Juvenile idiopathic arthritis
| Juvenile idiopathic arthritis | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis | |
| Specialty | Rheumatology |
| Frequency | 1 in 1,000[1] |
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), is the most common, chronic rheumatic disease of childhood, affecting approximately one per 1,000 children.[1] Juvenile, in this context, refers to disease onset before 16 years of age, while idiopathic refers to a condition with no defined cause, and arthritis is inflammation within the joint.[2]
JIA is an autoimmune, noninfective, inflammatory joint disease, the cause of which remains poorly understood. It is characterised by chronic joint inflammation. JIA is a subset of childhood arthritis, but unlike other, more transient forms of childhood arthritis, JIA persists for at least 6 weeks, and in some children is a lifelong condition. It differs significantly from forms of arthritis commonly seen in adults (osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis), in terms of cause, disease associations, and prognosis.
The prognosis for children with JIA has improved dramatically over recent decades, particularly with the introduction of biological therapies and a shift towards more aggressive treatment strategies. JIA treatment aims for normal physical and psychosocial functioning, which is an achievable goal for many children with this condition.[3]
Signs and symptoms
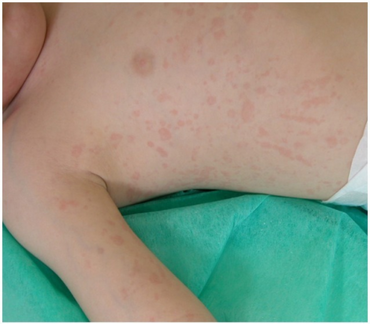
Arthritis means inflammation within the joint, and is usually recognised by swelling, pain, stiffness and restricted joint movement. Symptoms of JIA vary from individual to individual. This is mainly because JIA is an umbrella term for several subtypes of JIA, which differ according to the number of affected joints, severity of disease and presence or absence of inflammation in other parts of the body.[citation needed]
The key clinical feature in JIA is persistent swelling of the affected joints. Any joint can be affected, but large joints such as the knee and ankle are most commonly involved.[4] Involvement of small joints of the hands and feet is more likely when many joints are affected ('polyarthritis'). Swollen joints may also feel warmer to touch. Swelling may be difficult to detect clinically, especially for joints such as those of the spine, sacroiliac joints, shoulder, hip, and jaw; imaging techniques such as ultrasound or MRI can be very useful to identify the inflammation.[citation needed]
Joint pain is an important symptom, although some children experience minimal or no pain with their arthritis.[5] In these children, the first sign of arthritis may be limping, especially in the morning.[5] Young children are often very good at changing how they move when they have joint pain: they learn to move so that it doesn’t hurt. For example, a child will not push up using an inflamed wrist when climbing, instead putting their weight though the forearm. Morning stiffness that improves later in the day is a common feature (this implies inflammatory-type joint pain versus mechanical-type joint pain).
Swelling and pain usually result in limited movement of the affected joints, for example a knee held bent causing a limp, or being unable to make a full fist. Limited movement may reduce a child’s ability to fully participate in activities and undertake usual tasks such as those used for self-care. In some JIA subtypes, more non-specific symptoms of being unwell may be present, such as lethargy, fatigue and poor appetite. Children with systemic JIA usually present with fever and a classic rash and may become quite ill. Late effects of arthritis can include joint contractures (stiff, bent joints with loss of movement) due to joint damage; limb length discrepancies and muscle wasting. Children with JIA vary in the degree to which they are affected by particular symptoms.
Extra-articular
Eye disease: JIA is associated with inflammation in the front of the eye (specifically iridocyclitis, a form of chronic anterior uveitis), which affects about one in six children with JIA. Eye involvement occurs most commonly in girls, those with only a few joints involved (oligoarthritis), and those with a positive ANA antibody.[6] It usually follows the onset of arthritis or may be detected at the same time as arthritis; occasionally it may occur before joint involvement. The factors linking eye and joint disease are not clearly understood, and the two do not necessarily follow the same course. This complication is usually asymptomatic (without symptoms) and can occur when the joints are not active. It can be detected by an experienced optometrist or ophthalmologist using a slit lamp to look for inflammatory cells in the fluid inside the eye. Most children with JIA will require referral for regular slit lamp screening examinations. Poorly controlled chronic anterior uveitis may result in permanent eye damage, including blindness.
Systemic JIA: children with the Systemic JIA subtype often experience extra-articular manifestations including fever, rash, enlarged lymph nodes, enlarged liver or spleen, serositis and anaemia.[3]
Complications
JIA is a chronic disorder, which if neglected, can lead to serious complications. However, with regular follow-up and modern treatments, complications have reduced and outcomes improved. If inflammation is not treated, it can damage the joint, the cartilage and the bone. With the advent of modern therapies, these complications of JIA have become much less common.[7]
Children with JIA may have a reduced overall rate of growth, especially if the disease involves many joints or other body systems.[8] This may be due to a combination of the disease itself, as well as its treatments, particularly corticosteroid use. Paradoxically, limbs where a large joint (such as the knee) is inflamed may have increased growth in the short term, leading to limb-length discrepancy (ie one arm or leg is slightly longer than the other). This is due to increased blood supply to the bony growth plates surrounding the inflamed joints. Bone density and bone strength may be reduced through a combination of inflammation, corticosteroid use and reduced physical activity levels.[9] Other musculoskeletal complications may include joint contractures, muscle weakness or muscle wasting.[citation needed]
Uveitis, if left untreated, can result in scarring, glaucoma, cataracts, and even blindness. Regular monitoring allows for early detection and treatment. Steroid eye drops are usually the first line treatment for anterior uveitis. However, other treatments - many of which also treat arthritis (eg methotrexate, biologics) - may be required to keep the inflammation under control, and to minimise steroid use over the longer term. Long term steroid use can cause contribute to the development of cataracts.[6]
Macrophage activation syndrome (MAS) is a severe, potentially life-threatening complication that can occur in patients with the systemic subtype of JIA. MAS involves uncontrolled activation of the immune system, sometimes referred to as a 'cytokine storm', which can present with a sepsis-like picture of fever, rash, enlarged liver and spleen, enlarged lymph nodes and cardiorespiratory compromise. It is recognised by a series of characteristic changes in laboratory parameters, including a high ferritin and a paradoxically low erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
Causes
The cause of JIA remains unknown. However, the disorder is autoimmune[10] — meaning that the body's own immune system starts to attack and destroy cells and tissues (particularly in the joints) for no apparent reason. The immune system is thought to be provoked by changes in the environment, in combination with mutations in many associated genes[11] and/or other causes of differential expression of genes. Experimental studies have shown that certain mutated viruses may be able to trigger JIA. The disease appears to be more common in girls, and is most common in Caucasians.[12]
The cause of JIA, as the word "idiopathic" suggests, is unknown and an area of active research.[13] Current understanding of JIA suggests that it arises in a genetically susceptible individual due to environmental factors.[14]
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of JIA can be difficult, in part because joint pain in children is so common and may be from many causes other than JIA.[15] The characteristic feature of arthritis is joint swelling which is sometimes - but not always - associated with pain. The presence of joint stiffness is another typical feature, particularly when present in the morning and improving with activity.
