Jesse Francis McClendon
Jesse Francis McClendon | |
|---|---|
| Born | December 21, 1880 Lanett, Alabama, USA |
| Died | November 22, 1976 (aged 95) |
| Nationality | American |
| Alma mater | University of Texas at Austin, University of Pennsylvania |
| Known for | First measurement of human intragastric acidity in situ |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | chemistry, zoology, physiology |
| Institutions | University of Minnesota Medical School, Hahnemann Medical College, Albert Einstein Medical Center |
Jesse Francis McClendon (December 21, 1880 – November 22, 1976) was an American chemist, zoologist, and physiologist known for the first pH measurement of human stomach in situ.
McClendon made substantial contributions in a variety of fields, including invertebrate zoology, nutrition, life processes of cell membranes, the importance of pH control,[1][2][3] the role of iodine in human health, and specifically its relation to prevention of goiters.[4]
During the early 1930s, McClendon tested the healthfulness of hamburgers by putting a University of Minnesota medical student on a diet of only hamburgers and water for thirteen weeks.[5]
Biography
McClendon was born in Lanett, Alabama, on December 21, 1880. He completed his B.S. in 1903 and M.S. in 1904, both from the University of Texas. In 1903, he worked at the University of Texas under Dr. William Morton Wheeler.[6] He then received a Ph.D. in zoology from the University of Pennsylvania in 1906. His PhD dissertation was entitled, "On the Development of Parasitic Copepoda."[7]
From 1907 to 1910, McClendon taught biology at Randolph-Macon College; he then taught zoology at the University of Missouri.
From 1910 to 1914, McClendon was an assistant instructor in histology and embryology at the Weill Cornell Medical College of Cornell University.[8] He investigated frog blastomeres.[9]
During this time (in 1911), he married and began a family. He and his wife ultimately had two children.
From 1910 to 1939, McClendon worked at the Physiological Laboratory of the University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis, serving as professor of Physiological Chemistry between 1920 and 1939. During this time (in 1936), he married a second time.
It was also while working in this laboratory that McClendon achieved pioneering research, including his investigation of the relationsp between low iodine and goiter.[10] and Micromanipulation—Frog egg development.
Description of McClendon pH-probe
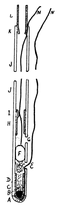
In measuring the acidity of the gastric contents, it was found possible to lower an electrode into the stomach. The apparatus designed for work on the stomach contents consists chiefly of a rubber tube 60 cm. long and 3 mm. bore, and two No. 40 silk covered copper wires, that were coated with rubber cement and dried several times. One wire, M, extends through the rubber tube, JJ, and the other, N, passes down outside of it until by entering the hole, E, it connects with a platinum wire that is fused into the lower end of a short piece of glass tube that is inserted into the rubber tube. The lower end of the glass tube and copper-platinum junction is covered with sealing wax, A. A drop of pure mercury is dropped into the lower end of the glass tube so as to connect with the platinum wire at the level of B. Above the mercury a little calomel washed with concentrated KCl solution, C, is placed, and the rest of the glass tube packed with moist KC1 crystals, D, and the hole, E, stuffed with cotton soaked in KC1 solution. This forms a calomel electrode, and is separated off from the remainder of the tube by a short piece of glass rod, F. Above F several holes are cut in the rubber tube at the level of G, and from this point a fine platinized platinum wire extends through the lumen of the tube and is held in place by fusion to a bump on the inside of a short piece of glass tube at the level of I. This platinum wire then connects with the wire M and the junction is coated with rubber. The rubber tube is connected at K with a tube, L, leading from a hydrogen generator, and a slow stream of H2 passes down the rubber tube and out at G, thus converting the platinum wire from H to F into a hydrogen electrode.[11]
Death
McClendon died on November 22, 1976, in Harleysville, Pennsylvania.
References
- ^ McClendon J. F. A direct reading potenciometer for measuring hydrogen ion concentration. Amer. J. Physiol., 1915, 38, 2, 186.
- ^ McClendon J. F. Acidity curves in the stomachs and duodenums of adults and infants plotted with the acid of imported methods of measuring hydrogen ion concentration. Amer. J. Physiol., 1915, 38, 2, 191.
- ^ McClendon J. F., Sheldon A., Ben Karpman. The hydrogen ion concentrations of the contents of the small intestine. J. of Biological Chemistry, Feb 19, 1918. XXXIV, No 1.
- ^ University of Minnesota Archives.
- ^ "An unusual hamburger experiment is part of the University of Minnesota's dietary research annals. Medical Bulletin. 2008, winter issue. Minnesota Medical Foundation". Archived from the original on 2008-08-04. Retrieved 2008-05-29.
- ^ McClendon J. F. Bulletin American Museum of Natural History. Vol. XXII, 1906, p. 119.
- ^ University of Pennsylvania, Graduate School (1912). Doctors of philosophy of the Graduate School, University of Pennsylvania, 1889-1912. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania. p. 69. hdl:2027/mdp.39015075957335.
- ^ Cornell University Information Database. Archived 2008-09-07 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Pynes Ch. Al.. Human Cloning and Moral Status. The Florida State University, 2003.
- ^ McClendon J. F. The distribution of iodine with special reference to goiter. Physiol Rev, Apr 1927; 7: 189–258.
- ^ McClendon J. F. New hydrogen electrodes and rapid methods of determining hydrogen ion concentrations. Amer. J. Physiol., 1915, 38, 2, 180.
External links
- Webarchive template wayback links
- Articles with hCards
- Articles with Internet Archive links
- Articles with FAST identifiers
- Articles with ISNI identifiers
- Articles with VIAF identifiers
- Articles with GND identifiers
- Articles with LCCN identifiers
- Articles with NTA identifiers
- Articles with SNAC-ID identifiers
- Articles with SUDOC identifiers
- 1880 births
- 1976 deaths
- University of Pennsylvania alumni
- People from Lanett, Alabama
- American physiologists
- 20th-century American chemists
- University of Texas at Austin alumni
- University of Missouri faculty
- University of Minnesota faculty
- Randolph–Macon College faculty