Migraine
| Migraine | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Woman with migraine headache | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
| Symptoms | Headaches, nausea, sensitivity to light, sensitivity to sound, sensitivity to smell[1][2] |
| Usual onset | Around puberty[1] |
| Duration | Recurrent, long term[1] |
| Causes | Environmental and genetic[3] |
| Risk factors | Family history, female[4][5] |
| Differential diagnosis | Subarachnoid hemorrhage, venous thrombosis, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, brain tumor, tension headache, sinusitis,[6] cluster headache[7] |
| Prevention | Metoprolol, valproate, topiramate[8][9] |
| Medication | Ibuprofen, paracetamol (acetaminophen), triptans, ergotamines[5][10] |
| Frequency | ~15%[11] |
A migraine is a primary headache disorder characterized by recurrent headaches that are moderate to severe.[1] Typically, the headaches affect one half of the head, are pulsating in nature, and last from a few hours to 3 days.[1] Associated symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light, sound, or smell.[2] The pain is generally made worse by physical activity.[12] Up to one-third of people affected have an aura: typically a short period of visual disturbance that signals that the headache will soon occur.[12] Occasionally, an aura can occur with little or no headache following it.[13]
Migraines are believed to be due to a mixture of environmental and genetic factors.[3] About two-thirds of cases run in families.[5] Changing hormone levels may also play a role, as migraines affect slightly more boys than girls before puberty and two to three times more women than men.[4][14] The risk of migraines usually decreases during pregnancy and after menopause.[4][15] The underlying mechanisms are not fully known.[15] They are, however, believed to involve the nerves and blood vessels of the brain.[5]
Initial recommended treatment is with simple pain medication such as ibuprofen and paracetamol (acetaminophen) for the headache, medication for the nausea, and the avoidance of triggers.[10] Specific medications such as triptans or ergotamines may be used in those for whom simple pain medications are not effective.[5] Caffeine may be added to the above.[16] A number of medications are useful to prevent attacks including metoprolol, valproate, and topiramate.[8][9]
Globally, approximately 15% of people are affected by migraines.[11] It most often starts at puberty and is worst during middle age.[1] As of 2016, it is one of the most common causes of disability.[17] An early description consistent with migraines is contained in the Ebers papyrus, written around 1500 BC in ancient Egypt.[18] The word migraine is from the Greek ἡμικρανία (hemikrania), 'pain in half of the head',[19] from ἡμι- (hemi-), 'half', and κρανίον (kranion), 'skull'.[20]
Signs and symptoms
Migraines typically present with self-limited, recurrent severe headache associated with autonomic symptoms.[5][21] About 15–30% of people with migraines experience them with an aura,[10][22] and they also frequently have migraines without aura.[23] The severity of the pain, duration of the headache, and frequency of attacks are variable.[5] A migraine lasting longer than 72 hours is termed status migrainosus.[24] There are four possible phases to a migraine, although not all the phases are necessarily experienced:[12]
- The prodrome, which occurs hours or days before the headache
- The aura, which immediately precedes the headache
- The pain phase, also known as headache phase
- The postdrome, the effects experienced following the end of a migraine attack
Migraines are associated with major depression, bipolar disorder, anxiety disorders, and obsessive compulsive disorder. These psychiatric disorders are approximately 2–5 times more common in people without aura, and 3–10 times more common in people with aura.[25]
Prodrome phase
Prodromal or premonitory symptoms occur in about 60% of those with migraines,[2][26] with an onset that can range from two hours to two days before the start of pain or the aura.[27] These symptoms may include a wide variety of phenomena,[28] including altered mood, irritability, depression or euphoria, fatigue, craving for certain food(s), stiff muscles (especially in the neck), constipation or diarrhea, and sensitivity to smells or noise.[26] This may occur in those with either migraine with aura or migraine without aura.[29] Neuroimaging indicates the limbic system and hypothalamus as the origin of prodromal symptoms in migraine.[30]
Aura phase
 |

|
 |

|
An aura is a transient focal neurological phenomenon that occurs before or during the headache.[2] Auras appear gradually over a number of minutes and generally last less than 60 minutes.[31] Symptoms can be visual, sensory or motor in nature and many people experience more than one.[32] Visual effects occur most frequently: they occur in up to 99% of cases and in more than 50% of cases are not accompanied by sensory or motor effects.[32]
Vision disturbances often consist of a scintillating scotoma (an area of partial alteration in the field of vision which flickers and may interfere with a person's ability to read or drive).[2] These typically start near the center of vision and then spread out to the sides with zigzagging lines which have been described as looking like fortifications or walls of a castle.[32] Usually the lines are in black and white but some people also see colored lines.[32] Some people lose part of their field of vision known as hemianopsia while others experience blurring.[32]
Sensory aura are the second most common type; they occur in 30–40% of people with auras.[32] Often a feeling of pins-and-needles begins on one side in the hand and arm and spreads to the nose–mouth area on the same side.[32] Numbness usually occurs after the tingling has passed with a loss of position sense.[32] Other symptoms of the aura phase can include speech or language disturbances, world spinning, and less commonly motor problems.[32] Motor symptoms indicate that this is a hemiplegic migraine, and weakness often lasts longer than one hour unlike other auras.[32] Auditory hallucinations or delusions have also been described.[33]
Pain phase
Classically the headache is unilateral, throbbing, and moderate to severe in intensity.[31] It usually comes on gradually[31] and is aggravated by physical activity.[12] The feeling of pulsating pain is not in phase with the pulse.[34] In more than 40% of cases, however, the pain may be bilateral and neck pain is commonly associated with it.[35] Bilateral pain is particularly common in those who have migraines without an aura.[2] Less commonly pain may occur primarily in the back or top of the head.[2] The pain usually lasts 4 to 72 hours in adults,[31] however in young children frequently lasts less than 1 hour.[36] The frequency of attacks is variable, from a few in a lifetime to several a week, with the average being about one a month.[37][38]
The pain is frequently accompanied by nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light, sensitivity to sound, sensitivity to smells, fatigue and irritability.[2] Many thus seek a dark and quiet room.[39] In a basilar migraine, a migraine with neurological symptoms related to the brain stem or with neurological symptoms on both sides of the body,[40] common effects include a sense of the world spinning, light-headedness, and confusion.[2] Nausea occurs in almost 90% of people, and vomiting occurs in about one-third.[39] Other symptoms may include blurred vision, nasal stuffiness, diarrhea, frequent urination, pallor, or sweating.[41] Swelling or tenderness of the scalp may occur as can neck stiffness.[41] Associated symptoms are less common in the elderly.[42]
Rarely, an aura occurs without a subsequent headache.[32] This is known as an acephalgic migraine or silent migraine; however, it is difficult to assess the frequency of such cases because people who do not experience symptoms severe enough to seek treatment may not realize that anything unusual is happening to them and dismiss it without reporting any problems.
Postdrome
The migraine postdrome could be defined as that constellation of symptoms occurring once the acute headache has settled.[43] Many report a sore feeling in the area where the migraine was, and some report impaired thinking for a few days after the headache has passed. The person may feel tired or "hung over" and have head pain, cognitive difficulties, gastrointestinal symptoms, mood changes, and weakness.[44] According to one summary, "Some people feel unusually refreshed or euphoric after an attack, whereas others note depression and malaise."[45] For some individuals this can vary each time.
Cause
The underlying causes of migraines are unknown.[46] However, they are believed to be related to a mix of environmental and genetic factors.[3] They run in families in about two-thirds of cases[5] and rarely occur due to a single gene defect.[47] While migraines were once believed to be more common in those of high intelligence, this does not appear to be true.[48] A number of psychological conditions are associated, including depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder,[49] as are many biological events or triggers.