No single test can confirm a diagnosis of JIA: a combination of presenting signs and symptoms, blood tests, and if necessary medical imaging, is used to make the diagnosis. The blood tests may measure levels of inflammatory markers, as well as the presence of specific immune markers which may include Anti-nuclear antibody, HLA-B27, Rheumatoid factor and Anti–citrullinated protein antibody. These serological markers may be negative in children with JIA, and are often present in healthy children; as such they should not be interpreted in isolation but in the context of the clinical presentation. Many children with JIA have normal blood work. X-rays may be required to ensure that the joint pain and swelling is not from a fracture, cancer, infection, or congenital abnormality. In some cases, fluid from the joint can be aspirated and analysed to assist in making a diagnosis. This test can assist by ruling out other causes of arthritis such as infection.
Classification
The current classification system by the International League of Associations for Rheumatology (ILAR) recognizes 7 distinct subtypes of JIA, based on their presentation within the first 6 months: [16] Each subtype has a specific pattern of features as outlined in the table and descriptions below. (The seventh category, not included in the table, is 'Undifferentiated' and includes any patient with JIA who does not meet criteria for other subtypes, or who meets criteria for two or more subtypes).
| Oligoarticular | Polyarticular (RF negative) | Polyarticular (RF positive) | Systemic Onset | Psoriatic | Enthesitis Related Arthritis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % of JIA | 50-60 | 20-30 | 5-10 | 10-20 | 5-15 | 15 |
| Gender (F:M) | 4:1 | 4:1 | 9:1 | 1:1 | 3:2 | 1:9 |
| Typical age of onset (years) | 2-12 (peak 2-3) | 2-12 (peak 2-3) | Adolescence | Any | Mid childhood | Adolescence |
| Joint Pattern | Asymmetric; often large joints (knee, ankle, wrist, elbow) | Often asymmetric; multiple small and large joints | Symmetric; multiple small and large joints | Symmetric; multiple small and large joints | Asymmetric; small and large joints including hips and especially DIPs | Asymmetric; large joints; axial
skeleton |
| Extra-articular Involvement | Uveitis in 20% | Painless uveitis (especially if ANA positive) | Rheumatoid Nodules | Fever, rash, lymphadenopathy, enlarged liver and spleen, Serositis | Psoriasis, nail pitting, dactylitis, uveitis in 10%, enthesitis | Symptomatic uveitis in 20%, enthesitis, IBD, aortitis |
Oligoarticular Arthritis
Oligoarticular (or pauciarticular) JIA is the most common JIA subtype, and occurs when there are up to 4 joints involved during the first 6 months of disease. Two subtypes of oligoarticular arthritis exist: persistent oligoarthritis, where no more than 4 joints are affected throughout the whole disease course; and extended oligoarthritis, where more than 4 joints are affected after the first 6 months of disease. Patients in this subtype are often young, typically aged 2–3 years and with a female preponderance. The most commonly involved joint is the knee, but other affected joints may include the ankles, wrists, elbows and others. The Anti-nuclear antigen (ANA) is positive in up to 80% of patients with oligoarthritis and is associated with a higher risk of associated eye disease (Uveitis), particularly in younger patients.[6] The prefixes "oligo-" and "pauci-" mean "few".
Polyarticular (Rheumatoid Factor Negative) Arthritis
Arthritis involving 5 or more joints in the first 6 months of disease. In this subtype of arthritis both small and large joints are typically involved, usually in an asymmetric pattern. Involved joints may include the jaw (Temperomandibular joint) and cervical spine. Patients in this subtype are Rheumatoid factor negative; Anti-nuclear antibody is positive in approximately 25% of patients. Children with polyarticular JIA are also at risk of developing Uveitis and should also be monitored by an optometrist or ophthalmologist.
Polyarticular (Rheumatoid Factor Positive) Arthritis
Arthritis involving 5 or more joints in the first 6 months, with a positive Rheumatoid factor on at least 2 occasions, tested 3 months apart. In this subtype of arthritis both small and large joints are typically involved, usually in a symmetric pattern. The Anti-nuclear antibody may also be positive in up to 75% of patients. This subtype of arthritis behaves in a very similar fashion to the equivalent adult disease Rheumatoid arthritis. It affects mostly adolescent girls and is typically more aggressive than other forms of JIA in terms of joint damage and the development of erosions in surrounding bone. The clinical presentation is similar to that of Rheumatoid arthritis with a symmetric polyarthritis typically involving the PIP and MCP joints. Children may develop rheumatoid nodules and similar complications to adult disease, including joint erosions.
Systemic-onset Arthritis
This subtype is an arthritis which involves one or more joints and is associated with a fever of at least 2 weeks’ duration that is documented to be daily for at least 3 days. The fever is typically ‘quotidian’ in nature, occurring once or twice a day (often in the late afternoon or evening) with normal baseline temperatures in between. It is also associated with one or more of the following: a transient erythematous rash that often occurs in association with the fever; enlargement of multiple lymph nodes; the presence of an enlarged liver or spleen; or the presence of Serositis (inflammation surrounding the heart, lungs or abdominal cavity). The rash is often discrete, salmon-pink macules of different sizes which may migrate to different parts of the body. Patients with Systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis are at risk of a potentially life-threatening complication called Macrophage activation syndrome. Rheumatoid factor and ANA are generally negative in systemic JIA.[citation needed]
Enthesitis Related Arthritis
This subtype of arthritis is diagnosed by the presence of arthritis and enthesitis, or by the presence of arthritis or enthesitis alone with 2 or more of the following features: (1) Presence or history of sacroiliac joint tenderness and/or inflammatory back pain; (2) Presence of the HLA-B27 antigen; (3) Onset of arthritis in a male over 6 years of age; (4) Acute (symptomatic) anterior uveitis; or (5) a history of Ankylosing spondylitis, enthesitis related arthritis, sacroiliitis with Inflammatory bowel disease, or acute anterior Uveitis in a first-degree relative. Enthesitis is tenderness at the insertion sites of tendons, ligaments and fascia caused by inflammation. This type of arthritis is common in adolescent boys and typically affects large joints in the lower limbs, including the hips. It can also involve the Sacroiliac joint and the spine.
