Pramocaine
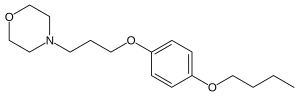 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Analpram, Fleet Pain-Relief, Itch-X, Preparation H, others |
| Other names | Pramoxine, pramoxine HCI |
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Main uses | Pain, itching[1][2] |
| Side effects | Burning at the site of application[1] |
| Routes of use | Topical, rectal, Vaginal |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682429 |
| Legal | |
| Legal status |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H27NO3 |
| Molar mass | 293.407 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Pramocaine, also known as pramoxine, is a medication used to improve pain and itching such as occurs in hemorrhoids or insect bites.[1][2] It is applied to the skin.[1] There are versions that come mixed with corticosteroids.[1]
Common side effects include burning at the site of application.[1] Other side effects may include allergic reactions, though it is generally safe even if someone has reactions to other local anesthetics.[1] It works by stabilizing the cell membrane of neurons.[1]
Pramocaine was described in 1953.[3] It is available over the counter.[1] In the United States a bottle costs about 5 USD as of 2021.[4]
Medical use
Topical anesthetics are used to relieve pain and itching caused by conditions such as sunburn or other minor burns, insect bites or stings, poison ivy, poison oak, poison sumac, and minor cuts and scratches.[5] The popular itch creams Gold Bond and some forms of calamine lotion use pramocaine hydrochloride to numb sensitive skin, as does the pain relief variant of Neosporin and some formulations of Sarna. The hydrochloride salt form of pramocaine is water-soluble.
Pramocaine is a common component of over the counter hemorrhoid preparations.
History
During research and development, pramocaine hydrochloride stood out among a series of alkoxy aryl alkamine ethers as an especially good topical local anesthetic agent.[3]
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 "Pramoxine Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on March 4, 2021. Retrieved October 29, 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 BNF 81: March-September 2021. BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. 2021. p. 103. ISBN 978-0857114105.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 SCHMIDT, JL; BLOCKUS, LE; RICHARDS, RK (November 1953). "The pharmacology of pramoxine hydrochloride: a new topical local anesthetic". Current researches in anesthesia & analgesia. 32 (6:1): 418–25. PMID 13107298.
- ↑ "Compare Pramoxine Hcl Prices - GoodRx". GoodRx. Retrieved October 29, 2021.
- ↑ "Pramoxine". MedlinePlus Drug Information. National Library of Medicine. September 25, 2013. Archived from the original on April 20, 2015. Retrieved October 9, 2013.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|
|---|
- Pages using duplicate arguments in template calls
- Use mdy dates from October 2013
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Chemical articles without CAS registry number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without UNII source
- Chemicals using indexlabels
- Drugs missing an ATC code
- Drugboxes which contain changes to verified fields
- Drugboxes which contain changes to watched fields
- Local anesthetics
- Morpholines
- Phenol ethers
- RTT