Portal:Biology
Introduction


Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary information encoded in genes, which can be transmitted to future generations. Another major theme is evolution, which explains the unity and diversity of life. Energy processing is also important to life as it allows organisms to move, grow, and reproduce. Finally, all organisms are able to regulate their own internal environments.
Biologists are able to study life at multiple levels of organization, from the molecular biology of a cell to the anatomy and physiology of plants and animals, and evolution of populations. Hence, there are multiple subdisciplines within biology, each defined by the nature of their research questions and the tools that they use. Like other scientists, biologists use the scientific method to make observations, pose questions, generate hypotheses, perform experiments, and form conclusions about the world around them.
Life on Earth, which emerged more than 3.7 billion years ago, is immensely diverse. Biologists have sought to study and classify the various forms of life, from prokaryotic organisms such as archaea and bacteria to eukaryotic organisms such as protists, fungi, plants, and animals. These various organisms contribute to the biodiversity of an ecosystem, where they play specialized roles in the cycling of nutrients and energy through their biophysical environment. (Full article...)
Selected article -

Chromatophores are cells that produce color, of which many types are pigment-containing cells, or groups of cells, found in a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopods. Mammals and birds, in contrast, have a class of cells called melanocytes for coloration.
Chromatophores are largely responsible for generating skin and eye colour in ectothermic animals and are generated in the neural crest during embryonic development. Mature chromatophores are grouped into subclasses based on their colour under white light: xanthophores (yellow), erythrophores (red), iridophores (reflective / iridescent), leucophores (white), melanophores (black/brown), and cyanophores (blue). While most chromatophores contain pigments that absorb specific wavelengths of light, the color of leucophores and iridophores is produced by their respective scattering and optical interference properties. (Full article...)Selected picture -

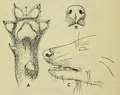
Chimaeras are cartilaginous fish in the order Chimaeriformes, known informally as ghost sharks, ratfish, spookfish, or rabbitfishes. They grow up to 150 cm (4.9 ft) in length, and have elongated, soft bodies, with a bulky head and a single gill-opening. For defense, most chimaeras have a venomous spine located in front of the dorsal fin. At one time a "diverse and abundant" group (based on the fossil record), their closest living relatives are sharks, though in evolutionary terms they branched off from sharks nearly 400 million years ago and have remained isolated ever since, typically confined to deep water.
Major topics
Selected biography -
Antonie Philips van Leeuwenhoek FRS (/ˈɑːntəni vɑːn ˈleɪvənhuːk, -hʊk/ AHN-tə-nee vahn LAY-vən-hook, -huuk; Dutch: [ˈɑntoːni vɑn ˈleːu.ə(n)ˌɦuk] ⓘ; 24 October 1632 – 26 August 1723) was a Dutch microbiologist and microscopist in the Golden Age of Dutch science and technology. A largely self-taught man in science, he is commonly known as "the Father of Microbiology", and one of the first microscopists and microbiologists. Van Leeuwenhoek is best known for his pioneering work in microscopy and for his contributions toward the establishment of microbiology as a scientific discipline.
Raised in Delft, Dutch Republic, Van Leeuwenhoek worked as a draper in his youth and founded his own shop in 1654. He became well-recognized in municipal politics and developed an interest in lensmaking. In the 1670s, he started to explore microbial life with his microscope. (Full article...)General images -
Did you know -

- ... that the p19 protein (dimer pictured) evolved in an arms race between plants and viruses?
- ...that there are about a million nephrons in a human kidney?
- ... that the semi-aquatic grasshopper Cornops aquaticum is being trialled in South Africa as a biological control agent for the invasive water hyacinth?
Things you can do
Related portals
Biology portals
Categories

Anatomy - Anthropology - Astrobiology - Biochemistry - Bioengineering - Bioinformatics - Biotechnology - Botany - Cell biology - Conservation biology - Developmental biology - Ecology - Environmental science - Evolutionary biology - Genetics - Mathematical biology - Medicine - Microbiology - Immunology - Molecular biology - Mycology - Neuroscience - Paleontology - Palynology Parasitology - Pharmacology -
Phylogenetics - Physiology - Systems biology - Taxonomy - Toxicology - Virology - ZoologyMore topics
WikiProjects

WikiProjects connected with biology:
A complete list of scientific WikiProjects can be found here. See also Wikispecies, a Wikimedia project dedicated to classification of biological species.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
- Pages using the Phonos extension
- Portals with triaged subpages from June 2018
- All portals with triaged subpages
- All portals
- Portals with no named maintainer
- Random portal component with 31–40 available image subpages
- Pages using Template:Post-nominals with customized linking
- Pages with Dutch IPA
- Pages including recorded pronunciations
- Random portal component with 2–5 available subpages
- Biology portals
- Biology