Paromomycin
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Catenulin, Aminosidine, others[1] |
| Other names | monomycin, aminosidine[2] |
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Aminoglycoside[3] |
| Main uses | Amebiasis, giardiasis, leishmaniasis, tapeworm infection[3] |
| Side effects | Loss of appetite, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea[3] |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | By mouth, intramuscular, topical[3] |
| Defined daily dose | 3 gram[4] |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a601098 |
| Legal | |
| License data |
|
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Bioavailability | Poorly absorbed in the GI tract |
| Metabolism | Not available |
| Excretion | Fecal |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H47N5O18S |
| Molar mass | 713.71 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Paromomycin is an antimicrobial used to treat a number of parasitic infections including amebiasis, giardiasis, leishmaniasis, and tapeworm infection.[3] It is a first-line treatment for amebiasis or giardiasis during pregnancy.[3] Otherwise it is generally a second line treatment option.[3] It is used by mouth, applied to the skin, or by injection into a muscle.[3]
Common side effects when taken by mouth include loss of appetite, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.[3] When applied to the skin side effects include itchiness, redness, and blisters.[3] When given by injection there may be fever, liver problems, or hearing loss.[3] Use during breastfeeding appears to be safe.[5] Paromomycin is in the aminoglycoside family of medications and causes microbe death by stopping the creation of bacterial proteins.[3]
Paromomycin was discovered in the 1950s from a type of streptomyces and came into medical use in 1960.[1][5] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[6] Paromomycin is available as a generic medication.[7] In India the injectable form is about 4.19 to 8.38 pounds for a course of treatment as of 2007.[5] In the United States a typical course of treatment is more than US$200 as of 2015.[7]
Medical uses
It is an antimicrobial used to treat intestinal parasitic infections such as cryptosporidiosis[8] and amoebiasis,[9] and other diseases such as leishmaniasis.[10] Paromomycin was demonstrated to be effective against cutaneous leishmaniasis in clinical studies in the USSR in the 1960s, and in trials with visceral leishmaniasis in the early 1990s.[2]
The route of administration is intramuscular injection and capsule. Paromomycin topical cream with or without gentamicin is an effective treatment for ulcerative cutaneous leishmaniasis, according to the results of a phase-3, randomized, double-blind, parallel group–controlled trial.[11]
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
The medication is poorly absorbed.[12] The effect it may have on the baby is still unknown.[13]
There is limited data regarding the safety of taking paromomycin while breastfeeding but because the drug is poorly absorbed minimal amounts of drug will be secreted in breastmilk.[14]
HIV/AIDS
There is limited evidence that paromomycin can be used in persons coinfected with HIV and Cryptosporidium. A few small trials have showed a reduction in oocyst shedding after treatment with paromomycin.[15]
Dosage
The defined daily dose is 3 gram (by mouth).[4]
Side effects
The most common side effects associated with paromomycin sulfate are abdominal cramps, diarrhea, heartburn, nausea, and vomiting. Long-term use of paromomycin increases the risk for bacterial or fungal infection. Signs of overgrowth include white patches in the oral cavities. Other less common adverse events include myasthenia gravis, kidney damage, enterocolitis, malabsorption syndrome, eosinophilia, headache, hearing loss, ringing in the ear, itching, severe dizziness, and pancreatitis.[16]
Interactions
Paromomycin belongs to the aminoglycoside drug class and therefore are toxic to the kidneys and to ears. These toxicities are additive and are more likely to occur when used with other drugs that cause ear and kidney toxicity.[17] Concurrent use of foscarnet increases the risk of kidney toxicity.[18] Concurrent use of colistimethate and paromomycin can cause a dangerous slowing of breathing known as respiratory depression, and should be done with extreme caution if necessary.[18] When used with systemic antibiotics such as paromomycin, the cholera vaccine can cause an immune response.[18] Use with strong diuretics, which can also harm hearing, should be avoided.[19] Paromomycin may have dangerous reactions when used with the paralytic succinylcholine by increasing its neuromuscular effects.[20]
There are no known food or drink interactions with paromomycin.[18]
Mechanism
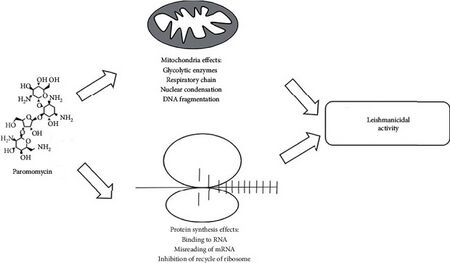
Paromomycin is a protein synthesis inhibitor in nonresistant cells by binding to 16S ribosomal RNA.[21] This broad-spectrum antibiotic soluble in water, is very similar in action to neomycin. Antimicrobial activity of paromomycin against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus has been shown.[22] Paromomycin works as an antibiotic by increasing the error rate in ribosomal translation. Paromomcyin binds to a RNA loop, where residues A1492 and A1493 are usually stacked, and expels these two residues. These two residues are involved in detection of correct Watson-Crick pairing between the codon and anti codon. When correct interactions are achieved, the binding provides energy to expel the two residues. Paromocyin binding provides enough energy for residue expulsion and thus results in the ribosome incorporating the incorrect amino acid into the nascent peptide chain.[23]
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
GI absorption is poor. Any obstructions or factors which impair GI motility may increase the absorption of the drug from the digestive tract. In addition, any structural damage, such as lesions or ulcerations, will tend to increase drug absorption.[24]
For intramuscular (IM) injection, the absorption is rapid. Paromomycin will reach peak plasma concentration within one hour following IM injection.[3] The in-vitro and in-vivo activities parallel those of neomycin.[25]
Distribution
Information not available.[25]
Elimination
Almost 100% of the oral dose is eliminated unchanged via feces. Any absorbed drug will be excreted in urine.[26]
History
Paromomycin was discovered in the 1950s amongst the secondary metabolites of a variety of Streptomyces then known as Streptomyces krestomuceticus, now known as Streptomyces rimosus. It came into medical use in 1960.[1][5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Publishing, William Andrew (2013). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia, 3rd Edition (3 ed.). Elsevier. p. 21p. ISBN 9780815518563. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Neal RA, Murphy AG, Olliaro P, Croft SL (1994). "Aminosidine ointments for the treatment of experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis". Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 88 (2): 223–5. doi:10.1016/0035-9203(94)90307-7. PMID 8036682.