Genetics
Studies of twins indicate a 34% to 51% genetic influence of likelihood to develop migraine headaches.[3] This genetic relationship is stronger for migraines with aura than for migraines without aura.[23] A number of specific variants of genes increase the risk by a small to moderate amount.[47]
Single gene disorders that result in migraines are rare.[47] One of these is known as familial hemiplegic migraine, a type of migraine with aura, which is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion.[50][51] Four genes have been shown to be involved in familial hemiplegic migraine.[52] Three of these genes are involved in ion transport.[52] The fourth is an axonal protein associated with the exocytosis complex.[52] Another genetic disorder associated with migraine is CADASIL syndrome or cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy.[2] One meta-analysis found a protective effect from an angiotensin converting enzyme polymorphisms on migraine.[53] The TRPM8 gene, which codes for a cation channel, has been linked to migraines.[54]
Triggers
Migraines may be induced by triggers, with some reporting it as an influence in a minority of cases[5] and others the majority.[55] Many things such as fatigue, certain foods, and weather have been labeled as triggers; however, the strength and significance of these relationships are uncertain.[55][56] Most people with migraines report experiencing triggers.[57] Symptoms may start up to 24 hours after a trigger.[5]
Physiological aspects
Common triggers quoted are stress, hunger, and fatigue (these equally contribute to tension headaches).[55] Psychological stress has been reported as a factor by 50 to 80% of people.[58] Migraines have also been associated with post-traumatic stress disorder and abuse.[59] Migraines are more likely to occur around menstruation.[58] Other hormonal influences, such as menarche, oral contraceptive use, pregnancy, perimenopause, and menopause, also play a role.[60] These hormonal influences seem to play a greater role in migraine without aura.[48] Migraines typically do not occur during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, or following menopause.[2]
Dietary aspects
Between 12 and 60% of people report foods as triggers.[61][62] Evidence for such triggers, however, mostly relies on self-reports and is not rigorous enough to prove or disprove any particular trigger.[63] A clear explanation for why food might trigger migraines is also lacking.[61]
There does not appear to be evidence for an effect of tyramine – which is naturally present in chocolate, alcoholic beverages, most cheeses and processed meats – on migraine.[64] Likewise, while monosodium glutamate (MSG) is frequently reported,[65] evidence does not consistently support that it is a dietary trigger.[66]
Environmental aspects
A review on potential triggers in the indoor and outdoor environment concluded that there is insufficient evidence to confirm environmental factors as causing migraines. They nevertheless suggested that people with migraines take some preventive measures related to indoor air quality and lighting. This includes ventilation and various black out items to reduce light at the maximum rate.[67]
Pathophysiology

Migraines are believed to be a neurovascular disorder,[5] with evidence supporting a mechanism starting within the brain and then spreading to the blood vessels.[68] Some researchers believe neuronal mechanisms play a greater role,[69] while others believe blood vessels play the key role.[70] Others believe both are likely important.[71] One theory is related to increased excitability of the cerebral cortex and abnormal control of pain neurons in the trigeminal nucleus of the brainstem.[72]
Aura
Cortical spreading depression, or spreading depression according to Leão, is a burst of neuronal activity followed by a period of inactivity, which is seen in those with migraines with an aura.[73] There are a number of explanations for its occurrence, including activation of NMDA receptors leading to calcium entering the cell.[73] After the burst of activity, the blood flow to the cerebral cortex in the area affected is decreased for two to six hours.[73] It is believed that when depolarization travels down the underside of the brain, nerves that sense pain in the head and neck are triggered.[73]
Pain
The exact mechanism of the head pain which occurs during a migraine is unknown.[74] Some evidence supports a primary role for central nervous system structures (such as the brainstem and diencephalon),[75] while other data support the role of peripheral activation (such as via the sensory nerves that surround blood vessels of the head and neck).[74] The potential candidate vessels include dural arteries, pial arteries and extracranial arteries such as those of the scalp.[74] The role of vasodilatation of the extracranial arteries, in particular, is believed to be significant.[76]
Neuromodulators
Adenosine, a neuromodulator, may be involved.[77] Released after the progressive cleavage of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), adenosine acts on adenosine receptors to put the body and brain in a low activity state by dilating blood vessels and slowing the heart rate, such as before and during the early stages of sleep. Adenosine levels have been found to be high during migraine attacks.[77][78] Caffeine's role as an inhibitor of adenosine may explain its effect in reducing migraine.[79] Low levels of the neurotransmitter serotonin, also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), are also believed to be involved.[80]
Calcitonin gene related peptides (CGRPs) have been found to play a role in the pathogenesis of the pain associated with migraine, as levels of it become elevated during an attack.[10][34]
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of a migraine is based on signs and symptoms.[5] Neuroimaging tests are not necessary to diagnose migraine, but may be used to find other causes of headaches in those whose examination and history do not confirm a migraine diagnosis.[81] It is believed that a substantial number of people with the condition remain undiagnosed.[5]
The diagnosis of migraine without aura, according to the International Headache Society, can be made according to the following criteria, the "5, 4, 3, 2, 1 criteria":[12]
- Five or more attacks—for migraine with aura, two attacks are sufficient for diagnosis.
- Four hours to three days in duration
- Two or more of the following:
- Unilateral (affecting half the head)
- Pulsating
- Moderate or severe pain intensity
- Worsened by or causing avoidance of routine physical activity
- One or more of the following:
- Nausea and/or vomiting;
- Sensitivity to both light (photophobia) and sound (phonophobia)
If someone experiences two of the following: photophobia, nausea, or inability to work or study for a day, the diagnosis is more likely.[82] In those with four out of five of the following: pulsating headache, duration of 4–72 hours, pain on one side of the head, nausea, or symptoms that interfere with the person's life, the probability that this is a migraine is 92%.[10] In those with fewer than three of these symptoms the probability is 17%.[10]
Classification
Migraines were first comprehensively classified in 1988.[23] The International Headache Society updated their classification of headaches in 2004.[12] A third version was published in 2018.[83] According to this classification migraines are primary headaches along with tension-type headaches and cluster headaches, among others.[84]
Migraines are divided into seven subclasses (some of which include further subdivisions):
- Migraine without aura, or "common migraine", involves migraine headaches that are not accompanied by an aura.
- Migraine with aura, or "classic migraine", usually involves migraine headaches accompanied by an aura. Less commonly, an aura can occur without a headache, or with a nonmigraine headache. Two other varieties are familial hemiplegic migraine and sporadic hemiplegic migraine, in which a person has migraines with aura and with accompanying motor weakness. If a close relative has had the same condition, it is called "familial", otherwise it is called "sporadic". Another variety is basilar-type migraine, where a headache and aura are accompanied by difficulty speaking, world spinning, ringing in ears, or a number of other brainstem-related symptoms, but not motor weakness. This type was initially believed to be due to spasms of the basilar artery, the artery that supplies the brainstem. Now that this mechanism is not believed to be primary, the symptomatic term migraine with brainstem aura (MBA) is preferred.[40]
- Childhood periodic syndromes that are commonly precursors of migraine include cyclical vomiting (occasional intense periods of vomiting), abdominal migraine (abdominal pain, usually accompanied by nausea), and benign paroxysmal vertigo of childhood (occasional attacks of vertigo).
- Retinal migraine involves migraine headaches accompanied by visual disturbances or even temporary blindness in one eye.
- Complications of migraine describe migraine headaches and/or auras that are unusually long or unusually frequent, or associated with a seizure or brain lesion.
- Probable migraine describes conditions that have some characteristics of migraines, but where there is not enough evidence to diagnose it as a migraine with certainty (in the presence of concurrent medication overuse).
- Chronic migraine is a complication of migraines, and is a headache that fulfills diagnostic criteria for migraine headache and occurs for a greater time interval. Specifically, greater or equal to 15 days/month for longer than 3 months.[85]
Abdominal migraine
The diagnosis of abdominal migraines is controversial.[86] Some evidence indicates that recurrent episodes of abdominal pain in the absence of a headache may be a type of migraine[86][87] or are at least a precursor to migraines.[23] These episodes of pain may or may not follow a migraine-like prodrome and typically last minutes to hours.[86] They often occur in those with either a personal or family history of typical migraines.[86] Other syndromes that are believed to be precursors include cyclical vomiting syndrome and benign paroxysmal vertigo of childhood.[23]
Differential diagnosis
Other conditions that can cause similar symptoms to a migraine headache include temporal arteritis, cluster headaches, acute glaucoma, meningitis and subarachnoid hemorrhage.[10] Temporal arteritis typically occurs in people over 50 years old and presents with tenderness over the temple, cluster headaches presents with one-sided nose stuffiness, tears and severe pain around the orbits, acute glaucoma is associated with vision problems, meningitis with fevers, and subarachnoid hemorrhage with a very fast onset.[10] Tension headaches typically occur on both sides, are not pounding, and are less disabling.[10]
Those with stable headaches that meet criteria for migraines should not receive neuroimaging to look for other intracranial disease.[88][89][90] This requires that other concerning findings such as papilledema (swelling of the optic disc) are not present. People with migraines are not at an increased risk of having another cause for severe headaches.
Prevention
Preventive treatments of migraines include medications, nutritional supplements, lifestyle alterations, and surgery. Prevention is recommended in those who have headaches more than two days a week, cannot tolerate the medications used to treat acute attacks, or those with severe attacks that are not easily controlled.[10] Recommended lifestyle changes include stopping tobacco use and receding behaviors that interfere with sleep.[91]
The goal is to reduce the frequency, painfulness, and duration of migraines, and to increase the effectiveness of abortive therapy.[92] Another reason for prevention is to avoid medication overuse headache. This is a common problem and can result in chronic daily headache.[93][94]
Medication
Preventive migraine medications are considered effective if they reduce the frequency or severity of the migraine attacks by at least 50%.[95] Guidelines are fairly consistent in rating topiramate, divalproex/sodium valproate, propranolol, and metoprolol as having the highest level of evidence for first-line use.[96] Propranolol and topiramate have the best evidence in children; however, evidence only supports short term benefit as of 2020.[91][97]
Recommendations regarding effectiveness varied however for gabapentin and pregabalin.[96] Timolol is also effective for migraine prevention and in reducing migraine attack frequency and severity, while frovatriptan is effective for prevention of menstrual migraine.[96] Tentative evidence also supports the use of magnesium supplementation.[98] Increasing dietary intake may be better.[99]
Amitriptyline and venlafaxine are probably also effective.[100] Angiotensin inhibition by either an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor antagonist may reduce attacks.[101]
Medications in the anti-calcitonin gene-related peptide, including eptinezumab, erenumab, fremanezumab, and galcanezumab, appear to decrease the frequency of migraines by one to two per month.[102] They are, however, expensive: a year of erenumab costs $6,900 as of 2019.[103]
Alternative therapies
Acupuncture has a small effect in reducing the number of migraines, compared to sham acupuncture, a practice where needles are placed randomly or do not penetrate the skin.[104] Physiotherapy, massage and relaxation, and chiropractic manipulation might be as effective as propranolol or topiramate in the prevention of migraine headaches; however, the research had some problems with methodology.[105][106] Another review, however, found evidence to support spinal manipulation to be poor and insufficient to support its use.[107] There is tentative evidence for yoga.[108]
Tentative evidence supports the use of stress reduction techniques such as cognitive behavioral therapy, biofeedback, and relaxation techniques.[58] Regular physical exercise may decrease the frequency.[109]
Among alternative medicines, butterbur has the best evidence for its use.[110][111] However, unprocessed butterbur contains chemicals called pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs) which can cause liver damage, however there are versions that are PA free.[112] In addition, butterbur may cause allergic reactions in people who are sensitive to plants such as ragweed.[113] There is tentative evidence that coenzyme Q10 reduces migraine frequency.[114]
There is tentative evidence for melatonin as an add-on therapy for prevention and treatment of migraine.[115][116] The data on melatonin are mixed and certain studies have had negative results.[115] The reasons for the mixed findings are unclear but may stem from differences in study design and dosage.[115] Melatonin's possible mechanisms of action in migraine are not completely clear, but may include improved sleep, direct action on melatonin receptors in the brain, and anti-inflammatory properties.[115][117]
Devices and surgery
Medical devices, such as biofeedback and neurostimulators, have some advantages in migraine prevention, mainly when common anti-migraine medications are contraindicated or in case of medication overuse. Biofeedback helps people be conscious of some physiological parameters so as to control them and try to relax and may be efficient for migraine treatment.[118][119] Neurostimulation uses noninvasive or implantable neurostimulators similar to pacemakers for the treatment of intractable chronic migraines with encouraging results for severe cases.[120][121] A transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulator and a transcranial magnetic stimulator are approved in the United States for the prevention of migraines.[122][123] There is also tentative evidence for transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation decreases the frequency of migraines.[124] Migraine surgery, which involves decompression of certain nerves around the head and neck, may be an option in certain people who do not improve with medications.[125]
Management
There are three main aspects of treatment: trigger avoidance, acute symptomatic control, and medication for prevention.[5] Medications are more effective if used earlier in an attack.[5] The frequent use of medications may result in medication overuse headache, in which the headaches become more severe and more frequent.[12] This may occur with triptans, ergotamines, and analgesics, especially opioid analgesics.[12] Due to these concerns simple analgesics are recommended to be used less than three days per week at most.[126]
Analgesics
Recommended initial treatment for those with mild to moderate symptoms are simple analgesics such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or the combination of paracetamol (also known as acetaminophen), aspirin, and caffeine.[10] Several NSAIDs, including diclofenac and ibuprofen have evidence to support their use.[127][128] Aspirin can relieve moderate to severe migraine pain, with an effectiveness similar to sumatriptan.[129] Ketorolac is available in intravenous and intramuscular formulations.[10]
Paracetamol, either alone or in combination with metoclopramide, is another effective treatment with a low risk of adverse effects.[130] Intravenous metoclopramide is also effective by itself.[131][132] In pregnancy, paracetamol and metoclopramide are deemed safe as are NSAIDs until the third trimester.[10]
Triptans
Triptans such as sumatriptan are effective for both pain and nausea in up to 75% of people.[5][133] When sumatriptan is taken with naproxen it works better.[134] They are the initially recommended treatments for those with moderate to severe pain or those with milder symptoms who do not respond to simple analgesics.[10] The different forms available include oral, injectable, nasal spray, and oral dissolving tablets.[5] In general, all the triptans appear equally effective, with similar side effects. However, individuals may respond better to specific ones.[10] Most side effects are mild, such as flushing; however, rare cases of myocardial ischemia have occurred.[5] They are thus not recommended for people with cardiovascular disease,[10] who have had a stroke, or have migraines that are accompanied by neurological problems.[135] In addition, triptans should be prescribed with caution for those with risk factors for vascular disease.[135] While historically not recommended in those with basilar migraines there is no specific evidence of harm from their use in this population to support this caution.[40] They are not addictive, but may cause medication-overuse headaches if used more than 10 days per month.[136]
Ergotamines
Ergotamine and dihydroergotamine are older medications still prescribed for migraines, the latter in nasal spray and injectable forms.[5][137] They appear equally effective to the triptans[138] and experience adverse effects that typically are benign.[139] In the most severe cases, such as those with status migrainosus, they appear to be the most effective treatment option.[139] They can cause vasospasm including coronary vasospasm and are contraindicated in people with coronary artery disease.[140]
Other
Intravenous metoclopramide, intravenous prochlorperazine, or intranasal lidocaine are other potential options.[10][132] Metoclopramide or prochlorperazine are the recommended treatment for those who present to the emergency department.[10][132] Haloperidol may also be useful in this group.[132][137] A single dose of intravenous dexamethasone, when added to standard treatment of a migraine attack, is associated with a 26% decrease in headache recurrence in the following 72 hours.[141] Spinal manipulation for treating an ongoing migraine headache is not supported by evidence.[107] It is recommended that opioids and barbiturates not be used due to questionable efficacy, addictive potential, and the risk of rebound headache.[10] There is tentative evidence that propofol may be useful if other measures are not effective.[142]
Occipital nerve stimulation, may be effective but has the downsides of being cost-expensive and has a significant amount of complications.[143]
Children
Ibuprofen helps decrease pain in children with migraines and is the initially recommended treatment.[144][145] Paracetamol does not appear to be effective in providing pain relief.[144] Triptans are effective, though there is a risk of causing minor side effects like taste disturbance, nasal symptoms, dizziness, fatigue, low energy, nausea, or vomiting.[144] Ibuprofen should be used less than half the days in a month and triptans less than a third of the days in a month to decrease the risk of medication overuse headaches.[145] There is tentative evidence for relaxation, biofeedback, and counselling in children.[146]
Chronic migraine
Topiramate and botulinum toxin (Botox) have evidence in treating chronic migraine.[100][147] Botulinum toxin has been found to be useful in those with chronic migraines (decreasing headaches from 13 to 11 days a month) but not those with episodic ones.[148][149][150] The anti-CGRP monoclonal antibody erenumab was found in one study to decrease chronic migraines by 2.4 days more than placebo.[151]
Prognosis
Long-term prognosis in people with migraines is variable.[21] Most people with migraines have periods of lost productivity due to their disease;[5] however typically the condition is fairly benign[21] and is not associated with an increased risk of death.[152] There are four main patterns to the disease: symptoms can resolve completely, symptoms can continue but become gradually less with time, symptoms may continue at the same frequency and severity, or attacks may become worse and more frequent.[21]
Migraines with aura appear to be a risk factor for ischemic stroke[153] doubling the risk.[154] Being a young adult, being female, using hormonal birth control, and smoking further increases this risk.[153] There also appears to be an association with cervical artery dissection.[155] Migraines without aura do not appear to be a factor.[156] The relationship with heart problems is inconclusive with a single study supporting an association.[153] Overall however migraines do not appear to increase the risk of death from stroke or heart disease.[152] Preventative therapy of migraines in those with migraines with auras may prevent associated strokes.[157] People with migraines, particularly women, may develop higher than average numbers of white matter brain lesions of unclear significance.[158]
Epidemiology

