Nepafenac
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Nevanac, Ilevro, Amnac, others |
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | NSAID |
| Main uses | Pain and inflammation from cataract surgery[1] |
| Side effects | Irritation of the eye[1] |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of use | Eye drops |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a606007 |
| Legal | |
| License data | |
| Legal status |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
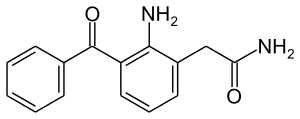
| Formula | C15H14N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 254.289 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Nepafenac, sold under the brand name Nevanac among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain and inflammation associated with cataract surgery.[1] It is used as an eye drop.[1]
Common side effects include irritation of the eye.[1] Other side effects may include keratitis and hyphema.[3] It works by inhibiting COX-1 and COX-2 and therefore decreasing prostaglandins.[3][1]
Nepafenac was approved for medical use in the United States in 2005 and Europe in 2007.[3][1] In the United Kingdom a bottle costs the NHS about £15 as of 2021.[4] In the United States this amount costs about 290 USD.[5]
Medical uses
Nepafenac is indicated for use in the treatment of pain and inflammation following cataract surgery.[6][7][8][9]
In the European Union nepafenac is also indicated for the reduction in the risk of postoperative macular edema associated with cataract surgery in people with diabetes.[9]
Dosage
It is used once to three times per day depending on the strength of the formulation.[1] It is started once day before the surgery and continued for 2 to 9 weeks.[1]
Side effects
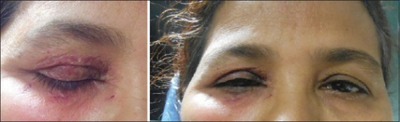
Side effects include headache; runny nose; pain or pressure in the face; nausea; vomiting; and dry, itchy, sticky eyes.[10] Serious side effects include red or bloody eyes; foreign body sensation in the eye; sensitivity to light; decreased visual acuity; seeing specks or spots; teary eyes; or eye discharge or crusting.[10]
Mechanism of action
Nepafenac is an NSAID, thought to be a prodrug of amfenac after conversion by ocular tissue hydrolases after penetration via the cornea.[7][8] Amfenac, like other NSAIDs, is thought to inhibit cyclooxygenase action.[7][8]
History
Nevanac
On February 25, 2005, Alcon filed a New Drug Application (NDA) with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for Nevanac 0.1%.[11] Results from the two trials referenced in the NDA (Phase 2/3 study C-02-53; Phase 3 study C-03-32) have not been published.[12] Study C-02-53 consisted of 228 patients across 10 centers in the United States.[13] Study C-03-32 consisted of 522 patients across 22 centers in the United States.[13] The efficacy results presented were confirmed in a study published in 2007.[14]
Nevanac was approved by the FDA on August 19, 2005, with application number 021–862.[15]
Ilevro
An NDA for Ilevro was filed on December 15, 2011.[16] In a one-month study, no new toxicities arose in the new formulation of nepafenac.[17] Safety and efficacy information was derived from the previous Nevanac application.[17] In June 2010, a confirmatory study began (Study C09055) consisting of over 2000 patients from 49 US sites and 37 European sites.[18][19] A second phase 3 trial (Study C11003) was conducted in a population of 1,342 patients at 37 sites across the United States which failed to demonstrate superiority over Nevanac in an altered dosing regimen.[18]
Ilevro was approved by the FDA on October 16, 2012, with application number 203–491.[20]
Society and culture
Cost
This medication has a cost in Canada of $4.40 (per ml) for 10 ml ilevro oph 0.1 % [21]
-
Nepafenac costs (US)
-
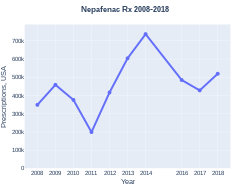
Nepafenac prescriptions (US)
Commercialization
Both Nevanac and Ilevro are manufactured and sold by Alcon, Inc.[7][8] Alcon is currently a division of Novartis International AG, which is primarily based out of Switzerland.[22] Alcon, Inc. also holds locations in both Switzerland and the United States.[23] The company has gone through several name changes, from Alcon Laboratories, Inc. to Alcon Universal, Ltd., to Alcon, Inc.[23]
Nevanac entered the market in 2005 as a product of Alcon, at the time a subsidiary of Nestlé.[24] On April 6, 2008, Novartis agreed to purchase approximately 74 million shares of Alcon from Nestlé at $143.18 per share.[24] On January 4, 2010, Novartis agreed to purchase all remaining shares of Alcon from Nestlé, totalling 156 million shares or 77% of the shares in the company.[24] At the time of the purchase, a proposal for a merger under Swiss merger law was given to the Alcon board of directors.[24] The merger was agreed upon on December 15, 2010, making Alcon "the second largest division within Novartis."[24] The merger was completed on April 8, 2011.[25]
Ilevro was launched by Alcon on January 21, 2013.[26] In 2014 and 2015, net sales by Alcon grew, contributed to in part by the increased volume in sales of Ilevro.[27][28][29] That financial year, Novartis reported $18 billion in total financial debt.[27] That figure has grown steadily since. In 2016, Novartis reported a total debt of $23.8 billion,[30] up from the $21.9 billion reported in 2015 [29] and the $20.4 billion reported in 2014.[28] As of May 2017, Novartis is estimated to be worth $193.2 billion.[31]
