, Baldado HM, Kronz JD, Kraus ES (December 2000). "Pure red cell aplasia caused by Parvovirus B19 infection in solid organ transplant recipients: a case report and review of literature". Clinical Transplantation. 14 (6): 586–91. doi:10.1034/j.1399-0012.2000.140612.x. PMID 11127313.
- ↑ Kwong YL, Wong KF (1998). "Association of pure red cell aplasia with T large granular lymphocyte leukaemia". J. Clin. Pathol. 51 (9): 672–5. doi:10.1136/jcp.51.9.672. PMC 500904. PMID 9930071.
- ↑ Miller AC, Rashid RM (2008). "Three episodes of acquired pure red cell aplasia restricted to pregnancy". Journal of Perinatal Medicine. 36 (3): 270–1. doi:10.1515/JPM.2008.041. PMID 18576941.
- ↑ Petrochko C (2009). "FDA Strengthens Warning on Transplant Drug." Archived 16 August 2018 at the Wayback Machine Medpage Today. 14 August 2009. Accessed 19 August 2009.
- ↑ Macdougall, IC (November 2007). "Epoetin-induced pure red cell aplasia: diagnosis and treatment". Current Opinion in Nephrology and Hypertension. 16 (6): 585–8. doi:10.1097/MNH.0b013e3282f0c4bf. PMID 18089975.
- ↑ Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): 105650
- ↑ Means, Robert T. (24 November 2016). "Pure red cell aplasia". Blood. 128 (21): 2504–2509. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-05-717140. Archived from the original on 18 August 2022. Retrieved 28 December 2022.
- ↑ Sawada K, Hirokawa M, Fujishima N, et al. (August 2007). "Long-term outcome of patients with acquired primary idiopathic pure red cell aplasia receiving cyclosporine A. A nationwide cohort study in Japan for the PRCA Collaborative Study Group". Haematologica. 92 (8): 1021–8. doi:10.3324/haematol.11192. PMID 17640861.
- ↑ Sawada K, Fujishima N, Hirokawa M (August 2008). "Acquired pure red cell aplasia: updated review of treatment". Br. J. Haematol. 142 (4): 505–14. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2008.07216.x. PMC 2592349. PMID 18510682.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
- Pages with script errors
- Webarchive template wayback links
- Use dmy dates from June 2020
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from November 2010
- Articles with unsourced statements from April 2014
- Articles with unsourced statements from April 2017
- Aplastic anemias