Psoriatic Arthritis
This subtype of arthritis is diagnosed by the combination of arthritis and Psoriasis or, arthritis and at least 2 of the following: Dactylitis, nail-pitting, or Psoriasis in a first-degree relative. Psoriatic arthritis is typically asymmetric in its pattern of joint involvement and can involve both large and small joints. A characteristic feature of this type of arthritis is dactylitis, which is caused by inflammation of the flexor tendon and synovium, resulting in sausage-shaped swelling of an entire finger or toe.
Undifferentiated Arthritis
This subtype is diagnosed when a child has JIA that fulfils criteria in none of the subtypes, or in 2 or more of the subtypes of JIA.
Differential diagnosis
There are several other disorders and diseases that present with symptoms like JIA. These causes include, but are not limited to, infectious (for example Septic arthritis or Osteomyelitis) and post-infectious conditions (Reactive arthritis, Acute rheumatic fever, and in some geographic areas Lyme disease); hematologic and neoplastic diseases such as leukemia or bony tumors; and other connective tissue diseases (such as Systemic lupus erythematosus). For the Systemic-onset form of JIA, the differential diagnosis also includes Kawasaki disease and periodic fever syndromes. Some genetic skeletal dysplasias as forms of Mucopolysaccharidosis especially type1 Scheie syndrome, progressive pseudorheumatoid dysplasia[17] and Multicentric Osteolysis, Nodulosis, and Arthropathy syndrome[18][19] may also mimic JIA, as they may present with joint swelling, joint restriction, stiffness, and pain. The clinical and radiologic overlap between genetic skeletal dysplasias and JIA can be great that molecular analysis may be need to confirm the diagnosis[17][18][19]. Rarely, metabolic diseases, such as Farber disease may also mimic JIA. Patients with Farber disease typically have subcutaneous nodules and a hoarse or weak voice due to growth of nodules on the larynx.
Treatment
The major emphasis of the treatment of JIA is helping the child or young person regain normal levels of physical and social functioning by controlling inflammation and extra-articular symptoms. Clinical remission should be the primary target for all patients and treatment should be adjusted until this is achieved.[20] Prompt recognition and management is important as early initiation of therapy increases the likelihood of a response to first-line treatments and of achieving drug-free remission later in life.[21] While overarching consensus treatment guidelines exist, all treatments should be specifically tailored to the individual's needs in discussion with the child or young person and their family.[22][23][24]
Optimal management of JIA requires a multidisciplinary team working to address the needs of an individual patient. Optimising physical and social functioning is accomplished via a two-pronged approach: non-pharmacological strategies such as physical therapies, pain management strategies, and social supports; and the swift use of medication to control inflammation and extra-articular symptoms.[22][25] Early diagnosis and treatment are imperative in helping reduce joint damage and other symptoms, which will help reduce levels of permanent damage leading to long term disability.
Pharmacological treatments
Major advances in drug treatments have been made over recent decades. Intra-articular steroid injections and Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including ibuprofen and naproxen, are often used as first line treatments for most subtypes of JIA. NSAIDs have useful analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties, although they are generally unlikely to lead to remission if used in isolation.
Systemic corticosteroids (oral or intravenous), such as prednisolone, dexamethasone and methylprednisolone, are highly effective treatments, however their utility is limited by their side-effect profile. They have a role in short-term disease control for some patients, but should generally be avoided as long-term treatment options.[20]
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are required to achieve sustained clinical remission in some patients. Conventional DMARDs include Methotrexate, Sulfasalazine and Leflunomide.
Biologic DMARDs are generally reserved as second-line therapy for patients where treatment with a conventional DMARD has failed. These medications target specific inflammatory cytokines such as Tumor necrosis factor alpha (etanercept, adalimumab, infliximab), Interleukin 6 (tocilizumab) and Interleukin 1 (anakinra).
There are several research groups exploring novel treatments for patients with JIA. Several new biologic DMARDs (anti-interleukin-17A, anti-interferon-gamma) and targeted small molecules (Janus kinase inhibitors) have shown promise in other diseases and are currently undergoing clinical trials in patients with JIA.
Evidence regarding the efficacy of complementary and alternative treatments in managing JIA is generally lacking. There are no controlled studies looking at dietary interventions for JIA and current recommendations suggest a healthy, balanced, age-appropriate diet that meets all nutritional needs.
Non-pharmacological treatments
The optimal approach to treating a child with JIA typically involves a team of medical professionals, which may include (but is not limited to) paediatric rheumatologists, paediatric rheumatology nurses, general paediatricians, general practitioners, adult rheumatologists, physical therapists, occupational therapists, podiatrists, psychologists, social workers, pharmacists, ophthalmologists and orthopaedic surgeons. The multi-disciplinary team (MDT) work in conjunction with the child and their parents, the local health service and medical team, the child's school and teachers, community leaders and sports coaches to best support the child and their family.[22]
Together, the team help children to participate as fully and independently as possible in their daily activities by maximising quality of life, maximising function and minimising disruption to the life of the child or young person.
The multidisciplinary team work together to provide the child and their family with support and education about JIA, strategies to promote age-appropriate self-sufficiency and help the child to adapt and adjust to any challenges they face. There are many ways to make daily tasks easier or more manageable. One of the key ways the multidisciplinary team helps children with JIA is to involve them, and their families, in the decision-making process regarding their treatment and rehabilitation.
In young children with JIA, symptoms may result in either delay or regression in developmental milestones such as walking, running or climbing. Upper limb function may also be affected. Members of the multidisciplinary team can perform developmental assessments to identify deficits and guide treatments. The information gathered can be shared with schools and child care facilities.
One of the key ways occupational or physical therapists help young children with JIA is by developing a home therapy program based around play. Exercises are prescribed by both PTs and OTs to increase the range a child can move a joint, to strengthen the muscles around a joint, to decrease pain and stiffness and to prevent further limitations in their joint movements. OTs and PTs can provide children with age-appropriate games and activities to allow the children to practice their exercises while playing and socializing with friends. Examples are crafts, swimming, and sports.[26]
Children with JIA may experience challenges with low mood, social interaction, reduced self-confidence and negative self-image. Psychologists, OT's, nurses, social workers and other team members can work with the child and their family to develop strategies to help with these issues. Many JIA support organisations run camps and activities for children with JIA and their families.
