Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis
| Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica of Bazex; Acrokeratosis neoplastica[1] | |
 | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Causes | Unknown[2] |
| Frequency | Rare, white males[2] |
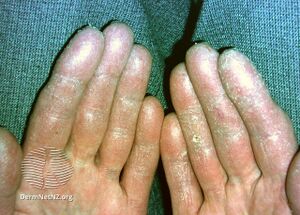
Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis, also known as Bazex syndrome, is a skin sign associated with cancer.[2] It is characterized by psoriasiform changes of hands, feet, ears, and nose, with involvement of the nails and periungual tissues being characteristic and indistinguishable from psoriatic nails. The condition is associated with carcinomas of the upper aerodigestive tract.[3]: 665
It is rare, and seen most frequently in white males.[2] A case was first reported by Henri Gougerot and C. Grupper in 1922.[4][5] Andre Bazex described it as a paraneoplastic syndrome in 1965.[4][6]
Signs and symptoms
-
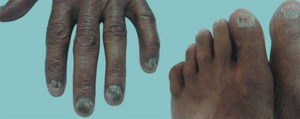
Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis
-
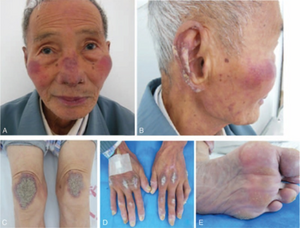
a) Dark red, infiltrative, desquamative plaques on nose/cheeks b) dark red, infiltrative plaques with scales on auricle c) confluent erythema on knees d) infiltrative erythematous plaques with scales ; all fingernails were yellow-brown/thickened e) both plantar pedis were discolored/hyperkeratotic
-
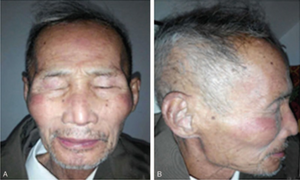
a-b) After treatment with gefinitib
-
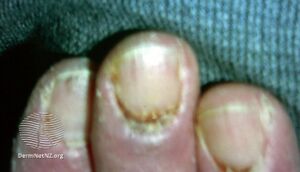
Dystrophic nails in a patient with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
See also
- List of skin conditions associated with internal cancer
- List of cutaneous conditions associated with increased risk of nonmelanoma skin cancer
References
- ↑ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Pulickal, Joel K.; Kaliyadan, Feroze (2023). "Acrokeratosis Paraneoplastica". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. PMID 29083711. Archived from the original on 2022-12-27. Retrieved 2023-08-08.
- ↑ Freedberg, et al. (2003). Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-138076-0.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Chiesa-Fuxench, Zelma C.; Ramírez, Liliana; Sánchez, Néstor P. (2011). "Cutaneous manifestations of internal malignancy and paraneoplastic syndromes". In Sánchez, Néstor P. (ed.). Atlas of Dermatology in Internal Medicine. New York: Springer. p. 66. ISBN 978-1-4614-0687-7. Archived from the original on 2023-08-05. Retrieved 2023-08-04.
- ↑ Gougerot, H. and Grupper, C., (1922). Dermatose érythémato-squameuse avec hyperkératose palmoplantaire, porectasies digitales et cancer de la langue latent. Paris Med, 43, pp.234-237
- ↑ Bazex, A.; Griffiths, A. (September 1980). "Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica--a new cutaneous marker of malignancy". The British Journal of Dermatology. 103 (3): 301–306. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1980.tb07248.x. ISSN 0007-0963. PMID 7000146. Archived from the original on 2023-08-05. Retrieved 2023-08-04.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |