Macula densa
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2015) |
| Macula densa | |
|---|---|
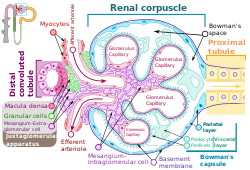 Renal corpuscle showing the macula densa. | |
| Identifiers | |
| FMA | 86333 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In the kidney, the macula densa is an area of closely packed specialized cells lining the wall of the distal tubule where it touches the glomerulus. Specifically, the macula densa is found in the terminal portion of the distal straight tubule (thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle), after which the distal convoluted tubule begins.[1][2][3]
The cells of the macula densa are sensitive to the concentration of sodium chloride in the thick ascending loop of henle. A decrease in sodium chloride concentration initiates a signal from the macula densa that has two effects: (1) it decreases resistance to blood flow in the afferent arterioles, which raises glomerular hydrostatic pressure and helps return the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) toward normal, and (2) it increases renin release from the juxtaglomerular cells of the afferent and efferent arterioles, which are the major storage sites for renin.[4]
As such, an increase in sodium chloride concentration would result in vasoconstriction of afferent arterioles, and reduced paracrine stimulation of juxtaglomerular cells. This demonstrates the macula densa feedback, where compensatory mechanisms act in order to return GFR to normal.
The release of renin is an essential component of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS), which regulates blood pressure and volume.
Histology
The cells of the macula densa are taller and have more prominent nuclei than surrounding cells of the distal straight tubule (cortical thick ascending limb).
The close proximity and prominence of the nuclei cause this segment of the distal tubule wall to appear darker in microscopic preparations,[5] hence the name macula densa.
Function

Macula densa cells sense changes in sodium chloride level, and will trigger an autoregulatory response to increase or decrease reabsorption of ions and water to the blood (as needed) in order to alter blood volume and return blood pressure to normal.
A decrease in afferent arteriole diameter causes a decrease in the GFR (glomerular filtration rate), resulting in a decreased concentration of sodium and chloride ions in the filtrate and/or decreased filtrate flow rate. Reduced blood pressure means decreased venous pressure and, hence, a decreased peritubular capillary pressure. This results in a smaller capillary hydrostatic pressure, which causes an increased absorption of sodium ions into the vasa recta at the proximal tubule.
Hence, a decrease in blood pressure results in less sodium chloride present at the distal tubule, where the macula densa is located. The macula densa senses this drop in salt concentration and responds through two mechanisms, both of which are mediated by prostaglandin release.[6] First, prostaglandins preferentially vasodilate the renal afferent arteriole, decreasing afferent arteriole resistance and, thus, offsetting the decrease in glomerular hydrostatic pressure caused by the drop in blood pressure. Second, prostaglandin activates prostaglandin-sensitive specialized smooth muscle cells of the renal afferent arterioles, juxtaglomerular cells (JG cells), to release renin into the bloodstream. The JG cells can also release renin independently of the macula densa. There are stretch-sensitive baroreceptors lining the arterioles that will release renin if a fall in blood pressure (i.e. decreased stretch of arteriole due to less blood flow) in the arterioles is detected. Furthermore, JG cells contain beta-1 adrenergic receptors, and so activation of the sympathetic nervous system will further stimulate renin release.
Thus, a drop in blood pressure results in preferential vasodilation of the afferent arterioles, increasing renal blood flow (RBF), renal plasma flow (RPF) and GFR due to greater blood flow to the glomerulus. Note that there is no change in filtration fraction, as both GFR and RPF are increased. It also results in the release of renin, which, through the renin–angiotensin system, causes constriction of the efferent arterioles, which ultimately increases hydrostatic pressure in the glomerulus.
The process triggered by the macula densa helps keep the GFR fairly steady in response to varying artery pressure.
Damage to the macula densa would impact blood flow to the kidneys because the afferent arterioles would not dilate in response to a decrease in filtrate osmolarity and pressure at the glomerulus would not be increased. As part of the body's blood pressure regulation, the macula densa monitors filtrate osmolarity; if it falls too far, the macula densa causes the efferent arterioles of the kidney to contract, thus increasing the pressure at the glomerulus and increasing the glomerular filtration rate.
See also
References
- ^ Gonzalez-Vicente, Agustin; Saez, Fara; Monzon, Casandra M.; Asirwatham, Jessica; Garvin, Jeffrey L. (2019). "Thick Ascending Limb Sodium Transport in the Pathogenesis of Hypertension". Physiological Reviews. 99 (1): 235–309. doi:10.1152/physrev.00055.2017. PMC 6335098. PMID 30354966.
- ^ "Tubuloglomerular Feedback - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics".
- ^ Mount, David B. (2014). "Thick Ascending Limb of the Loop of Henle". Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 9 (11): 1974–1986. doi:10.2215/CJN.04480413. PMC 4220766. PMID 25318757.
- ^ Guyton & Hall Textbook Of Physiology, 11th Edition 2006, p. 324
- ^ Histology image:16010loa from Vaughan, Deborah (2002). A Learning System in Histology: CD-ROM and Guide. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0195151732.
- ^ Peti-Peterdi, János; Harris, Raymond C. (July 2010). "Macula Densa Sensing and Signaling Mechanisms of Renin Release". Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 21 (7): 1093–1096. doi:10.1681/ASN.2009070759. ISSN 1046-6673. PMC 4577295. PMID 20360309.
External links
- Anatomy photo: Urinary/mammal/cortex1/cortex5 - Comparative Organology at University of California, Davis - "Mammal, kidney cortex (LM, Medium)"
- Nosek, Thomas M. "Section 7/7ch03/7ch03p17". Essentials of Human Physiology. Archived from the original on 2016-03-24. - "The Nephron: Juxtaglomerular Apparatus"