Paintball marker
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2009) |

A paintball marker, also known as a paintball gun, paint gun, or simply marker, is an air gun used in the shooting sport of paintball, and the main piece of paintball equipment. Paintball markers use compressed gas, such as carbon dioxide (CO2) or compressed air (HPA), to propel dye-filled gel capsules called paintballs through the barrel and quickly strike a target. The term "marker" is derived from its original use as a tool for forestry personnel to mark trees and ranchers to mark wandering cattle.[1][2]
The muzzle velocity of paintball markers is approximately 90 m/s (300 ft/s); most paintball fields restrict speed to 280–300 ft/s,[3] and small indoor fields may further restrict it down to 250 ft/s.[4] While greater muzzle velocity is possible, it has been ruled unsafe for use on most commercial paintball fields.[5]
Marker types
Paintball markers fall into two main categories in terms of mechanism – mechanical and solenoid driven electropneumatic.[6]
Mechanically operated
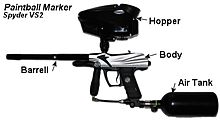
Mechanically operated paintball markers operate using solely mechanical means, and as such do not use electro-pneumatic solenoids controlled by an electronic board to fire.
Electropneumatically operated

In electromagnetic designs, the trigger, instead of being mechanically linked to the action of the marker, simply activates an electronic micro-switch (or more recently, a magnetic or optical sensor). That information is passed through control circuitry to a computer-controlled solenoid valve which can open and close very quickly and precisely, allowing gas to move into or out of various pressure chambers in the marker to move the bolt and fire the paintball.[citation needed]
Marker body

Most of the marker's functions and aesthetic features are contained in its body, which contains the main components of the firing mechanism: the trigger frame, bolt and valve. Most paintball marker bodies are constructed from aluminium to reduce the marker's weight, and feature custom milling and color anodizing.
Loaders
Loaders, commonly known as hoppers, hold paintballs for the marker to fire. The main types are gravity feed, agitating and force-feed. Stick feeds are also used to hold paintballs, although they are not considered to be "hoppers".
While agitating and force-feed hoppers facilitate a higher rate of fire, they are subject to battery failure, as well as degradation if they come into contact with moisture. Such hoppers which are not fitted with photoreceptors are prone to problems with ball breaks. When a paintball leaks paint into the hopper from a break in the hopper, the gelatin shells of the paintballs can deteriorate, causing them to stick together as well as jam in the barrel.
Propellant system

The tank holds compressed gas, which is used to propel the paintballs through the marker barrel. The tank is usually filled with carbon dioxide or compressed air. High Pressure Air (HPA) is also known as "nitrogen", as air is 78% nitrogen, or because these systems can be filled with industrial nitrogen. Due to the instabilities of carbon dioxide, HPA tanks are required for consistent velocity. Other propulsion methods include the combustion of small quantities of propane or electromechanically operated spring-plunger combinations similar to that used in an airsoft gun.
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a propellant used in paintball, especially in inexpensive markers. It is usually available in a 12 gram powerlet, mainly used in stock paintball and in paintball pistols, or a tank. The capacity of a carbon dioxide tank is measured in ounces of liquid and it is filled with liquid CO2, at room temperatures the vapour pressure is about 5,500 kilopascals (800 psi).
The CO2 liquid must vaporize into a gas before it can be used. This causes problems such as inconsistent velocity. Cold weather can cause problems with this system, reducing the vapour pressure and increasing the chance for liquefied gas to be drawn into the marker. The low-temperature liquid can damage the internal mechanisms. Anti-siphon tanks have a tube inside the cylinder, which is bent to prevent liquid carbon dioxide from being drawn into the gun.
On the other hand, a number of paintguns were designed with specific valves to operate on liquid CO2, including some early Tippmann models and the Mega-Z from Montneel – thus solving the problem caused by phase changes.[7] Siphon equipped CO2 tanks are easily identified by the clunking sound their weight makes when the tank is tipped.
After many years of use, Carbon dioxide has almost been universally replaced with High Pressure Air systems (see below)
High-pressure air
High-pressure air, compressed air or nitrogen, is stored in the tank at a very high pressure, typically 21,000–31,000 kPa (3,000–4,500 psi). Output is controlled with an attached regulator, regulating the pressure between 1,700 kPa (250 psi) and 5,900 kPa (860 psi), depending on the type of tank. The advantage of using regulated HPA over carbon dioxide (CO2) is pressure consistency and temperature stability where CO2 reacts to temperature changes causing inaccuracy and freezing during heavy use. The most popular tank size is 1,100 cubic centimetres (67 cu in) at 31,000 kPa (4,500 psi) providing 800–1100 shots.