Worldwide, migraines affect nearly 15% or approximately one billion people.[11] It is more common in women at 19% than men at 11%.[11] In the United States, about 6% of men and 18% of women get a migraine in a given year, with a lifetime risk of about 18% and 43% respectively.[5] In Europe, migraines affect 12–28% of people at some point in their lives with about 6–15% of adult men and 14–35% of adult women getting at least one yearly.[14] Rates of migraines are slightly lower in Asia and Africa than in Western countries.[48][159] Chronic migraines occur in approximately 1.4 to 2.2% of the population.[160]
These figures vary substantially with age: migraines most commonly start at between 15 and 24 years of age and occur most frequently in those 35 to 45 years of age.[5] In children, about 1.7% of 7 year olds and 3.9% of those between 7 and 15 have migraines, with the condition being slightly more common in boys before puberty.[161] Children as young as two years may be affected.[144] During adolescence migraines become more common among women[161] and this persists for the rest of the lifespan, being twice as common among elderly females than males.[162] In women migraines without aura are more common than migraines with aura; however in men the two types occur with similar frequency.[48]
During perimenopause symptoms often get worse before decreasing in severity.[162] While symptoms resolve in about two thirds of the elderly, in 3 to 10% they persist.[42]
History

An early description consistent with migraines is contained in the Ebers papyrus, written around 1500 BCE in ancient Egypt.[18] In 200 BCE, writings from the Hippocratic school of medicine described the visual aura that can precede the headache and a partial relief occurring through vomiting.[163]
A second-century description by Aretaeus of Cappadocia divided headaches into three types: cephalalgia, cephalea, and heterocrania.[164] Galen of Pergamon used the term hemicrania (half-head), from which the word migraine was eventually derived.[164] He also proposed that the pain arose from the meninges and blood vessels of the head.[163] Migraines were first divided into the two now used types – migraine with aura (migraine ophthalmique) and migraine without aura (migraine vulgaire) in 1887 by Louis Hyacinthe Thomas, a French Librarian.[163] The mystical visions of Hildegard von Bingen, which she described as “reflections of the living light", are consistent with the visual auras experienced during migraines.[165]
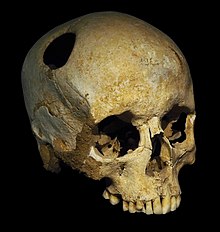
Trepanation, the deliberate drilling of holes into a skull, was practiced as early as 7,000 BCE.[18] While sometimes people survived, many would have died from the procedure due to infection.[166] It was believed to work via "letting evil spirits escape".[167] William Harvey recommended trepanation as a treatment for migraines in the 17th century.[168]
While many treatments for migraines have been attempted, it was not until 1868 that use of a substance which eventually turned out to be effective began.[163] This substance was the fungus ergot from which ergotamine was isolated in 1918.[169] Methysergide was developed in 1959 and the first triptan, sumatriptan, was developed in 1988.[169] During the 20th century with better study-design, effective preventive measures were found and confirmed.[163]
Society and culture
Migraines are a significant source of both medical costs and lost productivity. It has been estimated that they are the most costly neurological disorder in the European Community, costing more than €27 billion per year.[170] In the United States, direct costs have been estimated at $17 billion, while indirect costs — such as missed or decreased ability to work — is estimated at $15 billion.[171] Nearly a tenth of the direct cost is due to the cost of triptans.[171] In those who do attend work with a migraine, effectiveness is decreased by around a third.[170] Negative impacts also frequently occur for a person's family.[170]
Research
Transcranial magnetic stimulation shows promise[10][172] as does transcutaneous supraorbital nerve stimulation.[173] There is preliminary evidence that a ketogenic diet may help prevent episodic and long-term migraine.[174][175]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 "Headache disorders Fact sheet N°277". October 2012. Archived from the original on 16 February 2016. Retrieved 15 February 2016.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 Simon, Roger P; Aminoff, Michael J; Greenberg, David A (2009). Clinical neurology (7 ed.). New York, N.Y: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill. pp. 85–88. ISBN 9780071664332.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Piane M, Lulli P, Farinelli I, Simeoni S, De Filippis S, Patacchioli FR, Martelletti P (December 2007). "Genetics of migraine and pharmacogenomics: some considerations". The Journal of Headache and Pain. 8 (6): 334–9. doi:10.1007/s10194-007-0427-2. PMC 2779399. PMID 18058067.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Lay CL, Broner SW (May 2009). "Migraine in women". Neurologic Clinics. 27 (2): 503–11. doi:10.1016/j.ncl.2009.01.002. PMID 19289228.
- ↑ 5.00 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 5.09 5.10 5.11 5.12 5.13 5.14 5.15 5.16 5.17 5.18 5.19 5.20 5.21 Bartleson JD, Cutrer FM (May 2010). "Migraine update. Diagnosis and treatment". Minnesota Medicine. 93 (5): 36–41. PMID 20572569.
- ↑ Olesen, Jes (2006). The Headaches. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 424. ISBN 9780781754002. Archived from the original on 2017-09-08.
- ↑ "Cluster Headache". American Migraine Foundation. 2017-02-15. Archived from the original on 2018-05-09. Retrieved 2017-10-23.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Armstrong C (April 2013). "AAN/AHS update recommendations for migraine prevention in adults". American Family Physician. 87 (8): 584–5. PMID 23668450.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Linde M, Mulleners WM, Chronicle EP, McCrory DC (June 2013). "Valproate (valproic acid or sodium valproate or a combination of the two) for the prophylaxis of episodic migraine in adults". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (6): CD010611. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010611. PMID 23797677.
- ↑ 10.00 10.01 10.02 10.03 10.04 10.05 10.06 10.07 10.08 10.09 10.10 10.11 10.12 10.13 10.14 10.15 10.16 10.17 10.18 10.19 Gilmore B, Michael M (February 2011). "Treatment of acute migraine headache". American Family Physician. 83 (3): 271–80. PMID 21302868.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, et al. (December 2012). "Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010". Lancet. 380 (9859): 2163–96. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2. PMC 6350784. PMID 23245607.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 12.5 12.6 12.7 Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society (2004). "The International Classification of Headache Disorders: 2nd edition". Cephalalgia. 24 (Suppl 1): 9–160. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2004.00653.x. PMID 14979299. as PDF Archived 2010-03-31 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Pryse-Phillips, William (2003). Companion to clinical neurology (2nd ed.). Oxford: Oxford university press. p. 587. ISBN 9780195159387. Archived from the original on 2017-03-13.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Stovner LJ, Zwart JA, Hagen K, Terwindt GM, Pascual J (April 2006). "Epidemiology of headache in Europe". European Journal of Neurology. 13 (4): 333–45. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2006.01184.x. PMID 16643310.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 "NINDS Migraine Information Page". National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. November 3, 2015. Archived from the original on 16 February 2016. Retrieved 15 February 2016.
- ↑ Diener HC, Charles A, Goadsby PJ, Holle D (October 2015). "New therapeutic approaches for the prevention and treatment of migraine". The Lancet. Neurology. 14 (10): 1010–22. doi:10.1016/s1474-4422(15)00198-2. PMID 26376968.
- ↑ Vos T, Abajobir AA, Abate KH, Abbafati C, Abbas KM, Abd-Allah F, et al. (GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators) (September 2017). "Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016". Lancet. 390 (10100): 1211–1259. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32154-2. PMC 5605509. PMID 28919117.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 Miller, Neil (2005). Walsh and Hoyt's clinical neuro-ophthalmology (6 ed.). Philadelphia, Pa.: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 1275. ISBN 9780781748117. Archived from the original on 2017-03-12.
- ↑ Liddell, Henry George; Scott, Robert. "ἡμικρανία". A Greek-English Lexicon. Archived from the original on 2013-11-08. on Perseus
- ↑ Anderson, Kenneth; Anderson, Lois E.; Glanze, Walter D. (1994). Mosby's Medical, Nursing & Allied Health Dictionary (4 ed.). Mosby. p. 998. ISBN 978-0-8151-6111-0.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 21.3 Bigal ME, Lipton RB (June 2008). "The prognosis of migraine". Current Opinion in Neurology. 21 (3): 301–8. doi:10.1097/WCO.0b013e328300c6f5. PMID 18451714. S2CID 34805084.
- ↑ Gutman, Sharon A. (2008). Quick reference neuroscience for rehabilitation professionals: the essential neurologic principles underlying rehabilitation practice (2 ed.). Thorofare, NJ: SLACK. p. 231. ISBN 9781556428005. Archived from the original on 2017-03-12.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 23.2 23.3 23.4 The Headaches, Pg 232–233
- ↑ Jes Olesen (2006). The headaches (3 ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 512. ISBN 9780781754002. Archived from the original on 2016-12-22.
- ↑ Baskin SM, Lipchik GL, Smitherman TA (October 2006). "Mood and anxiety disorders in chronic headache". Headache. 46 Suppl 3: S76-87. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2006.00559.x. PMID 17034402.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 Lynn, D. Joanne; Newton, Herbert B.; Rae-Grant, Alexander (2004). The 5-minute neurology consult. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 26. ISBN 9780683307238. Archived from the original on 2017-03-13.
- ↑ Buzzi MG, Cologno D, Formisano R, Rossi P (October–December 2005). "Prodromes and the early phase of the migraine attack: therapeutic relevance". Functional Neurology. 20 (4): 179–83. PMID 16483458.
- ↑ Rossi P, Ambrosini A, Buzzi MG (October–December 2005). "Prodromes and predictors of migraine attack". Functional Neurology. 20 (4): 185–91. PMID 16483459.
- ↑ Ropper, Allan H; Adams, Raymond Delacy; Victor, Maurice; Samuels, Martin A (2009). Adams and Victor's principles of neurology (9 ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. pp. Chapter 10. ISBN 9780071499927.
- ↑ May A, Burstein R (November 2019). "Hypothalamic regulation of headache and migraine". Cephalalgia. 39 (13): 1710–1719. doi:10.1177/0333102419867280. PMC 7164212. PMID 31466456.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 31.2 31.3 Tintinalli, Judith E. (2010). Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide (Emergency Medicine (Tintinalli)). New York: McGraw-Hill Companies. pp. 1116–1117. ISBN 978-0-07-148480-0.
- ↑ 32.00 32.01 32.02 32.03 32.04 32.05 32.06 32.07 32.08 32.09 32.10 The Headaches, pp. 407–419
- ↑ Slap, GB (2008). Adolescent medicine. Philadelphia, PA: Mosby/Elsevier. p. 105. ISBN 9780323040730. Archived from the original on 2017-03-13.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 Qubty W, Patniyot I (June 2020). "Migraine Pathophysiology". Pediatric Neurology. 107: 1–6. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2019.12.014. PMID 32192818.