On January 27, 2016, Alcon was moved to become a branch of the Innovative Medicines Division at Novartis.[30] Early in 2016, Alcon formed agreements with both TrueVision and PowerVision, and acquired Transcend Medical.[30] As of January 2017, Novartis is weighing options for Alcon in the business structure.[30]
Alcon faced declining growth in 2016, having faced challenges in development and marketing of new products.[30]
Marketing
Novartis maintains a detailing unit geared toward health professionals consisting of over 3,000 employees within the United States and an additional 21,000 worldwide.[30] Novartis is also seeking to expand direct-to-consumer advertising and entrance into specialty product markets.[30] Novartis also notes the influence of position and preference on US Centers for Medicare & Medicaid formularies in expanding their market value.[30]
Nepafenac, Nevanac, and Ilevro are all absent from the 2016 Annual Report issued from Novartis.[30]
Intellectual property
There are currently[when?] seven U.S. patents filed that are directly associated with the modernized formulations of nepafenac, all stemming from Novartis.[32] There are three patents associated with Nevanac that are still[when?] active[33] and four associated with Ilevro.[34] The earliest patent related to the modern formulations of nepafenac was approved on June 11, 2002, after being filed in 1999, by Bahram Asgharian.[35] A patent was filed by Warren Wong, associated with Alcon, Inc. based out of Fort Worth, Texas, on December 2, 2005, for aqueous suspensions of nepafenac.[36] Another patent for a nepafenac-based drug was filed on May 8, 2006, by Geoffrey Owen, Amy Brooks, and Gustav Graff.[37] A patent was filed by Masood A. Chowhan and Huagang Chen on February 9, 2007, and approved on May 24, 2011,[38] followed closely by a patent filed by Warren Wong on September 23, 2010, and approved on December 6, 2011.[39] Masood A. Chowhan, Malay Ghosh, Bahram Asgharian, and Wesley Wehsin Han filed another patent on December 1, 2010, and approved on December 30, 2014.[40] The most recent[when?] patent was filed by Masood A. Chowhan, Malay Ghosh, Bahram Asgharian, and Wesley Weshin Han on November 12, 2014, and approved on May 30, 2017.[41] These patents are in effect until dates ranging between July 17, 2018, and March 31, 2032.[34]
Novartis also maintains patents on nepafenac in 26 countries outside the United States.[42]
A lawsuit was filed by Alcon on March 4, 2016, against Watson Laboratories in Delaware for the manufacture of a generic version of the 0.3% nepafenac formulation, Ilevro.[43] The complaint was amended on June 14, 2017.[44]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 "Nevanac". Archived from the original on 7 July 2020. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Nepafenac ophthalmic Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 6 June 2019. Archived from the original on 25 January 2021. Retrieved 13 September 2020.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Nepafenac Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 22 April 2016. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ↑ BNF 81: March-September 2021. BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. 2021. p. 1206. ISBN 978-0857114105.
- ↑ "Nevanac Prices, Coupons & Savings Tips - GoodRx". GoodRx. Archived from the original on 27 May 2020. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ↑ Nepafenac Monograph
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 "Nevanac- nepafenac suspension/ drops". DailyMed. 9 September 2019. Archived from the original on 6 July 2020. Retrieved 6 July 2020.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 "Ilevro- nepafenac suspension". DailyMed. 9 September 2019. Archived from the original on 7 July 2020. Retrieved 6 July 2020.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "Nevanac EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). Archived from the original on 7 July 2020. Retrieved 6 July 2020.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "Nepafenac Ophthalmic". MedlinePlus. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on November 7, 2017. Retrieved October 31, 2017.
- ↑ "Nevanac Approval Package" (PDF). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Archived (PDF) from the original on March 1, 2017. Retrieved October 31, 2017.
- ↑ Gaynes BI, Onyekwuluje A (June 2008). "Topical ophthalmic NSAIDs: a discussion with focus on nepafenac ophthalmic suspension". Clinical Ophthalmology. 2 (2): 355–68. doi:10.2147/opth.s1067. PMC 2693998. PMID 19668727.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "Nevanac Statistical Review" (PDF). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Archived (PDF) from the original on February 18, 2017. Retrieved October 31, 2017.
- ↑ Lane SS, Modi SS, Lehmann RP, Holland EJ (January 2007). "Nepafenac ophthalmic suspension 0.1% for the prevention and treatment of ocular inflammation associated with cataract surgery". Journal of Cataract and Refractive Surgery. 33 (1): 53–8. doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2006.08.043. PMID 17189793. S2CID 38881826.
- ↑ "Drug Approval Package: Nevanac (Nepafenac) Ophthalmic Suspension NDA #021862". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). January 6, 2005. Archived from the original on October 29, 2020. Retrieved October 27, 2017.