HPA tanks are more expensive because they must accommodate very high pressures. They are manufactured as steel, aluminium or wrapped carbon fiber tanks, the latter being the most expensive and most lightweight. Most players with electronic markers use HPA because if CO2 is used, the marker's electronic Solenoid valve can be damaged if liquid CO2 enters it.
Users are warned not put any type of lubricant in the 'fill nipple' port of a HPA tank, as petroleum may burn when subjected to highly compressed air, causing an explosion, like in a diesel engine.
Propane
A far less common propellant is propane, featured only in the Tippmann C3. Rather than simply releasing gas as in high-pressure air and CO2 markers, the propane is ignited in a combustion chamber, increasing pressure and opening a valve that lets the expanding gas propel the paintball. There are a number of advantages, mainly shots per tank, ranging from 30,000 to 50,000 shots (depending on the size of the tank) as opposed to the typical 1000 to 2000 shots that are standard with High Pressure Air or CO2 tanks. Another advantage includes availability, as propane is readily available in many stores, whereas CO2 and High Pressure Air are most commonly filled from compressors or pre-filled tanks, which are less common. It can also be considered safer too, because a typical high-pressure air tank holds air at 21,000–31,000 kPa (3,000–4,500 psi), and a CO2 tank at 5,500 kPa (800 psi), but propane is stored at 2,100 kPa (300 psi).
However, propane produces heat, which (when firing for an extended period at high rates of fire) can cause burns if improperly handled. It can also be a fire hazard: the Tippmann C3 releases small amounts of flames from the vents in the combustion chamber and out of the barrel when firing. If a marker develops a leak from improper maintenance, it could cause a fire.
Gas regulation
Marker systems have a variety of regulator configurations, ranging from completely unregulated to high-end systems using four regulators, some with multiple stages.
The regulator system affects both the accuracy and the firing velocity. Carbon dioxide regulators must also prevent liquid gas from entering the marker and expanding, causing a dangerous surge in velocity. Regulators used with carbon dioxide often sacrifice throughput and accuracy to ensure the marker operates safely. HPA-only regulators tend to have an extremely high throughput and are designed to ensure uniform pressure between shots to ensure marker accuracy at high rates of fire.
Tournament markers usually are equipped with two regulators, and another on the tank, each with a specific function. The tank regulator decreases the pressure of air from 21,000–31,000 kPa (3,000–4,500 psi) to 4,100–5,500 kPa (590–800 psi). A second regulator is used to further reduce this pressure to near the firing pressure. This reduction allows for greater consistency. The air is then supplied to a regulator on the marker body, where the final output pressure is selected. This can be between 5,500 kPa (800 psi) for entirely unregulated carbon dioxide markers to approximately 1,000 kPa (150 psi) for extremely low pressure markers. After the firing pressure is decided, tournament-oriented markers use another regulator to supply gas to a separate pneumatic system, to power any other functions, such as bolt movement. This is an extremely low volume, extremely low pressure regulator, usually under 690 kPa (100 psi).
Barrels
The marker's barrel directs the paintball and controls the release of the gas pocket behind it. Several different bore sizes are made, to fit different sizes of paintball, and there are many lengths and styles. Most modern paintball markers have barrels that screw into the front receiver. Older types slide the barrel on and screw it in place. Barrel threading must be matched to that of the marker. Common threads are: Angel, Autococker, Impulse/Ion, Shocker, Spyder, A-5, and 98 Custom.
Barrels are manufactured in three basic configurations: one piece, two piece and three piece. A barrel with interchangeable bores, with either two or three piece, is called a barrel system, rather than a two-piece or three-piece barrel. This prevents confusion, as many two-piece barrel systems do not use an interchangeable bore system.
Length
Typical barrels are between 76 mm (3.0 in) and 530 mm (21 in) long, although custom barrels may be up to 910 mm (36 in) long. Longer barrels are usually quieter than shorter barrels, allowing excess gas to escape slowly. Players usually choose a barrel length between 300 mm (12 in) and 410 mm (16 in), as a compromise between accuracy, range, and portability. Many players favor longer barrels as they permit them to push aside the large inflatable bunkers commonly used in paintball tournaments while still staying behind cover.