- ↑ Tepper, Stewart J; Tepper, Deborah E. (2011-01-01). The Cleveland Clinic manual of headache therapy. New York: Springer. p. 6. ISBN 9781461401780. Archived from the original on 2016-12-22.
- ↑ Bigal ME, Arruda MA (July 2010). "Migraine in the pediatric population--evolving concepts". Headache. 50 (7): 1130–43. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2010.01717.x. PMID 20572878.
- ↑ Jes Olesen (2006). The headaches (3 ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 238. ISBN 9780781754002. Archived from the original on 2017-03-13.
- ↑ Dalessio (2001). Silberstein SD, Lipton RB, Dalessio DJ (eds.). Wolff's headache and other head pain (7 ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 122. ISBN 9780195135183. Archived from the original on 2021-04-28. Retrieved 2020-08-05.
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 Lisak, Robert P.; Truong, Daniel D.; Carroll, William; Bhidayasiri, Roongroj (2009). International neurology: a clinical approach. Chichester, UK: Wiley-Blackwell. p. 670. ISBN 9781405157384. Archived from the original on 2021-04-28. Retrieved 2020-08-05.
- ↑ 40.0 40.1 40.2 Kaniecki RG (June 2009). "Basilar-type migraine". Current Pain and Headache Reports. 13 (3): 217–20. doi:10.1007/s11916-009-0036-7. PMID 19457282. S2CID 22242504.
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 Joel S. Glaser (1999). Neuro-ophthalmology (3 ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 555. ISBN 9780781717298. Archived from the original on 2017-03-13.
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 Sirven, Joseph I.; Malamut, Barbara L. (2008). Clinical neurology of the older adult (2 ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 197. ISBN 9780781769471. Archived from the original on 2017-03-12.
- ↑ Bose P, Goadsby PJ (June 2016). "The migraine postdrome". Current Opinion in Neurology. 29 (3): 299–301. doi:10.1097/WCO.0000000000000310. PMID 26886356.
- ↑ Kelman L (February 2006). "The postdrome of the acute migraine attack". Cephalalgia. 26 (2): 214–20. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2005.01026.x. PMID 16426278. S2CID 21519111.
- ↑ Halpern AL, Silberstein SD (2005). "Ch. 9: The Migraine Attack—A Clinical Description". In Kaplan PW, Fisher RS (eds.). Imitators of Epilepsy (2 ed.). New York: Demos Medical. ISBN 978-1-888799-83-5. NBK7326. Archived from the original on 2011-08-27. Retrieved 2020-08-05.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|chapterurl=ignored (help) - ↑ Robbins MS, Lipton RB (April 2010). "The epidemiology of primary headache disorders". Seminars in Neurology. 30 (2): 107–19. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1249220. PMID 20352581.
- ↑ 47.0 47.1 47.2 Schürks M (January 2012). "Genetics of migraine in the age of genome-wide association studies". The Journal of Headache and Pain. 13 (1): 1–9. doi:10.1007/s10194-011-0399-0. PMC 3253157. PMID 22072275.
- ↑ 48.0 48.1 48.2 48.3 The Headaches, pp. 238–40
- ↑ The Headaches, pp. 246–247
- ↑ de Vries B, Frants RR, Ferrari MD, van den Maagdenberg AM (July 2009). "Molecular genetics of migraine". Human Genetics. 126 (1): 115–32. doi:10.1007/s00439-009-0684-z. PMID 19455354. S2CID 20119237.
- ↑ Montagna P (September 2008). "Migraine genetics". Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics. 8 (9): 1321–30. doi:10.1586/14737175.8.9.1321. PMID 18759544. S2CID 207195127.
- ↑ 52.0 52.1 52.2 Ducros A (May 2013). "[Genetics of migraine]". Revue Neurologique. 169 (5): 360–71. doi:10.1016/j.neurol.2012.11.010. PMID 23618705.
- ↑ Wan D, Wang C, Zhang X, Tang W, Chen M, Dong Z, Yu S (1 January 2016). "Association between angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism and migraine: a meta-analysis". The International Journal of Neuroscience. 126 (5): 393–9. doi:10.3109/00207454.2015.1025395. PMID 26000817. S2CID 34902092.
- ↑ Dussor G, Cao YQ (October 2016). "TRPM8 and Migraine". Headache. 56 (9): 1406–1417. doi:10.1111/head.12948. PMC 5335856. PMID 27634619.
- ↑ 55.0 55.1 55.2 Levy D, Strassman AM, Burstein R (June 2009). "A critical view on the role of migraine triggers in the genesis of migraine pain". Headache. 49 (6): 953–7. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2009.01444.x. PMID 19545256.
- ↑ Martin PR (June 2010). "Behavioral management of migraine headache triggers: learning to cope with triggers". Current Pain and Headache Reports. 14 (3): 221–7. doi:10.1007/s11916-010-0112-z. PMID 20425190. S2CID 5511782.
- ↑ Pavlovic JM, Buse DC, Sollars CM, Haut S, Lipton RB (2014). "Trigger factors and premonitory features of migraine attacks: summary of studies". Headache. 54 (10): 1670–9. doi:10.1111/head.12468. PMID 25399858.
- ↑ 58.0 58.1 58.2 Radat F (May 2013). "[Stress and migraine]". Revue Neurologique. 169 (5): 406–12. doi:10.1016/j.neurol.2012.11.008. PMID 23608071.
- ↑ Peterlin BL, Katsnelson MJ, Calhoun AH (October 2009). "The associations between migraine, unipolar psychiatric comorbidities, and stress-related disorders and the role of estrogen". Current Pain and Headache Reports. 13 (5): 404–12. doi:10.1007/s11916-009-0066-1. PMC 3972495. PMID 19728969.
- ↑ Chai NC, Peterlin BL, Calhoun AH (June 2014). "Migraine and estrogen". Current Opinion in Neurology. 27 (3): 315–24. doi:10.1097/WCO.0000000000000091. PMC 4102139. PMID 24792340.
- ↑ 61.0 61.1 Finocchi C, Sivori G (May 2012). "Food as trigger and aggravating factor of migraine". Neurological Sciences. 33 Suppl 1 (1): S77-80. doi:10.1007/s10072-012-1046-5. PMID 22644176. S2CID 19582697.
- ↑ Rockett FC, de Oliveira VR, Castro K, Chaves ML, Perla A, Perry ID (June 2012). "Dietary aspects of migraine trigger factors". Nutrition Reviews. 70 (6): 337–56. doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.2012.00468.x. PMID 22646127.
- ↑ Holzhammer J, Wöber C (April 2006). "[Alimentary trigger factors that provoke migraine and tension-type headache]" [Alimentary trigger factors that provoke migraine and tension-type headache]. Schmerz (in German). 20 (2): 151–9. doi:10.1007/s00482-005-0390-2. PMID 15806385.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ↑ Jansen SC, van Dusseldorp M, Bottema KC, Dubois AE (September 2003). "Intolerance to dietary biogenic amines: a review". Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. 91 (3): 233–40, quiz 241–2, 296. doi:10.1016/S1081-1206(10)63523-5. PMID 14533654.[permanent dead link]
- ↑ Sun-Edelstein C, Mauskop A (June 2009). "Foods and supplements in the management of migraine headaches" (PDF). The Clinical Journal of Pain. 25 (5): 446–52. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.530.1223. doi:10.1097/AJP.0b013e31819a6f65. PMID 19454881. S2CID 3042635. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-08-13.
- ↑ Freeman M (October 2006). "Reconsidering the effects of monosodium glutamate: a literature review". Journal of the American Academy of Nurse Practitioners. 18 (10): 482–6. doi:10.1111/j.1745-7599.2006.00160.x. PMID 16999713. S2CID 21084909.
- ↑ Friedman DI, De ver Dye T (June 2009). "Migraine and the environment". Headache. 49 (6): 941–52. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2009.01443.x. PMID 19545255.
- ↑ The Headaches Chp. 29, Pg. 276
- ↑ Goadsby PJ (January 2009). "The vascular theory of migraine--a great story wrecked by the facts". Brain. 132 (Pt 1): 6–7. doi:10.1093/brain/awn321. PMID 19098031.
- ↑ Brennan KC, Charles A (June 2010). "An update on the blood vessel in migraine". Current Opinion in Neurology. 23 (3): 266–74. doi:10.1097/WCO.0b013e32833821c1. PMC 5500293. PMID 20216215.
- ↑ Dodick DW (April 2008). "Examining the essence of migraine--is it the blood vessel or the brain? A debate". Headache. 48 (4): 661–7. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2008.01079.x. PMID 18377395.
- ↑ Dodick DW, Gargus JJ (August 2008). "Why migraines strike". Scientific American. 299 (2): 56–63. Bibcode:2008SciAm.299b..56D. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0808-56. PMID 18666680.