- ↑ "Ilevro Approval Package" (PDF). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Archived (PDF) from the original on March 1, 2017. Retrieved October 31, 2017.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 "203491 Pharmacology Review" (PDF). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Archived (PDF) from the original on March 1, 2017. Retrieved October 31, 2017.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 "Ilevro Statistical Review" (PDF). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Archived (PDF) from the original on February 28, 2017. Retrieved October 31, 2017.
- ↑ "Confirmatory Study Nepafenac 0.3%". ClinicalTrials.gov. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on November 7, 2017. Retrieved October 31, 2017.
- ↑ "Drug Approval Package: Nepafenac Ophthalmic Suspension, 0.3% NDA #203491". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). April 8, 2013. Archived from the original on April 3, 2021. Retrieved October 27, 2017.
- ↑ "Nepafenac (ilevro oph) Price Comparisons - Discounts, Cost & Coupons". PharmacyChecker.com. Archived from the original on 19 January 2021. Retrieved 5 April 2021.
- ↑ "About Us". Novartis. Archived from the original on September 1, 2017. Retrieved October 27, 2017.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 "Nevanac Administrative Documents and Correspondence" (PDF). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Archived (PDF) from the original on March 1, 2017. Retrieved October 27, 2017.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 24.2 24.3 24.4 "Alcon Annual Report 2010" (PDF). SEC EDGAR. United States Securities and Exchange Commission. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 10, 2017. Retrieved October 30, 2017.
- ↑ "Alcon Form 15". SEC EDGAR. United States Securities and Exchange Commission. Archived from the original on November 7, 2017. Retrieved October 30, 2017.
- ↑ "Alcon Launches ILEVRO™ (nepafenac ophthalmic suspension) 0.3%, a New Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug, for the Treatment of Pain and Inflammation Associated with Cataract Surgery". Alcon. Archived from the original on December 15, 2018. Retrieved October 30, 2017.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 "Form 20-F". SEC EDGAR. United States Securities and Exchange Commission. Archived from the original on December 15, 2018. Retrieved October 30, 2017.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 "Form 20-F". SEC EDGAR. United States Securities and Exchange Commission. Archived from the original on October 18, 2017. Retrieved October 30, 2017.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 "Form 20F". SEC EDGAR. United States Securities and Exchange Commission. Archived from the original on July 14, 2017. Retrieved October 30, 2017.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 30.2 30.3 30.4 30.5 30.6 30.7 30.8 "Form 20-F". SEC EDGAR. United States Securities and Exchange Commission. Archived from the original on May 8, 2017. Retrieved October 31, 2017.
- ↑ "Novartis on the Forbes Top Multinational Performers List". Forbes. Archived from the original on November 14, 2017. Retrieved October 31, 2017.
- ↑ "Nepafenac". U.S. Patents. PharmaCompass. Archived from the original on November 7, 2017. Retrieved October 30, 2017.
- ↑ "Generic Nevanac Availability". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on November 7, 2017. Retrieved October 31, 2017.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 "Generic Ilevro Availability". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on November 7, 2017. Retrieved October 31, 2017.
- ↑ "United States Patent Application: 6403609". United States Patent and Trademark Office. Archived from the original on November 7, 2017. Retrieved October 31, 2017.
- ↑ "United States Patent Application: 0060122277". United States Patent and Trademark Office. Archived from the original on August 29, 2021. Retrieved October 30, 2017.
- ↑ "United States Patent Application: 0060257487". United States Patent and Trademark Office. Archived from the original on August 29, 2021. Retrieved October 27, 2017.
- ↑ "United States Patent: 7947295". United States Patent and Trademark Office. Archived from the original on November 7, 2017. Retrieved October 31, 2017.
- ↑ "United States Patent: 8071648". United States Patent and Trademark Office. Archived from the original on August 29, 2021. Retrieved October 31, 2017.
- ↑ "United States Patent: 8921337". United States Patent and Trademark Office. Archived from the original on November 7, 2017. Retrieved October 31, 2017.
- ↑ "United States Patent: 9662398". United States Patent and Trademark Office. Archived from the original on November 7, 2017. Retrieved October 31, 2017.
- ↑ "Nepafenac - Generic Drug Details". DrugPatentWatch. thinkBiotech LLC. Archived from the original on November 7, 2017. Retrieved October 31, 2017.
- ↑ "Complaint". RPX Insight. Archived from the original on November 7, 2017. Retrieved October 31, 2017.
- ↑ "Amended Complaint". RPX Insight. Archived from the original on November 7, 2017. Retrieved October 31, 2017.
External links
| External sites: | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers: |
|
- Pages using duplicate arguments in template calls
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Chemical articles without CAS registry number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs missing an ATC code
- Drug has EMA link
- Drugboxes which contain changes to verified fields
- Drugboxes which contain changes to watched fields
- All articles with vague or ambiguous time
- Vague or ambiguous time from July 2020
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- Acetamides
- 2-Aminobenzophenones
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Novartis brands
- Prodrugs
- RTT