Bore
The bore is the interior diameter of the barrel. The bore must properly match the type of paint being fired, the most critical aspect of a barrel. A mismatched selection will result in velocity variations, which causes difficulty in maintaining a close match to field velocity limits and in extreme cases it can affect accuracy. Two and three-piece barrels let the barrel bore be matched to the paint diameter without needing new barrels. Correct matching is especially important in closed-bolt markers that lack ball detents because the ball will roll down, and potentially out of, the barrel. This results in either a dry fire in the event that the ball fell out of the barrel, or a lower velocity shot.
Firing and trigger modes
Since the advent of semi-automatic markers in the early 1990s, both insurance and competitive rules have specified that markers must be semi-automatic only; only one paintball may be fired per trigger pull. While this was a perfectly clear definition when markers were all based on mechanical and pneumatic designs, the introduction of electronically controlled markers in the late 1990s meant that technology had allowed for easy circumvention of this rule. Electronic markers are often controlled by a programmable microcontroller, on which any software might be installed. For example, software may allow the marker to fire more than once per trigger pull, called shot ramping.
Velocity ramping is an electronic firing mode where a consistent, fully automatic firing rate will be triggered as long as the player maintains a low rate of trigger pulls per second.
Pump action
Pump action markers must be manually re-cocked after every shot, much like a pump action shotgun.
Some pump action paintball markers such as the Sterling and many Nelson-based markers like the PMI Tracer and CCI Phantom offer slam-fire action, also known as an auto-trigger, which occurs when the trigger is squeezed and the marker fires with every ensuing recocking of the marker via the pump.[8]
Semi-automatic
A paintball marker that reloads itself with the next load from the magazine after one shot is called semi-automatic. Semi-automatic markers use a variety of designs to automatically cycle a bolt and load a new paintball into the chamber with each trigger pull. This frees the player from manually pumping the marker, allowing him or her to increase the rate-of-fire. Semi-automatic markers may have a mechanical trigger or an electronic trigger frames. An electronic trigger frame typically has a lighter trigger pull and less space between the trigger and the pressure point, allowing the player to shoot at higher rates of fire. Such frames are commonly available as upgrades to fully mechanical markers, or are integrated into the design of electropneumatic markers.
With the popularity of electronic trigger frames allowing players with such frames to achieve very high rates of fire, tournament leagues began placing limits on the maximum rate of fire of electronic markers used in their events. Manufacturers also often place their own limit on the maximum rate of fire the marker will support, to ensure reliable cycling. Such limits are called caps; tournament caps generally range from 12 to 15 balls per second, while mechanical caps vary according to the design of the marker and the firmware used. If such a cap is enforced, the marker will prevent a ball being fired less than a certain time after the last one, the time delay resulting in the desired maximum rate of fire. A trigger pull occurring before this time has elapsed will be "queued", and the marker will fire again after the delay, but most markers will limit the number of shots that can be "queued" to avoid the marker firing a number of shots after the trigger was last pulled, a so-called "runaway marker".
Fully automatic
Fully automatic markers fire continually when the trigger is pressed. The Tippmann SMG 60 was the first fully automatic paintball marker. Most electropneumatic paintball guns feature this mode. The fully automatic mode can be added to any electropneumatic marker by installing a customized logic board, or buying a completely new electronic trigger frame.
Similarly, markers can be equipped with burst modes. Ranging from between three and nine shot bursts, these modes allow the player to take accurate shots with a quick pull of the trigger, using more than one ball to increase their chances of hitting the target. In burst mode, the rate of fire can equal that of the fully automatic mode, which is useful in close range situations.
Ramping
Ramping is a feature in some electronic markers that automatically changes the mode of fire from semi-automatic to fully automatic under certain conditions;[9] normally upon a certain number of rapid shots being fired or a minimum rate of fire achieved and sustained. Ramping can be difficult to detect because ramping modes may be inconsistently used. Ramping modes can further be hidden in the software, ensuring that a marker will fire in a legal, semi-auto mode when being tested, but an illegal ramping mode may be engaged by the player under certain conditions.
