Laugier–Hunziker syndrome
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Laugier–Hunziker syndrome | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
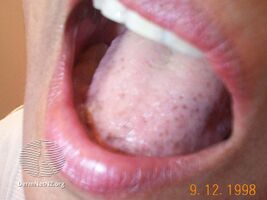
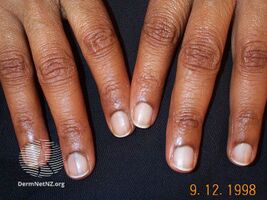
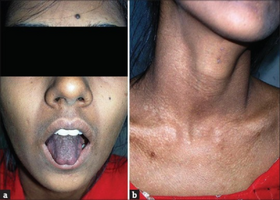
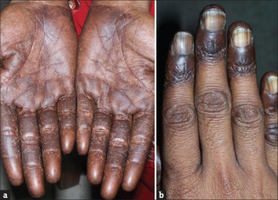
Laugier–Hunziker syndrome (/ˈloʊʒieɪ ˈhʊntsɪkər/) is a cutaneous condition characterized by hyperpigmentation of the oral mucosa,[1] longitudinal melanonychia,[1] and genital melanosis.[2]
The hyperpigmentation presented in Laugier-Hunziker syndrome is benign and should be differentiated from Peutz-Jeghers syndrome.
-
Laugier-Hunziker syndrome
-
Laugier-Hunziker syndrome
-
-
-