Surgery is only used to treat the most severe cases of JIA and is now rarely required.[3]
Physical therapy and Exercise
Maintaining physical activity is important in all children, but especially for children with JIA. The physical therapist has a role in guiding physical rehabilitation (muscle stretching and strengthening, enhancing joint range of movement, improving balance, etc); optimising physical functioning; goal-setting; and improving a child’s confidence in their own body. They usually work with the child and family to develop a home exercise program which changes over time as the child makes progress.
Arthritis in childhood can be associated with muscle weakness and wasting around the affected joints. It can also lead to low bone density, which may predispose to osteoporosis and fractures in adulthood. Getting regular exercise is an important part of the management of JIA to promote bone and muscle health.[27][28]
There is variation in the exact exercise prescription which best promotes musculoskeletal health whilst reducing fatigue, pain and swelling. Consensus is that children with JIA should be following national public health standards of physical activity and participating in moderate fitness, flexibility, and strengthening exercises, compatible with their abilities and disease restrictions.[29][30]
It is important that - across the week - the exercise is a combination of moderate to vigorous cardiovascular activity (eg walking to school, scooting, bike-riding, playing tag, dancing, doing P.E, sports such as basketball or football) and strengthening exercises. Bone strengthening activities build up muscles; by having the muscles push and pull against the bone, the bones themselves get stronger. This can include things like playing on climbing equipment, swinging on monkey-bars, using weights, carrying groceries, skipping or running.
A Cochrane meta-analysis looking at existing RCT’s showed in all studies that exercise does not have a detrimental effect on JIA. In fact, there is evidence to show that both low and high-intensity exercise programs result in improved physical function and reduced pain in children with JIA. Guidelines indicate that children with JIA should be encouraged to be physically active and can safely participate in sports without disease exacerbation. Those with actively inflamed joints should limit activities within pain limits, then gradually return to full activity following a disease flare.[29][31]
It may be necessary to use aids like splints or casts to correct biomechanics, but prolonged splinting and casting are now rarely indicated for children with JIA. Following joint injections, children are often advised to ‘take it easy’, often undertaking 1–2 days of low activity, although advice around this varies.[32] When a joint (usually a knee) loses range of motion due to prolonged inflammation and pain, a series of plaster casts may be used to gradually extend shortened muscles and restore range. These serial casts are usually applied over days to weeks. Active strengthening and lengthening is used in conjunction with serial casting for optimal results.
Some children may benefit from foot orthotics to support and correct body position and function. Orthotics maintain biomechanical alignment and may reduce discomfort in the legs and back when children participate in physical activities such as sports.
Occupational Therapy
Many children with JIA will benefit from seeing an Occupational Therapist, who can provide strategies to assist in to maximizing independence in activities and routines. For example, thinking about how to simplify tasks or using aids or equipment can allow a child to complete tasks themselves; OT’s also provide advice on how to make tasks easier, less painful and more enjoyable. This may include suggestions around types of clothes or shoes to wear; using ergonomic cutlery or pens to make writing and eating easier; and learning how to conserve energy and protect joints while completing routine tasks. Pacing is an important skill, so that children learn to make the most of their energy by prioritizing jobs, learning to break tasks down into smaller components, to be flexible with changing plans and to build up muscle strength and stamina to maximize fitness.
During periods of flare, splints may be used to support the joints during activity, to reduce the children's pain and increase participation in their preferred leisure activities. If prescribed, these are only for short periods of time as prolonged splinting can result in further muscle weakness. Resting splints, usually worn at night, are now rarely prescribed.
Nursing care in JIA
Paediatric rheumatology nurses provide health and medical care for children and young people with rheumatic disease, from birth through to late adolescence. They are employed by many large hospitals, and also in some private rheumatology practices. They work as part of the multidisciplinary team to support the child and their family at the time of diagnosis and throughout the child’s illness. Paediatric rheumatology nurses have specialist skills and experience which allow them to work with children, young people and their families to address any concerns, fears and problems, including those around treatment and medication administration.
Paediatric rheumatology nurses work holistically with the entire family unit. They are often involved with the child and family in the planning of care, determining the child’s capabilities and working with day care, early childhood education and schools to ensure the patient has comprehensive support in all aspects of their life.
The diagnosis of a rheumatological condition can be devastating for the child and parents, and often has a ripple effect on the family unit. The paediatric rheumatology nurse provides support, education, advocacy, information, empathy and understanding to both the patient and their family, and assists in alleviating the anxieties and concerns of the parents / carers.
The goals of paediatric rheumatology nursing care include: assisting in normalising the life of the child after diagnosis; minimising the impact of the child's condition; optimising growth and development; assisting the family in developing realistic, functional and coordinated home care plans; respecting the roles of the families in the care of their children; prevention of disease; and promotion of the overall health of the child.
Education on paediatric rheumatology conditions and medications is a core part of the role of the paediatric rheumatology nurse. Empowering the patient, and their family, with age appropriate knowledge and understanding of the child’s condition is crucial. Nurses also work with patients to help them accept and adjust to the hospital setting, and prepare them for medical treatments and procedures in the event they are required. They often provide advice and instruction at a time of disease flare or other acute medical issue.
Many of the medications used in paediatric rheumatology suppress the immune system. It is imperative that an understanding of all facets of all prescribed medications is imparted to the patient (age dependant) and their families. This is usually the combined role of the rheumatologist and the rheumatology nurse.
Self Management
Pain is the most common and often the most distressing symptom of JIA (although some children with JIA do have joint inflammation without any pain at all). Pain can occur even when children are receiving effective doses of therapies which are managing their underlying disease.
Pain has been found to negatively impact all aspects of quality of life and is associated with a reduction in physical, social and emotional functioning. Children who have higher levels of pain, tend to have reduced levels of socialization, school attendance and participation in activities. Increased pain is also correlated with poor sleep and higher fatigue in children with JIA.
The causation of pain in JIA is multifactorial. There are disease related factors, which relate to the inflammatory process, and anatomical or biomechanical changes that are associated with joint swelling and joint disease. There are psychological factors around dealing with stress, coping with a chronic illness and managing anxiety or depression which can influence the perception of pain and the degree of functional impairment. There are also social factors, which relate to family and peer relationships, parental distress and social and financial supports.