Some leagues allow a specific ramping mode to prevent problems with enforcement, and to provide a more level playing field with regard to technical skill and marker quality (and price). The rule specifies a minimum time between shots resulting in a maximum rate of fire, and that a certain number of semi-automatic shots must be fired before ramping may engage. With players consistently using a standard ramping mode, players using a different mode are more easily detected.
The rate of fire is enforced by a "PACT" timer, a standard firearms timing device that measures the time between shots. The following are common league-specific ramping modes, preset in the marker's firmware:
- PSP Ramping – Ramping begins after 3 shots; the player must maintain at least one pull per second to achieve/maintain ramping. The marker may then fire up to (and no more than) three balls per trigger pull in a "burst" fashion. Rate of fire cannot exceed 12.5 balls per second (as of 2011), even if the player pulls the trigger 5 times per second or faster.
- NXL Ramping – Ramping begins after three shots; the player needs only to hold down the trigger to maintain fully automatic fire. Rate of fire cannot exceed 15 balls per second. Firing must cease immediately upon the trigger being released.
- Millennium Ramping – Ramping begins after six trigger pulls at a minimum rate of 7.5 pulls per second; the player must maintain 7.5 trigger pulls per second to maintain ramping. Rate of fire cannot exceed 10.5 balls per second. When the player ceases to pull the trigger during ramping, no more than one extra ball may be fired after the last pull.
Safety
When paintballs hit an object at high speed they have the potential to cause damage; a paintball colliding with human skin, even protected by cloth, may cause bruising or further tissue damage. However, the damage depends on the paintball's velocity, distance, its impact angle, whether it breaks, and which part of the body it hits. Because of the potential for serious soft tissue damage, paintball players must wear a quality paintball mask to protect their eyes, mouth, and ears when barrel blocking devices are not preventing paintball markers from firing. A good paintball mask is one which has an anti-fog, dual-pane, scratch less, and UV coated lens. Before making a buying decision, the mask must be checked for its glasses comparability, internal space, and ventilation.
Paintball guns have been documented to have been used by riot police against protesters globally, including against those partaking in the Black Lives Matter protests of 2020.[10] Among documented cases, protesters in Iran, Chile and the United States have suffered catastrophic eye injuries as a result of being shot directly in the face at close range by paintball guns.[11][12][13]
See also
References
- ^ "SPLAT!; South Sound Plays Host to Some of the Best in the World of Paintball". News Tribune, The. Archived from the original on July 15, 2011. Retrieved September 15, 2009.
- ^ Gaines, Charles (December 6, 2004). "Who Thought This Was A Good Idea?". CNN. Archived from the original on June 4, 2011. Retrieved 5 March 2010.
- ^ paintball, David Muhlestein David Muhlestein is a; Mid-1990s, Woodsball Enthusiast Who Has Been Playing Since the; Equipment, Has Extensive Knowledge of Paintball. "Exactly How Fast Does a Paintball Gun Fire?". LiveAbout. Retrieved 2019-08-03.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Paintball Safety Rules". LVL UP Sports Paintball Park. Retrieved 2019-08-03.
- ^ "EMR PAINTBALL PARK | Scenario Paintball | Recball | Tournament Paintball | Castle Conquest | Paintball Safety". Emrpaintball.com. Archived from the original on December 19, 2005. Retrieved 2009-07-13.
- ^ "Solenoid Theory [ZDSPB Tech]".
- ^ "WARPIG - World And Regional Paintball Information Guide: antisiphon". WARPIG.com. Retrieved 2013-11-09.
- ^ "Sterling STP Bronze manual" (PDF). Retrieved 2013-11-09.
- ^ "A look at Ramping | Snipers den". Archived from the original on 2014-10-31. Retrieved 2014-10-31.
- ^ Gross, Jenny (2020-06-12). "The Latest Police Tool in Protests: Paintball Guns". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2023-09-30.
- ^ "Chilean youth injured by paintball wants ban on use of weapon - UPI.com". UPI. Retrieved 2023-09-30.
- ^ "Man shot in eye with paintball gun at fly protest". BBC News. 2017-07-25. Retrieved 2023-09-30.
- ^ Ghajar, Aida; Shams, Omid (2023-01-19). "Blinding as a Weapon of War". IranWire. Retrieved 2023-09-30.
External links
- CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list
- Articles with short description
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Articles needing additional references from April 2009
- All articles needing additional references
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from December 2023
- Paintball markers
- Pneumatic weapons
- Air guns
- Rifles
- Recreational weapons