Losartan/hydrochlorothiazide
| Combination of | |
|---|---|
| Losartan | Angiotensin II receptor antagonist |
| Hydrochlorothiazide | Thiazide diuretic |
| Names | |
| Trade names | Anzaplus, Cozaar comp, Hyzaar, Ocsaar Plus |
| Clinical data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | By mouth |
| Defined daily dose | not established[1] |
| Legal | |
| Legal status |
|
Losartan/hydrochlorothiazide, sold under the trade name Hyzaar among others, is a combination medication used to treat high blood pressure when losartan is not sufficient.[2] It consists of losartan (an angiotensin II receptor antagonist) and hydrochlorothiazide (a diuretic).[2] It is taken by mouth.[2]
Common side effects include dizziness, back pain, and upper respiratory tract infections.[3] Serious side effects may include low blood pressure, kidney problems, allergic reactions, and electrolyte problems.[3] Use in pregnancy and breastfeeding is not recommended.[4] Losartan works by blocking the effects of angiotensin II while hydrochlorothiazide works by decreasing the ability of the kidneys to absorb electrolytes.[3] Interactions include with lithium, agents which increase potassium, and NSAIDs.[3]
The combination was approved for medical use in the United States in 1995.[3] It is available as a generic medication.[2] A month supply in the United Kingdom costs the NHS about 1.50 £ per month as of 2019.[2] In the United States the wholesale cost of this amount is about US$2.50.[5] In 2017, it was the 67th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than eleven million prescriptions.[6][7]
Medical uses
It is used for high blood pressure (hypertension) once a day. Based on the initial blood pressure response and/or losartan-hydrochlorothiazide side effects, the dosage may be increased or decreased. With each change in dosage, it may take up to a month to see the full effect.
Dosage
The defined daily dose is not established[1]
Side Effects
Common side effects include dizziness, headache, back pain, rash, fever, diarrhea, cough, and upper respiratory tract infections. [3] Serious side effects may include low blood pressure, kidney problems, allergic reactions, and electrolyte problems.[3]
Drug interactions
Drug interactions to be aware of include lithium, agents increasing serum levels of potassium, and the use of hydrochlorothiazide with antidiabetic drugs both oral agents and insulin.[3]
Mechanisms
Losartan works by blocking the effects of angiotensin II by preventing it from binding to the angiotensin I receptor while hydrochlorothiazide works by decreasing the ability of the kidneys to absorb electrolytes. The effects of hydrochlorothiazide indirectly lower the levels of serum potassium. However, with coadministration of losartan which is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist, the low levels of potassium are reversed.[3]
Brand names
The losartan/hydrochlorothiazide combination preparation is marketed by Merck under the trade name Hyzaar and by Xeno Pharmaceuticals under the name Anzaplus. Merck, Sharp & Dohme market it as Ocsaar Plus in Israel. It is marketed as Cozaar comp in Sweden and South Africa.
Society and culture
Cost
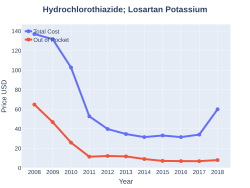
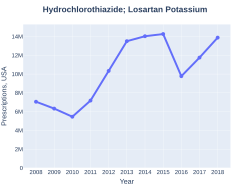
A month supply in the United Kingdom costs the NHS about 1.50 £ per month as of 2019.[2] In the United States the wholesale cost of this amount is about US$2.50.[5] In 2017, it was the 67th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than eleven million prescriptions.[6][7]
-
Losartan/hydrochlorothiazide costs (US)
-
Losartan/hydrochlorothiazide prescriptions (US)
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "WHOCC - ATC/DDD Index". www.whocc.no. Archived from the original on 1 July 2021. Retrieved 10 September 2020.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. p. 176. ISBN 9780857113382.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 "Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide - FDA prescribing information, side effects and uses". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 29 June 2019. Retrieved 6 March 2019.
- ↑ "Hydrochlorothiazide / losartan Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Warnings". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 29 June 2019. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "NADAC as of 2019-02-27". Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Archived from the original on 2019-03-06. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "The Top 300 of 2020". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 12 February 2021. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Hydrochlorothiazide; Losartan Potassium - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 11 April 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|---|
- Pages using duplicate arguments in template calls
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Chemical articles without CAS registry number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs missing an ATC code
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Drugs that are a combination of chemicals
- Combination drugs
- Angiotensin II receptor antagonists
- Merck & Co. brands
- RTT
- All stub articles
- Cardiovascular system drug stubs