Given the waxing and waning nature of JIA, children’s physical abilities, pain and mood can change during periods of flare or remission. Coping with chronic illness during childhood and adolescence is associated with significant stress that can put children at risk for emotional or behavioural distress and can interfere with compliance and adherence to treatment regimes. Managing JIA can be a challenge and it is important to have a toolbox of skills, supports and strategies to draw upon to manage the ups and downs of having a chronic illness.
There are many things that can help children with JIA to grow up to have full and active lives. Having good sleep habits and routines gives a child the best chance of having a refreshing night's sleep and preventing daytime fatigue. This in turn affects concentration, energy levels, memory and mood. Most children need between 8 to 12 hours of sleep to feel refreshed, depending on age.[33] Simple strategies like maintaining regular bed-times, limiting screen time to two-hours before bed, having a sleep ritual, avoiding napping during the day, avoiding sugary and caffeinated drinks, having a healthy well-balanced diet, regular exercise and using relaxation techniques can assist in having good night’s sleep.
Relaxation techniques can also help to reduce stress, physical tension and be a useful pain management technique. There are a variety of mindfulness strategies which include things like deep breathing, guided-imagery or progressive muscle relaxation. All techniques need to be practiced over time, and it may be necessary to try different combinations to find the method that works best for each individual. These techniques are readily available online, in books, recordings, apps or by seeing a trained professional such as a psychologist.
Education and Employment
Most children with JIA will be able to consistently attend school, without too many disruptions, even during a disease flare. However, they may require extra help or adaptations in order to do so. Maximising school attendance involves collaboration between the family, the school and the health care team. Prolonged or repeated school absences can have academic, social and emotional implications; except in rare circumstances they are rarely necessary (other than absences for medical or therapy appointments).
These adaptations may include requiring extra time to get between classes or during examinations, using specialised pens or switching to typing rather than handwriting, or minimising the load of heavy books or equipment to be carried in a child’s school bag. The exact requirements will vary from child-to-child and will depend on the joints affected. In many instances, the child’s treating team will be able to provide specific advice and information for teachers and coaches to smooth the transition back to school.[34] This may take the form of an individualized plan outlining any extra measures that need to be taken at school, what to do in the case of unexpected events or medication administration during school hours. It is important to remember that JIA can be disruptive not just to the academic aspects of school. It is equally important to optimise school attendance so that the child can maintain friendships and keep up with opportunities to socialize with peers.
As adolescents progress through high school, they may need to factor their current medical status and functional abilities into decisions around their future education and employment plans. Most children with JIA will not be restricted in their study goals or professional aspirations. Students with JIA can usually apply for special arrangements during assessment periods, such as additional time to allow for rest / stretch periods and use of adaptive equipment in some situations. These applications often need to be supported by the treating medical team. The treating team can assist adolescents in finding ways to tell their employers about their condition in a positive way. OTs and social workers can also help teenagers understand their rights as an employee with a chronic illness. It is important that adolescents with JIA understand how to take care of themselves and manage their disease when working full-time or attending higher education. The team will also support those patients who still require medical input through the transition process from paediatric to adult services.
eHealth and mobile Health (mHealth) interventions
A new emerging area of support for disease management is through digital technology using eHealth and mobile health (mHealth) interventions. These interventions have to potential to support the development of self-management skills, or assist the healthcare team to monitor symptoms. For JIA, current studies have focused on the health issues pain, health related quality of life, physical activity and disease management. Children and adolescents have used these interventions through a range of devices including computers, laptops, personal digital assistants, multimedia-players, and wearable accelerometers synchronised to smart phone. This allows access to these interventions from home. Early usability studies have been gaining positive feedback by children and adolescents. They are familiar with this type of technology and report liking these interventions. However further research is still needed to understand their full potential in supporting children and adolescents living with complex needs.[35]
Prognosis
At the time of receiving a JIA diagnosis, children and their families often have many questions regarding prognosis. Recent therapeutic advances in the management of JIA have made inactive disease and clinical remission achievable goals for the majority of children with access to modern treatments. Clinical remission can be defined as the absence of signs and symptoms of inflammatory disease activity, including extra-articular manifestations of the disease. Differentiating subtypes of JIA helps to target treatment and leads to more positive outcomes, however subtype is not the only predictor of JIA outcome. Poor prognostic factors include arthritis of the hip, cervical spine, ankles or wrists; prolonged elevation of inflammatory markers; and radiographic evidence of joint damage including erosions or joint space narrowing. Patients with RF-positive polyarthritis often have worse outcomes associated with more aggressive disease. Despite this, the probability of this subgroup achieving inactive disease at least once within 5 years was shown to be 90% in a large Canadian study.[36] Research is currently being undertaken into clinical prediction models to allow earlier identification of children who are likely to have a worse prognosis.[37] Compliance with therapy, especially medication, has a positive correlation with disease outcome.
Research into specific JIA biomarkers is currently underway, with the goal of forming more personalized treatment plans, reducing medication side effects and improving remission rates. Current areas of investigation include clinical, protein, genetic and radiological markers, amongst others.[38]
Children with JIA demonstrate similar levels of depression and anxiety to children with other chronic diseases however causality has not been established. The unpredictable and undulating course of JIA disease activity and the need for ongoing procedural interventions may contribute.
It has been previously suggested that children with JIA are at an increased risk of malignancies when being treated with anti-TNF therapy. More recent data has not confirmed this association: it is thought that the disease itself is linked with a slightly higher background risk of malignancy. Ongoing data analysis on large patient populations continues in this area.[39]
Epidemiology
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis is the most common, chronic rheumatic disease of childhood. In high-income countries, yearly incidence has been estimated at 2–20 cases per 100 000 population; prevalence in these areas is estimated at 16–150 cases per 100 000 population.[40] However, there is also a suggestion that these numbers underestimate disease prevalence: one community-based survey of school children in Western Australia reported a prevalence of 400 per 100 000.[41] Overall prevalence is often summarised as 1 per thousand children.[1][42][34][43]
Incidence and prevalence data vary across different population and ethnic groups, with lower overall prevalence in Afro-Caribbean and Asian populations. There are also ethnic differences in the frequency of JIA subtypes: for example, oligoarthritis is the most common subtype in European populations, whilst polyarticular disease predominates in many other countries including Costa Rica, India, New Zealand, and South Africa.[44]
There are differences in age of onset, gender and disease outcomes based on JIA subtype: these are outlined in the table above.
Terminology
The terminology used to describe JIA is evolving, and each term has some limitations.