- ↑ 73.0 73.1 73.2 73.3 The Headaches, Chp. 28, pp. 269–72
- ↑ 74.0 74.1 74.2 Olesen J, Burstein R, Ashina M, Tfelt-Hansen P (July 2009). "Origin of pain in migraine: evidence for peripheral sensitisation". The Lancet. Neurology. 8 (7): 679–90. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70090-0. PMID 19539239. S2CID 20452008.
- ↑ Akerman S, Holland PR, Goadsby PJ (September 2011). "Diencephalic and brainstem mechanisms in migraine". Nature Reviews. Neuroscience. 12 (10): 570–84. doi:10.1038/nrn3057. PMID 21931334. S2CID 8472711.
- ↑ Shevel E (March 2011). "The extracranial vascular theory of migraine--a great story confirmed by the facts". Headache. 51 (3): 409–417. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2011.01844.x. PMID 21352215.
- ↑ 77.0 77.1 Burnstock, Geoffrey (2016-01-01), Barrett, James E. (ed.), "Chapter Four - Purinergic Mechanisms and Pain", Advances in Pharmacology, Pharmacological Mechanisms and the Modulation of Pain, Academic Press, 75: 91–137, doi:10.1016/bs.apha.2015.09.001, PMID 26920010, archived from the original on 2021-08-28, retrieved 2019-12-19
- ↑ Davidoff, Robert A. (2002-02-14). Migraine: Manifestations, Pathogenesis, and Management. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-803135-2. Archived from the original on 2021-08-28. Retrieved 2020-08-05.
- ↑ Lipton RB, Diener HC, Robbins MS, Garas SY, Patel K (October 2017). "Caffeine in the management of patients with headache". The Journal of Headache and Pain. 18 (1): 107. doi:10.1186/s10194-017-0806-2. PMC 5655397. PMID 29067618.
- ↑ Hamel E (November 2007). "Serotonin and migraine: biology and clinical implications". Cephalalgia. 27 (11): 1293–300. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2007.01476.x. PMID 17970989. S2CID 26543041.
- ↑
- American Headache Society (September 2013). "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question". Choosing Wisely: An Initiative of the ABIM Foundation. Archived from the original on 6 December 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- Lewis DW, Dorbad D (September 2000). "The utility of neuroimaging in the evaluation of children with migraine or chronic daily headache who have normal neurological examinations". Headache. 40 (8): 629–32. doi:10.1046/j.1526-4610.2000.040008629.x. PMID 10971658.
- Silberstein SD (September 2000). "Practice parameter: evidence-based guidelines for migraine headache (an evidence-based review): report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology". Neurology. 55 (6): 754–62. doi:10.1212/WNL.55.6.754. PMID 10993991.
- Medical Advisory Secretariat (2010). "Neuroimaging for the evaluation of chronic headaches: an evidence-based analysis". Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series. 10 (26): 1–57. PMC 3377587. PMID 23074404.
- ↑ Cousins G, Hijazze S, Van de Laar FA, Fahey T (Jul–Aug 2011). "Diagnostic accuracy of the ID Migraine: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Headache. 51 (7): 1140–8. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2011.01916.x. PMID 21649653.
- ↑ "Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition". Cephalalgia. 38 (1): 1–211. January 2018. doi:10.1177/0333102417738202. PMID 29368949.
- ↑ Nappi G (September 2005). "Introduction to the new International Classification of Headache Disorders". The Journal of Headache and Pain. 6 (4): 203–4. doi:10.1007/s10194-005-0185-y. PMC 3452009. PMID 16362664.
- ↑ Negro A, Rocchietti-March M, Fiorillo M, Martelletti P (December 2011). "Chronic migraine: current concepts and ongoing treatments". European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences. 15 (12): 1401–20. PMID 22288302.
- ↑ 86.0 86.1 86.2 86.3 Davidoff, Robert A. (2002). Migraine : manifestations, pathogenesis, and management (2 ed.). Oxford [u.a.]: Oxford Univ. Press. p. 81. ISBN 9780195137057. Archived from the original on 2016-12-22.
- ↑ Russell G, Abu-Arafeh I, Symon DN (2002). "Abdominal migraine: evidence for existence and treatment options". Paediatric Drugs. 4 (1): 1–8. doi:10.2165/00128072-200204010-00001. PMID 11817981. S2CID 12289726.
- ↑ Lewis DW, Dorbad D (September 2000). "The utility of neuroimaging in the evaluation of children with migraine or chronic daily headache who have normal neurological examinations". Headache. 40 (8): 629–32. doi:10.1046/j.1526-4610.2000.040008629.x. PMID 10971658.
- ↑ Silberstein SD (September 2000). "Practice parameter: evidence-based guidelines for migraine headache (an evidence-based review): report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology". Neurology. 55 (6): 754–62. doi:10.1212/WNL.55.6.754. PMID 10993991.
- ↑ Medical Advisory Secretariat (2010). "Neuroimaging for the evaluation of chronic headaches: an evidence-based analysis". Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series. 10 (26): 1–57. PMC 3377587. PMID 23074404.
- ↑ 91.0 91.1 Oskoui M, Pringsheim T, Billinghurst L, Potrebic S, Gersz EM, Gloss D, et al. (September 2019). "Practice guideline update summary: Pharmacologic treatment for pediatric migraine prevention: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society". Neurology. 93 (11): 500–509. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000008105. PMC 6746206. PMID 31413170.
- ↑ Modi S, Lowder DM (January 2006). "Medications for migraine prophylaxis". American Family Physician. 73 (1): 72–8. PMID 16417067. Archived from the original on 2020-03-02. Retrieved 2020-08-05.
- ↑ Diener HC, Limmroth V (August 2004). "Medication-overuse headache: a worldwide problem". The Lancet. Neurology. 3 (8): 475–83. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(04)00824-5. PMID 15261608. S2CID 43840120.
- ↑ Fritsche G, Diener HC (November 2002). "Medication overuse headaches -- what is new?". Expert Opinion on Drug Safety. 1 (4): 331–8. doi:10.1517/14740338.1.4.331. PMID 12904133. S2CID 23422679.
- ↑ Kaniecki R, Lucas S (2004). "Treatment of primary headache: preventive treatment of migraine". Standards of care for headache diagnosis and treatment. Chicago: National Headache Foundation. pp. 40–52.
- ↑ 96.0 96.1 96.2 Loder E, Burch R, Rizzoli P (June 2012). "The 2012 AHS/AAN guidelines for prevention of episodic migraine: a summary and comparison with other recent clinical practice guidelines". Headache. 52 (6): 930–45. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2012.02185.x. PMID 22671714.
- ↑ Locher C, Kossowsky J, Koechlin H, Lam TL, Barthel J, Berde CB, et al. (February 2020). "Efficacy, Safety, and Acceptability of Pharmacologic Treatments for Pediatric Migraine Prophylaxis: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis". JAMA Pediatrics. 174 (4): 341. doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.5856. PMC 7042942. PMID 32040139.
- ↑ Rajapakse T, Pringsheim T (April 2016). "Nutraceuticals in Migraine: A Summary of Existing Guidelines for Use". Headache. 56 (4): 808–16. doi:10.1111/head.12789. PMID 26954394.
- ↑ Teigen L, Boes CJ (September 2015). "An evidence-based review of oral magnesium supplementation in the preventive treatment of migraine". Cephalalgia. 35 (10): 912–22. doi:10.1177/0333102414564891. PMID 25533715. S2CID 25398410.
- ↑ 100.0 100.1 Silberstein SD, Holland S, Freitag F, Dodick DW, Argoff C, Ashman E (April 2012). "Evidence-based guideline update: pharmacologic treatment for episodic migraine prevention in adults: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society". Neurology. 78 (17): 1337–45. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182535d20. PMC 3335452. PMID 22529202.
- ↑ Shamliyan TA, Choi JY, Ramakrishnan R, Miller JB, Wang SY, Taylor FR, Kane RL (September 2013). "Preventive pharmacologic treatments for episodic migraine in adults". Journal of General Internal Medicine. 28 (9): 1225–37. doi:10.1007/s11606-013-2433-1. PMC 3744311. PMID 23592242.
- ↑ Ibekwe, A.; Perras, C.; Mierzwinski-Urban, M. (2016). "Monoclonal Antibodies to Prevent Migraine Headaches". PMID 30855775.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ Loder E, Renthal W (March 2019). "Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Monoclonal Antibody Treatments for Migraine". JAMA Internal Medicine. 179 (3): 421–422. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.7536. PMID 30640381. S2CID 58601441.
- ↑ Linde K, Allais G, Brinkhaus B, Fei Y, Mehring M, Vertosick EA, et al. (June 2016). "Acupuncture for the prevention of episodic migraine". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (6): CD001218. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001218.pub3. PMC 4977344. PMID 27351677.
- ↑ Chaibi A, Tuchin PJ, Russell MB (April 2011). "Manual therapies for migraine: a systematic review". The Journal of Headache and Pain. 12 (2): 127–33. doi:10.1007/s10194-011-0296-6. PMC 3072494. PMID 21298314.
- ↑ Millstine D, Chen CY, Bauer B (May 2017). "Complementary and integrative medicine in the management of headache". BMJ. 357: j1805. doi:10.1136/bmj.j1805. PMID 28512119. S2CID 19155758.
- ↑ 107.0 107.1 Posadzki P, Ernst E (June 2011). "Spinal manipulations for the treatment of migraine: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials". Cephalalgia. 31 (8): 964–70. doi:10.1177/0333102411405226. PMID 21511952. S2CID 31205541.
- ↑ Long, C; Ye, J; Chen, M; Gao, D; Huang, Q (2 May 2022). "Effectiveness of yoga therapy for migraine treatment: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies". The American journal of emergency medicine. 58: 95–99. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.050. PMID 35660369.
- ↑ Amin FM, Aristeidou S, Baraldi C, Czapinska-Ciepiela EK, Ariadni DD, Di Lenola D, et al. (September 2018). "The association between migraine and physical exercise". The Journal of Headache and Pain. 19 (1): 83. doi:10.1186/s10194-018-0902-y. PMC 6134860. PMID 30203180.
- ↑ Holland S, Silberstein SD, Freitag F, Dodick DW, Argoff C, Ashman E (April 2012). "Evidence-based guideline update: NSAIDs and other complementary treatments for episodic migraine prevention in adults: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society". Neurology. 78 (17): 1346–53. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182535d0c. PMC 3335449. PMID 22529203.
- ↑ Pringsheim T, Davenport W, Mackie G, Worthington I, Aubé M, Christie SN, et al. (March 2012). "Canadian Headache Society guideline for migraine prophylaxis". The Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences. 39 (2 Suppl 2): S1-59. PMID 22683887.
- ↑ "Butterbur: Uses, Side Effects, Interactions, Dosage, and Warning". www.webmd.com. Archived from the original on 2019-12-07. Retrieved 2019-12-07.
- ↑ "Butterbur". NCCIH. 2012-02-08. Archived from the original on 2019-12-07. Retrieved 2019-12-07.
- ↑ Littarru GP, Tiano L (November 2005). "Clinical aspects of coenzyme Q10: an update". Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care. 8 (6): 641–6. doi:10.1097/01.mco.0000171123.60665.16. PMID 16205466.
- ↑ 115.0 115.1 115.2 115.3 Gelfand AA, Goadsby PJ (September 2016). "The Role of Melatonin in the Treatment of Primary Headache Disorders". Headache (Review). 56 (8): 1257–66. doi:10.1111/head.12862. PMC 5012937. PMID 27316772.
- ↑ Long R, Zhu Y, Zhou S (January 2019). "Therapeutic role of melatonin in migraine prophylaxis: A systematic review". Medicine. 98 (3): e14099. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000014099. PMC 6370052. PMID 30653130.
- ↑ Nesbitt AD, Leschziner GD, Peatfield RC (September 2014). "Headache, drugs and sleep". Cephalalgia (Review). 34 (10): 756–66. doi:10.1177/0333102414542662. PMID 25053748. S2CID 33548757.
- ↑ Nestoriuc Y, Martin A (March 2007). "Efficacy of biofeedback for migraine: a meta-analysis". Pain. 128 (1–2): 111–27. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2006.09.007. PMID 17084028. S2CID 23351902.
- ↑ Nestoriuc Y, Martin A, Rief W, Andrasik F (September 2008). "Biofeedback treatment for headache disorders: a comprehensive efficacy review". Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback. 33 (3): 125–40. doi:10.1007/s10484-008-9060-3. PMID 18726688. S2CID 29122354.
- ↑ Schoenen J, Allena M, Magis D (2010). "Neurostimulation therapy in intractable headaches". In Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW (eds.). Headache. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Vol. 97. pp. 443–50. doi:10.1016/S0072-9752(10)97037-1. ISBN 9780444521392. PMID 20816443.
- ↑ Reed KL, Black SB, Banta CJ, Will KR (March 2010). "Combined occipital and supraorbital neurostimulation for the treatment of chronic migraine headaches: initial experience". Cephalalgia. 30 (3): 260–71. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2009.01996.x. PMID 19732075. S2CID 18639211.
- ↑ "FDA allows marketing of first medical device to prevent migraine headaches". Mar 11, 2014. Archived from the original on 25 July 2014. Retrieved 25 July 2014.
- ↑ "FDA approves transcranial magnetic stimulator" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2014-02-21.
- ↑ Tao H, Wang T, Dong X, Guo Q, Xu H, Wan Q (May 2018). "Effectiveness of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for the treatment of migraine: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials". The Journal of Headache and Pain. 19 (1): 42. doi:10.1186/s10194-018-0868-9. PMC 5975046. PMID 29845369.
We found significant reduction of monthly headache days
- ↑ Kung TA, Guyuron B, Cederna PS (January 2011). "Migraine surgery: a plastic surgery solution for refractory migraine headache". Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 127 (1): 181–9. doi:10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181f95a01. PMID 20871488. S2CID 18817383.
- ↑ "American Headache Society Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question". Choosing Wisely. Archived from the original on 3 December 2013. Retrieved 24 November 2013.
- ↑ Rabbie R, Derry S, Moore RA (April 2013). "Ibuprofen with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (4): CD008039. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008039.pub3. PMC 4161114. PMID 23633348.
- ↑ Derry S, Rabbie R, Moore RA (April 2013). "Diclofenac with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (4): CD008783. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008783.pub3. PMC 4164457. PMID 23633360.
- ↑ Kirthi V, Derry S, Moore RA (April 2013). "Aspirin with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (4): CD008041. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008041.pub3. PMC 4163048. PMID 23633350.
- ↑ Derry S, Moore RA (April 2013). "Paracetamol (acetaminophen) with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (4): CD008040. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008040.pub3. PMC 4161111. PMID 23633349.
- ↑ Eken C (March 2015). "Critical reappraisal of intravenous metoclopramide in migraine attack: a systematic review and meta-analysis". The American Journal of Emergency Medicine. 33 (3): 331–7. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2014.11.013. PMID 25579820.
- ↑ 132.0 132.1 132.2 132.3 Orr SL, Friedman BW, Christie S, Minen MT, Bamford C, Kelley NE, Tepper D (June 2016). "Management of Adults With Acute Migraine in the Emergency Department: The American Headache Society Evidence Assessment of Parenteral Pharmacotherapies". Headache. 56 (6): 911–40. doi:10.1111/head.12835. PMID 27300483.
- ↑ Johnston MM, Rapoport AM (August 2010). "Triptans for the management of migraine". Drugs. 70 (12): 1505–18. doi:10.2165/11537990-000000000-00000. PMID 20687618. S2CID 41613179.
- ↑ Law S, Derry S, Moore RA (April 2016). "Sumatriptan plus naproxen for the treatment of acute migraine attacks in adults". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 4: CD008541. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008541.pub3. PMC 6485397. PMID 27096438.
- ↑ 135.0 135.1 "Generic migraine drug could relieve your pain and save you money". Best Buy Drugs. Consumer Reports. Archived from the original on 2013-08-04.
- ↑ Tepper SJ, Tepper DE (April 2010). "Breaking the cycle of medication overuse headache". Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine. 77 (4): 236–42. doi:10.3949/ccjm.77a.09147. PMID 20360117. S2CID 36333666.
- ↑ 137.0 137.1 Sumamo Schellenberg, E.; Dryden, D. M.; Pasichnyk, D.; Ha, C.; Vandermeer, B.; Friedman, B. W.; Colman, I.; Rowe, B. H. (2012). "Acute migraine treatment in emergency settings". PMID 23304741.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ Kelley NE, Tepper DE (January 2012). "Rescue therapy for acute migraine, part 1: triptans, dihydroergotamine, and magnesium". Headache. 52 (1): 114–28. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2011.02062.x. PMID 22211870.
- ↑ 139.0 139.1 Morren JA, Galvez-Jimenez N (December 2010). "Where is dihydroergotamine mesylate in the changing landscape of migraine therapy?". Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 11 (18): 3085–93. doi:10.1517/14656566.2010.533839. PMID 21080856. S2CID 44639896.
- ↑ Tfelt-Hansen P, Saxena PR, Dahlöf C, Pascual J, Láinez M, Henry P, et al. (January 2000). "Ergotamine in the acute treatment of migraine: a review and European consensus". Brain. 123 ( Pt 1): 9–18. doi:10.1093/brain/123.1.9. PMID 10611116.
- ↑ Colman I, Friedman BW, Brown MD, Innes GD, Grafstein E, Roberts TE, Rowe BH (June 2008). "Parenteral dexamethasone for acute severe migraine headache: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials for preventing recurrence". BMJ. 336 (7657): 1359–61. doi:10.1136/bmj.39566.806725.BE. PMC 2427093. PMID 18541610.
- ↑ Piatka C, Beckett RD (February 2020). "Propofol for Treatment of Acute Migraine in the Emergency Department: A Systematic Review". Academic Emergency Medicine. 27 (2): 148–160. doi:10.1111/acem.13870. PMID 31621134.
- ↑ Vukovic Cvetkovic V, Jensen RH (January 2019). "Neurostimulation for the treatment of chronic migraine and cluster headache". Acta Neurologica Scandinavica. 139 (1): 4–17. doi:10.1111/ane.13034. PMID 30291633. S2CID 52923061.
- ↑ 144.0 144.1 144.2 144.3 Richer L, Billinghurst L, Linsdell MA, Russell K, Vandermeer B, Crumley ET, et al. (April 2016). "Drugs for the acute treatment of migraine in children and adolescents". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 4: CD005220. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005220.pub2. PMC 6516975. PMID 27091010.
- ↑ 145.0 145.1 Oskoui M, Pringsheim T, Holler-Managan Y, Potrebic S, Billinghurst L, Gloss D, et al. (September 2019). "Practice guideline update summary: Acute treatment of migraine in children and adolescents: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society". Neurology. 93 (11): 487–499. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000008095. PMID 31413171.
- ↑ Koechlin, H; Kossowsky, J; Lam, TL; Barthel, J; Gaab, J; Berde, CB; Schwarzer, G; Linde, K; Meissner, K; Locher, C (April 2021). "Nonpharmacological Interventions for Pediatric Migraine: A Network Meta-analysis". Pediatrics. 147 (4). doi:10.1542/peds.2019-4107. PMID 33688031.
- ↑ Herd CP, Tomlinson CL, Rick C, Scotton WJ, Edwards J, Ives N, et al. (June 2018). "Botulinum toxins for the prevention of migraine in adults". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 6: CD011616. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011616.pub2. PMC 6513576. PMID 29939406.
- ↑ Jackson JL, Kuriyama A, Hayashino Y (April 2012). "Botulinum toxin A for prophylactic treatment of migraine and tension headaches in adults: a meta-analysis". JAMA. 307 (16): 1736–45. doi:10.1001/jama.2012.505. PMID 22535858.
- ↑ Simpson DM, Hallett M, Ashman EJ, Comella CL, Green MW, Gronseth GS, et al. (May 2016). "Practice guideline update summary: Botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of blepharospasm, cervical dystonia, adult spasticity, and headache: Report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology". Neurology. 86 (19): 1818–26. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000002560. PMC 4862245. PMID 27164716.
- ↑ Ton, Joey (13 May 2019). "#235 Toxins for Health? Botulinum toxin for migraine". CFPCLearn. Archived from the original on 1 July 2023. Retrieved 15 June 2023.
- ↑ Markham A (July 2018). "Erenumab: First Global Approval". Drugs. 78 (11): 1157–1161. doi:10.1007/s40265-018-0944-0. PMID 29968151. S2CID 49559342.
- ↑ 152.0 152.1 Schürks M, Rist PM, Shapiro RE, Kurth T (September 2011). "Migraine and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Cephalalgia. 31 (12): 1301–14. doi:10.1177/0333102411415879. PMC 3175288. PMID 21803936.
- ↑ 153.0 153.1 153.2 Schürks M, Rist PM, Bigal ME, Buring JE, Lipton RB, Kurth T (October 2009). "Migraine and cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis". BMJ. 339: b3914. doi:10.1136/bmj.b3914. PMC 2768778. PMID 19861375.
- ↑ Kurth T, Chabriat H, Bousser MG (January 2012). "Migraine and stroke: a complex association with clinical implications". The Lancet. Neurology. 11 (1): 92–100. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70266-6. PMID 22172624. S2CID 31939284.
- ↑ Rist PM, Diener HC, Kurth T, Schürks M (June 2011). "Migraine, migraine aura, and cervical artery dissection: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Cephalalgia. 31 (8): 886–96. doi:10.1177/0333102411401634. PMC 3303220. PMID 21511950.
- ↑ Kurth T (March 2010). "The association of migraine with ischemic stroke". Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports. 10 (2): 133–9. doi:10.1007/s11910-010-0098-2. PMID 20425238. S2CID 27227332.
- ↑ Weinberger J (March 2007). "Stroke and migraine". Current Cardiology Reports. 9 (1): 13–9. doi:10.1007/s11886-007-0004-y. PMID 17362679. S2CID 46681674.
- ↑ Hougaard A, Amin FM, Ashina M (June 2014). "Migraine and structural abnormalities in the brain". Current Opinion in Neurology. 27 (3): 309–14. doi:10.1097/wco.0000000000000086. PMID 24751961.
- ↑ Wang SJ (March 2003). "Epidemiology of migraine and other types of headache in Asia". Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports. 3 (2): 104–8. doi:10.1007/s11910-003-0060-7. PMID 12583837. S2CID 24939546.
- ↑ Natoli JL, Manack A, Dean B, Butler Q, Turkel CC, Stovner L, Lipton RB (May 2010). "Global prevalence of chronic migraine: a systematic review". Cephalalgia. 30 (5): 599–609. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2009.01941.x. PMID 19614702. S2CID 5328642.
- ↑ 161.0 161.1 Hershey AD (February 2010). "Current approaches to the diagnosis and management of paediatric migraine". The Lancet. Neurology. 9 (2): 190–204. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70303-5. PMID 20129168. S2CID 12603488.
- ↑ 162.0 162.1 Nappi RE, Sances G, Detaddei S, Ornati A, Chiovato L, Polatti F (June 2009). "Hormonal management of migraine at menopause". Menopause International. 15 (2): 82–6. doi:10.1258/mi.2009.009022. PMID 19465675. S2CID 23204921.
- ↑ 163.0 163.1 163.2 163.3 163.4 Borsook, David (2012). The migraine brain : imaging, structure, and function. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 3–11. ISBN 9780199754564. Archived from the original on 2017-03-13.
- ↑ 164.0 164.1 Steven D. Waldman (2011). Pain management (2 ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders. pp. 2122–2124. ISBN 9781437736038. Archived from the original on 2021-04-28. Retrieved 2020-08-05.
- ↑ "Sex(ism), Drugs, and Migraines". Distillations. Science History Institute. January 15, 2019. Archived from the original on March 14, 2021. Retrieved February 6, 2020.
- ↑ Cox, Margaret; Mays, Simon (2002). Human osteology : in archaeology and forensic science (Repr. ed.). Cambridge [etc.]: Cambridge University Press. p. 345. ISBN 9780521691468. Archived from the original on 2013-06-17.
- ↑ Colen, Chaim (2008). Neurosurgery. Colen Publishing. p. 1. ISBN 9781935345039. Archived from the original on 2021-04-28. Retrieved 2020-08-05.
- ↑ Daniel, Britt Talley (2010). Migraine. Bloomington, IN: AuthorHouse. p. 101. ISBN 9781449069629. Archived from the original on 2017-03-13.
- ↑ 169.0 169.1 Tfelt-Hansen PC, Koehler PJ (May 2011). "One hundred years of migraine research: major clinical and scientific observations from 1910 to 2010". Headache. 51 (5): 752–78. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2011.01892.x. PMID 21521208.
- ↑ 170.0 170.1 170.2 Stovner LJ, Andrée C (June 2008). "Impact of headache in Europe: a review for the Eurolight project". The Journal of Headache and Pain. 9 (3): 139–46. doi:10.1007/s10194-008-0038-6. PMC 2386850. PMID 18418547.
- ↑ 171.0 171.1 Mennini FS, Gitto L, Martelletti P (August 2008). "Improving care through health economics analyses: cost of illness and headache". The Journal of Headache and Pain. 9 (4): 199–206. doi:10.1007/s10194-008-0051-9. PMC 3451939. PMID 18604472.
- ↑ Magis D, Jensen R, Schoenen J (June 2012). "Neurostimulation therapies for primary headache disorders: present and future". Current Opinion in Neurology. 25 (3): 269–76. doi:10.1097/WCO.0b013e3283532023. PMID 22543428.
- ↑ Jürgens TP, Leone M (June 2013). "Pearls and pitfalls: neurostimulation in headache". Cephalalgia. 33 (8): 512–25. doi:10.1177/0333102413483933. PMID 23671249. S2CID 42537455.
- ↑ Barbanti P, Fofi L, Aurilia C, Egeo G, Caprio M (May 2017). "Ketogenic diet in migraine: rationale, findings and perspectives". Neurological Sciences (Review). 38 (Suppl 1): 111–115. doi:10.1007/s10072-017-2889-6. PMID 28527061. S2CID 3805337.
- ↑ Gross EC, Klement RJ, Schoenen J, D'Agostino DP, Fischer D (April 2019). "Potential Protective Mechanisms of Ketone Bodies in Migraine Prevention". Nutrients. 11 (4): 811. doi:10.3390/nu11040811. PMC 6520671. PMID 30974836.
- Notes
- Olesen, Jes (2006). The headaches (3 ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 9780781754002. Archived from the original on 2021-04-28. Retrieved 2020-08-05.
External links
- Migraine at Curlie
- 2019 Guideline on migraine prevention in children Archived 2019-08-28 at the Wayback Machine
- 2019 Guideline on migraine treatment in children Archived 2019-08-28 at the Wayback Machine
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
- Pages with script errors
- Webarchive template wayback links
- CS1: long volume value
- CS1 errors: unsupported parameter
- CS1 maint: unrecognized language
- All articles with dead external links
- Articles with dead external links from September 2017
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- Articles with permanently dead external links
- CS1 errors: missing periodical
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Good articles
- Articles with medical app sidebar
- Articles with Curlie links
- Migraine
- RTT(full)
- RTTNEURO
- RTT
- WHRTT