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 "Paromomycin Sulfate". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 17 November 2016. Retrieved 3 December 2016.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "WHOCC - ATC/DDD Index". www.whocc.no. Archived from the original on 6 August 2020. Retrieved 21 September 2020.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Davidson RN, den Boer M, Ritmeijer K (2008). "Paromomycin". Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 103 (7): 653–60. doi:10.1016/j.trstmh.2008.09.008. PMID 18947845.
- ↑ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Hamilton, Richart (2015). Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2015 Deluxe Lab-Coat Edition. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 54. ISBN 9781284057560.
- ↑ Sweetman S, ed. (2002). Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference (33rd ed.). London: Pharmaceutical Press. ISBN 978-0-85369-499-1.
- ↑ "paromomycin" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ↑ Sundar S, Jha TK, Thakur CP, Sinha PK, Bhattacharya SK (2007). "Injectable paromomycin for visceral leishmaniasis in India". N. Engl. J. Med. 356 (25): 2571–81. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa066536. PMID 17582067.
- ↑ Ben Salah A, Ben Messaoud N, Guedri E, Zaatour A, Ben Alaya N, Bettaieb J, Gharbi A, Belhadj Hamida N, et al. (2013). "Topical Paromomycin with or without Gentamicin for Cutaneous Leishmaniasis". N. Engl. J. Med. 368 (6): 524–32. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1202657. PMID 23388004.
- ↑ Sweet, Richard L.; Gibbs, Ronald S. (2009). Infectious Diseases of the Female Genital Tract. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 364. ISBN 9780781778152. Archived from the original on 7 November 2016.
- ↑ Handbook of Antimicrobial Therapy. New Rochelle, New York: The Medical Letter Inc. 2015. p. 468. ISBN 978-0-9815278-8-8.
- ↑ "Paromomycin Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 10 November 2016. Retrieved 10 November 2016.
- ↑ Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett (2015). Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders. p. 3181. ISBN 978-1-4557-4801-3.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ "paromomycin oral : Uses, Side Effects, Interactions, Pictures, Warnings & Dosing - WebMD". WebMD. Archived from the original on 10 November 2016. Retrieved 10 November 2016.
- ↑ Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases: Edition 8. ISBN 978-1455748013.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 18.3 "Micromedex". Archived from the original on 18 August 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2022.
- ↑ Grayson, M. Lindsay, ed. (2012). Kucers' the use of antibiotics a clinical review of antibacterial, antifungal, antiparasitic and antiviral drugs (6th ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. p. 2144. ISBN 9781444147520. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017.
- ↑ Drug Therapy in Nursing. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2009. ISBN 978-1605472706.
- ↑ Vicens Q, Westhof E (2001). "Crystal Structure of Paromomycin Docked into the Eubacterial Ribosomal Decoding A Site". Structure. 9 (8): 647–58. doi:10.1016/S0969-2126(01)00629-3. PMID 11587639.
- ↑ "Paromomycin" (PDF). Toku-E. 12 January 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 April 2014. Retrieved 11 June 2012.
- ↑ Voet D, Voet J, 2011, Biochemistry, pp 1397
- ↑ Caraco Pharmaceutical Laboratories. Paromomycin sulfate capsules, USP prescribing information. Detroit, MI; 1997 Mar.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 DrugBank, ed. (17 August 2016). "Paromomycin". DrugBank. Archived from the original on 10 November 2016.
- ↑ Product Information: Humatin(R), paromomycin sulfate capsules. Parke-Davis, Division of Warner-Lambert Company, Morris Plains, NJ, 1999
External links
| Identifiers: |
|
|---|
- "Paromomycin". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 12 January 2020. Retrieved 12 January 2020.
- Pages using duplicate arguments in template calls
- CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list
- Use dmy dates from January 2020
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Chemical articles without CAS registry number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs missing an ATC code
- Drugboxes which contain changes to verified fields
- Articles with changed EBI identifier
- Aminoglycoside antibiotics
- Antiprotozoal agents
- Orphan drugs
- World Health Organization essential medicines
- RTT