Previous terminology included Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis and Juvenile Chronic Arthritis. These terms were replaced in 1997 with the release of the revised ILAR (International League of Associations for Rheumatology) classification criteria.[45]
There is currently an international movement underway to further revise the classification criteria for JIA, although this is in a preliminary phase.[46]
MeSH uses "juvenile arthritis" as the primary entry, and uses "idiopathic", "chronic" and "rheumatoid" in alternate entries.[47]
Society
Some famous people with this condition are:
- Antoni Gaudi, architect[48]
- Clark Middleton, actor
- Claire Cottrill, singer-songwriter
- Rosemary Sutcliff, author
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Harris, Julia G.; Kessler, Elizabeth A.; Verbsky, James W. (21 April 2013). "Update on the Treatment of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis". Current Allergy and Asthma Reports. 13 (4): 337–346. doi:10.1007/s11882-013-0351-2. PMC 3729726. PMID 23605168.
- ↑ Prakken, B; Albani, S; Martini, A (18 June 2011). "Juvenile idiopathic arthritis". Lancet. 377 (9783): 2138–49. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60244-4. PMID 21684384. S2CID 202802455. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 28 August 2021.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Giancane, Gabriella; Consolaro, Alessandro; Lanni, Stefano; Davì, Sergio; Schiappapietra, Benedetta; Ravelli, Angelo (12 August 2016). "Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Diagnosis and Treatment". Rheumatology and Therapy. 3 (2): 187–207. doi:10.1007/s40744-016-0040-4. PMC 5127964. PMID 27747582.
- ↑ Hemke, Robert; Nusman, Charlotte M.; van der Heijde, Désirée M. F. M.; Doria, Andrea S.; Kuijpers, Taco W.; Maas, Mario; van Rossum, Marion A. J. (14 August 2014). "Frequency of joint involvement in juvenile idiopathic arthritis during a 5-year follow-up of newly diagnosed patients: implications for MR imaging as outcome measure". Rheumatology International. 35 (2): 351–357. doi:10.1007/s00296-014-3108-x. PMID 25119829. S2CID 859955.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "American College of Rheumatology: Juvenile Arthritis". www.rheumatology.org. Archived from the original on 15 May 2020. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Sen, Ethan S.; Dick, Andrew D.; Ramanan, Athimalaipet V. (31 March 2015). "Uveitis associated with juvenile idiopathic arthritis". Nature Reviews Rheumatology. 11 (6): 338–348. doi:10.1038/nrrheum.2015.20. PMID 25825278. S2CID 12096252.
- ↑ Foster, H.; Rapley, T.; May, C. (17 November 2009). "Juvenile idiopathic arthritis: improved outcome requires improved access to care". Rheumatology. 49 (3): 401–403. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kep347. PMID 19920094.
- ↑ Bechtold, Susanne; Simon, Dominique (24 April 2014). "Growth abnormalities in children and adolescents with juvenile idiopathic arthritis". Rheumatology International. 34 (11): 1483–1488. doi:10.1007/s00296-014-3022-2. PMID 24760485. S2CID 10546793.
- ↑ Burnham, Jon M.; Shults, Justine; Dubner, Sarah E.; Sembhi, Harjeet; Zemel, Babette S.; Leonard, Mary B. (August 2008). "Bone density, structure, and strength in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Importance of disease severity and muscle deficits". Arthritis & Rheumatism. 58 (8): 2518–2527. doi:10.1002/art.23683. PMC 2705769. PMID 18668565.
- ↑ Prahalad S, Glass DN (2002). "Is juvenile rheumatoid arthritis/juvenile idiopathic arthritis different from rheumatoid arthritis?". Arthritis Research. 4 (Suppl 3): 303–310. doi:10.1186/ar594. PMC 3273047.
- ↑ Hinks A, Cobb J, Marion MC, Prahalad S, Sudman M, Bowes J, et al. (June 2013). "Dense genotyping of immune-related disease regions identifies 14 new susceptibility loci for juvenile idiopathic arthritis". Nature Genetics. 45 (6): 664–9. doi:10.1038/ng.2614. PMC 3673707. PMID 23603761.
- ↑ "Juvenile Arthritis". Archived from the original on 2021-08-29. Retrieved 2010-04-19.
- ↑ Phelan JD, Thompson SD (September 2006). "Genomic progress in pediatric arthritis: recent work and future goals". Current Opinion in Rheumatology. 18 (5): 482–9. doi:10.1097/01.bor.0000240359.30303.e4. PMID 16896287. S2CID 7356346.
- ↑ Førre O, Smerdel A (2002). "Genetic epidemiology of juvenile idiopathic arthritis". Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology. 31 (3): 123–8. doi:10.1080/713798345. PMID 12195624.
- ↑ Balan, Suma (9 January 2016). "Approach to Joint Pain in Children". The Indian Journal of Pediatrics. 83 (2): 135–139. doi:10.1007/s12098-015-2016-8. PMID 26747081. S2CID 207388664.
- ↑ Petty, RE; Southwood, TR; Manners, P; Baum, J; Glass, DN; Goldenberg, J; He, X; Maldonado-Cocco, J; Orozco-Alcala, J; Prieur, AM; Suarez-Almazor, ME; Woo, P; International League of Associations for, Rheumatology. (February 2004). "International League of Associations for Rheumatology classification of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: second revision, Edmonton, 2001". The Journal of Rheumatology. 31 (2): 390–2. PMID 14760812.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Torreggiani, S; Torcoletti, M; Campos-Xavier, B; Baldo, F; Agostoni, C; Superti-Furga, A; Filocamo, G (March 2019). "Progressive pseudorheumatoid dysplasia: a rare childhood disease". Rheumatology international. 39 (3): 441–452. doi:10.1007/s00296-018-4170-6. PMID 30327864.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Elsebaie, H; Mansour, MA; Elsayed, SM; Mahmoud, S; El-Sobky, TA (December 2021). "Multicentric Osteolysis, Nodulosis, and Arthropathy in two unrelated children with matrix metalloproteinase 2 variants: Genetic-skeletal correlations". Bone reports. 15: 101106. doi:10.1016/j.bonr.2021.101106. PMC 8283316. PMID 34307793.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 de Vos, IJHM; Wong, ASW; Welting, TJM; Coull, BJ; van Steensel, MAM (August 2019). "Multicentric osteolytic syndromes represent a phenotypic spectrum defined by defective collagen remodeling". American journal of medical genetics. Part A. 179 (8): 1652–1664. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.61264. PMID 31218820.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Ravelli, Angelo; Consolaro, Alessandro; Horneff, Gerd; Laxer, Ronald M; Lovell, Daniel J; Wulffraat, Nico M; Akikusa, Jonathan D; Al-Mayouf, Sulaiman M; Antón, Jordi; Avcin, Tadej; Berard, Roberta A; Beresford, Michael W; Burgos-Vargas, Ruben; Cimaz, Rolando; De Benedetti, Fabrizio; Demirkaya, Erkan; Foell, Dirk; Itoh, Yasuhiko; Lahdenne, Pekka; Morgan, Esi M; Quartier, Pierre; Ruperto, Nicolino; Russo, Ricardo; Saad-Magalhães, Claudia; Sawhney, Sujata; Scott, Christiaan; Shenoi, Susan; Swart, Joost F; Uziel, Yosef; Vastert, Sebastiaan J; Smolen, Josef S (11 April 2018). "Treating juvenile idiopathic arthritis to target: recommendations of an international task force". Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 77 (6): annrheumdis-2018-213030. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213030. hdl:11449/171016. PMID 29643108. S2CID 4830829.
- ↑ Minden, Kirsten; Horneff, Gerd; Niewerth, Martina; Seipelt, Eva; Aringer, Martin; Aries, Peer; Foeldvari, Ivan; Haas, Johannes‐Peter; Klein, Ariane; Tatsis, Stefanie; Tenbrock, Klaus; Zink, Angela; Klotsche, Jens (28 March 2019). "Time of Disease‐Modifying Antirheumatic Drug Start in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis and the Likelihood of a Drug‐Free Remission in Young Adulthood". Arthritis Care & Research. 71 (4): 471–481. doi:10.1002/acr.23709. PMID 30044538. S2CID 51715770.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 Davies, K.; Cleary, G.; Foster, H.; Hutchinson, E.; Baildam, E. (19 February 2010). "BSPAR Standards of Care for children and young people with juvenile idiopathic arthritis". Rheumatology. 49 (7): 1406–1408. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kep460. PMID 20173199.
- ↑ Ringold, Sarah; Angeles‐Han, Sheila T.; Beukelman, Timothy; Lovell, Daniel; Cuello, Carlos A.; Becker, Mara L.; Colbert, Robert A.; Feldman, Brian M.; Ferguson, Polly J.; Gewanter, Harry; Guzman, Jaime; Horonjeff, Jennifer; Nigrovic, Peter A.; Ombrello, Michael J.; Passo, Murray H.; Stoll, Matthew L.; Rabinovich, C. Egla; Schneider, Rayfel; Halyabar, Olha; Hays, Kimberly; Shah, Amit Aakash; Sullivan, Nancy; Szymanski, Ann Marie; Turgunbaev, Marat; Turner, Amy; Reston, James (25 April 2019). "2019 American College of Rheumatology/Arthritis Foundation Guideline for the Treatment of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Therapeutic Approaches for Non‐Systemic Polyarthritis, Sacroiliitis, and Enthesitis". Arthritis Care & Research. 71 (6): 717–734. doi:10.1002/acr.23870. PMC 6561125. PMID 31021516.
- ↑ Cellucci, Tania; Guzman, Jaime; Petty, Ross E.; Batthish, Michelle; Benseler, Susanne M.; Ellsworth, Janet E.; Houghton, Kristin M.; LeBlanc, Claire M.A.; Huber, Adam M.; Luca, Nadia; Schmeling, Heinrike; Shiff, Natalie J.; Soon, Gordon S.; Tse, Shirley M.L. (1 October 2016). "Management of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis 2015: A Position Statement from the Pediatric Committee of the Canadian Rheumatology Association". The Journal of Rheumatology. 43 (10): 1773–1776. doi:10.3899/jrheum.160074. PMID 27698103.
- ↑ Ringold, Sarah; Angeles‐Han, Sheila T.; Beukelman, Timothy; Lovell, Daniel; Cuello, Carlos A.; Becker, Mara L.; Colbert, Robert A.; Feldman, Brian M.; Ferguson, Polly J.; Gewanter, Harry; Guzman, Jaime; Horonjeff, Jennifer; Nigrovic, Peter A.; Ombrello, Michael J.; Passo, Murray H.; Stoll, Matthew L.; Rabinovich, C. Egla; Schneider, Rayfel; Halyabar, Olha; Hays, Kimberly; Shah, Amit Aakash; Sullivan, Nancy; Szymanski, Ann Marie; Turgunbaev, Marat; Turner, Amy; Reston, James (25 April 2019). "2019 American College of Rheumatology/Arthritis Foundation Guideline for the Treatment of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Therapeutic Approaches for Non‐Systemic Polyarthritis, Sacroiliitis, and Enthesitis". Arthritis Care & Research. 71 (6): 717–734. doi:10.1002/acr.23870. PMC 6561125. PMID 31021516.
- ↑ De Monte R, Rodger S, Jones F, Broderick S (August 2009). "Living with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: children's experiences of participating in home exercise programmes". British Journal of Occupational Therapy. 72 (8): 357–65. doi:10.1177/030802260907200806. S2CID 72219322.
- ↑ Stagi, Stefano; Cavalli, Loredana; Signorini, Carla; Bertini, Federico; Cerinic, Marco; Brandi, Maria; Falcini, Fernanda (2014). "Bone mass and quality in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: longitudinal evaluation of bone-mass determinants by using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry, peripheral quantitative computed tomography, and quantitative ultrasonography". Arthritis Research & Therapy. 16 (2): R83. doi:10.1186/ar4525. PMC 4060444. PMID 24684763.
- ↑ Long, Amy R; Rouster-Stevens, Kelly A (March 2010). "The role of exercise therapy in the management of juvenile idiopathic arthritis". Current Opinion in Rheumatology. 22 (2): 213–217. doi:10.1097/BOR.0b013e328335d1a2. PMID 20010296. S2CID 25442812.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 Philpott, John F; Houghton, Kristin; Luke, Anthony (May 2010). "Physical Activity Recommendations for Children With Specific Chronic Health Conditions: Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis, Hemophilia, Asthma, and Cystic Fibrosis". Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine. 20 (3): 167–172. doi:10.1097/JSM.0b013e3181d2eddd. PMC 2866314. PMID 20445355.
- ↑ "Time to Move: Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis" (PDF). Arthritis Australia. Archived (PDF) from the original on 28 March 2020. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- ↑ Takken, Tim; Van Brussel, Marco; Engelbert, Raoul H.H.; van der Net, Janjaap J; Kuis, Wietse; Helders, Paul PJM (23 April 2008). "Exercise therapy in juvenile idiopathic arthritis". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD005954. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005954.pub2. PMID 18425929.
- ↑ Gotte, Alisa (May 2009). "Intra-articular corticosteroids in the treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Safety, efficacy, and features affecting outcome. A comprehensive review of the literature". Open Access Rheumatology: Research and Reviews. 1: 37–49. doi:10.2147/oarrr.s5103. PMC 5074724. PMID 27789980.
- ↑ "How Much Sleep Do Babies and Kids Need? | National Sleep Foundation". www.sleepfoundation.org. Archived from the original on 2020-08-11. Retrieved 2021-08-28.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 "Teacher's guide to JIA". Arthritis Australia. Archived from the original on 2021-08-14. Retrieved 2021-08-28.
- ↑ "Archive copy". Archived from the original on 2021-01-21. Retrieved 2021-08-28.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ Guzman, Jaime; Oen, Kiem; Tucker, Lori B; Huber, Adam M; Shiff, Natalie; Boire, Gilles; Scuccimarri, Rosie; Berard, Roberta; Tse, Shirley M L; Morishita, Kimberly; Stringer, Elizabeth; Johnson, Nicole; Levy, Deborah M; Duffy, Karen Watanabe; Cabral, David A; Rosenberg, Alan M; Larché, Maggie; Dancey, Paul; Petty, Ross E; Laxer, Ronald M; Silverman, Earl; Miettunen, Paivi; Chetaille, Anne-Laure; Haddad, Elie; Houghton, Kristin; Spiegel, Lynn; Turvey, Stuart E; Schmeling, Heinrike; Lang, Bianca; Ellsworth, Janet; Ramsey, Suzanne; Bruns, Alessandra; Campillo, Sarah; Benseler, Susanne; Chédeville, Gaëlle; Schneider, Rayfel; Yeung, Rae; Duffy, Ciarán M (October 2015). "The outcomes of juvenile idiopathic arthritis in children managed with contemporary treatments: results from the ReACCh-Out cohort". Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 74 (10): 1854–1860. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205372. PMID 24842571. S2CID 44612457.
- ↑ Henrey, Andrew; Rypdal, Veronika; Rypdal, Martin; Loughin, Thomas; Nordal, Ellen; Guzman, Jaime (15 January 2020). "Validation of prediction models of severe disease course and non-achievement of remission in juvenile idiopathic arthritis part 2: results of the Nordic model in the Canadian cohort". Arthritis Research & Therapy. 22 (1): 10. doi:10.1186/s13075-019-2091-8. PMC 6964007. PMID 31941530.
- ↑ Duurland, Chantal L.; Wedderburn, Lucy R. (21 January 2014). "Current Developments in the Use of Biomarkers for Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis". Current Rheumatology Reports. 16 (3): 406. doi:10.1007/s11926-013-0406-3. PMC 3930839. PMID 24445961.
- ↑ Beukelman, Timothy; Xie, Fenglong; Chen, Lang; Horton, Daniel B; Lewis, James D; Mamtani, Ronac; Mannion, Melissa M; Saag, Kenneth G; Curtis, Jeffrey R (July 2018). "Risk of malignancy associated with paediatric use of tumour necrosis factor inhibitors". Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 77 (7): 1012–1016. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212613. PMC 6094159. PMID 29440001.
- ↑ Prakken, Berent; Albani, Salvatore; Martini, Alberto (June 2011). "Juvenile idiopathic arthritis". The Lancet. 377 (9783): 2138–2149. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60244-4. PMID 21684384. S2CID 202802455. Archived from the original on 2021-08-29. Retrieved 2021-08-28.
- ↑ Manners, PJ; Diepeveen, DA (July 1996). "Prevalence of juvenile chronic arthritis in a population of 12-year-old children in urban Australia". Pediatrics. 98 (1): 84–90. PMID 8668417.
- ↑ "Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis" (PDF). RACGP. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-07-20. Retrieved 2021-08-28.
- ↑ "Rheumatology: Information on JIA for young people". www.rch.org.au. Archived from the original on 2021-03-10. Retrieved 2021-08-28.
- ↑ Ravelli, Angelo; Martini, Alberto (March 2007). "Juvenile idiopathic arthritis". The Lancet. 369 (9563): 767–778. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60363-8. PMID 17336654. S2CID 53265788. Archived from the original on 2021-08-29. Retrieved 2021-08-28.
- ↑ Petty, RE; Southwood, TR; Baum, J; Bhettay, E; Glass, DN; Manners, P; Maldonado-Cocco, J; Suarez-Almazor, M; Orozco-Alcala, J; Prieur, AM (October 1998). "Revision of the proposed classification criteria for juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Durban, 1997". The Journal of Rheumatology. 25 (10): 1991–4. PMID 9779856.
- ↑ Martini, Alberto; Ravelli, Angelo; Avcin, Tadej; Beresford, Michael W.; Burgos-Vargas, Ruben; Cuttica, Ruben; Ilowite, Norman T.; Khubchandani, Raju; Laxer, Ronald M.; Lovell, Daniel J.; Petty, Ross E.; Wallace, Carol A.; Wulffraat, Nico M.; Pistorio, Angela; Ruperto, Nicolino (February 2019). "Toward New Classification Criteria for Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: First Steps, Pediatric Rheumatology International Trials Organization International Consensus". The Journal of Rheumatology. 46 (2): 190–197. doi:10.3899/jrheum.180168. PMID 30275259.
- ↑ "MeSH Browser". meshb.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 2020-11-24. Retrieved 2021-08-28.
- ↑ Azevedo, Valderílio F.; Diaz-Torne, Cesar (December 2008). "The Arthritis of Antoni Gaudí". JCR: Journal of Clinical Rheumatology. 14 (6): 367–369. doi:10.1097/RHU.0b013e31818ee74c. PMID 19060668.
External links
- Arthritis Australia, Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Archived 2021-08-14 at the Wayback Machine
- JIA@NRAS (UK) Archived 2021-08-13 at the Wayback Machine
- JIA Archived 2015-09-05 at the Wayback Machine - NIH Medline Plus.
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
- Pages with script errors
- CS1 maint: archived copy as title
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from June 2020
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- Webarchive template wayback links
- Arthritis
- Pediatrics
- Rheumatology
- Connective tissue diseases
- Inflammatory polyarthropathies
- Idiopathic diseases