Insulin lispro
 Insulin lispro | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Humalog, Liprolog, Admelog, others |
| Other names | URLi, LY900014, LY-275585, insulin lispro-aabc |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Insulin (short acting) |
| Main uses | Diabetes[1] |
| Side effects | Low blood sugar, low blood potassium[1] |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of use | Subcutaneous |
| Onset of action | Within 30 min[1] |
| Duration of action | ~5 hrs[1] |
| Defined daily dose | 40 units[3] |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a697021 |
| Legal | |
| License data |
|
| Legal status | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C257H389N65O77S6 |
| Molar mass | 5813.63 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Insulin lispro, sold under the brand name Humalog among others, is a type of insulin used to treat type 1 and type 2 diabetes.[1] Typically it is taken around the time of eating.[1] It is used by injection under the skin or within an insulin pump.[1][5] Onset of effects typically occurs within 30 minutes and lasts about 5 hours.[1] Often a longer acting insulin like NPH is also needed.[1]
Common side effects include low blood sugar.[1] Other serious side effects may include low blood potassium.[1] Use in pregnancy and breastfeeding is generally safe.[6] It works the same as human insulin by increasing the amount of glucose that tissues take in and decreasing the amount of glucose made by the liver.[1]
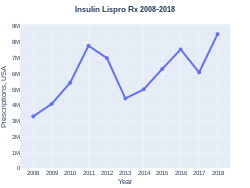
Insulin lispro was first approved for use in the United States in 1996.[1][7][8] It is a manufactured form of human insulin where an amino acid has been switched.[9] In the United Kingdom it costs the NHS about GB£19 per 1000 units as of 2019.[5] In the United States the wholesale cost of this amount is about US$300.[10] In 2024 the price had decreased to about US$20.[11] In 2017, it was the 124th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than six million prescriptions.[12][13]
Medical uses
Insulin lispro is used to treat people with type 1 diabetes or type 2 diabetes.[1] People doing well on regular insulin should not generally be changed to insulin lispro.[1]
Dosage
The defined daily dose is 40 units by injection.[3]
Side effects
Common side effects include skin irritation at the site of injection, hypoglycemia, hypokalemia, and lipodystrophy.[7] Other serious side effects include anaphylaxis, and hypersensitivity reactions.[7]
Contraindications
Do not administer insulin lispro during episodes of hypoglycemia, or if a person has a hypersensitivity to insulin lispro or any of its excipients.[7]
Mechanism of action
Through recombinant DNA technology, the final lysine and proline residues on the C-terminal end of the B-chain are reversed. This modification does not alter receptor binding, but blocks the formation of insulin dimers and hexamers. This allows larger amounts of active monomeric insulin to be immediately available for postprandial injections.[14]
Chemistry
It is a manufactured form of human insulin where the amino acids lysine and proline have been switched at the end of the B chain of the insulin molecule.[9]
History
Insulin lispro (brand name Humalog) was granted marketing authorization in the European Union in April 1996,[15] and it was approved for use in the United States in June 1996.[8][16]
Insulin lispro (brand name Liprolog) was granted marketing authorization in the European Union in May 1997,[17] and again in August 2001.[18]
Combination drugs combining insulin lispro and other forms of insulin were approved for use in the United States in December 1999.[19][20][21]
Insulin lispro Sanofi was granted marketing authorization as a biosimilar in the European Union in July 2017.[22]
Insulin lispro injection (brand name Admelog) was approved for use in the United States in December 2017.[23][24][25]
In January 2020, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) in the European Union recommended granting of a marketing authorization for insulin lispro acid (brand name Liumjev) for the treatment of diabetes mellitus in adults.[26][27] Insulin lispro (Liumjev) was approved for use in the European Union in March 2020, and in the United States on June 18, 2020 as reported by Medscape.[28]
Society and culture
Cost
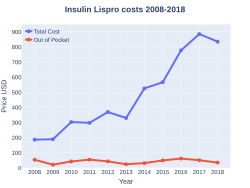
In the United States, in 2015, the cost was between US$10.06 and US$29.36 per 100 units.[29] In April 2019, Eli Lilly and Company announced they would produce a version selling for US$137.35 per vial, about half the then current cost. The chief executive said that this was a contribution "to fix the problem of high out-of-pocket costs for Americans living with chronic conditions", but Patients for Affordable Drugs Now said this was just a public relations move, as "other countries pay US$20 for a vial of insulin."[30]
The cost in the United Kingdom was between GB£1.66 and GB£1.96 per 100 units, in 2017.[31]
In the United Kingdom it costs the NHS about GB£1.89 per 100 units as of 2019.[5] In the United States the wholesale cost of this amount is about US$30.00.[10] In 2017, it was the 124th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than six million prescriptions.[12][13]
-
Insulin lispro costs (US)
-
Insulin lispro prescriptions (US)
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 "Insulin Lispro Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 6 March 2019. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Insulin lispro Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 7 October 2019. Archived from the original on 19 September 2020. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "WHOCC - ATC/DDD Index". www.whocc.no. Archived from the original on 7 August 2020. Retrieved 6 September 2020.
- ↑ "Humalog 100 units/ml, solution for injection in vial - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 30 January 2020. Archived from the original on 23 February 2020. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. p. 698. ISBN 9780857113382.
- ↑ "Insulin lispro Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Warnings". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 19 September 2020. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 "Humalog- insulin lispro injection, solution Humalog Kwikpen- insulin lispro injection, solution Humalog Junior Kwikpen- insulin lispro injection, solution Humalog Tempo Pen- insulin lispro injection, solution". DailyMed. 25 November 2019. Archived from the original on 24 September 2019. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "Humalog approval" (PDF). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 14 June 1996. Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 February 2020. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Koivisto VA (June 1998). "The human insulin analogue insulin lispro". Annals of Medicine. 30 (3): 260–6. doi:10.3109/07853899809005853. PMID 9677011.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "NADAC as of 2019-02-27". Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Archived from the original on 6 March 2019. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ↑ "Insulin Lisprogeneric Humalog". GoodRx. Archived from the original on 31 January 2022. Retrieved 19 January 2024.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 "The Top 300 of 2020". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 12 February 2021. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "Insulin Lispro - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 12 April 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ↑ Noble SL, Johnston E, Walton B (January 1998). "Insulin lispro: a fast-acting insulin analog". American Family Physician. 57 (2): 279–86, 289–92. PMID 9456992. Archived from the original on 29 September 2007. Retrieved 5 September 2007.
- ↑ "Humalog EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 11 February 2020. Archived from the original on 24 February 2020. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
- ↑ "Humalog: FDA-Approved Drugs". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Archived from the original on 27 November 2020. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
- ↑ "Liprolog EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 1 August 2001. Archived from the original on 24 February 2020. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
- ↑ "Liprolog EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 11 February 2020. Archived from the original on 24 February 2020. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
- ↑ "Drug Approval Package: Humalog Mix (75/25 & 50/50) NDA# 21-017 & 21-018". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 24 December 1999. Archived from the original on 24 February 2020. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
- ↑ "Humalog Mix50/50- insulin lispro injection, suspension Humalog Mix50/50 Kwikpen- insulin lispro injection, suspension". DailyMed. 19 November 2019. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
- ↑ "Humalog Mix75/25- insulin lispro injection, suspension Humalog Mix75/25 Kwikpen- insulin lispro injection, suspension". DailyMed. 3 February 2020. Archived from the original on 30 November 2020. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
- ↑ "Insulin lispro Sanofi EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 17 June 2019. Archived from the original on 24 February 2020. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
- ↑ "Drug Approval Package: Admelog (insulin lispro)". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 17 May 2018. Archived from the original on 24 February 2020. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
- ↑ "FDA Approves Sanofi's Admelog (insulin lispro injection) - Dec 11, 2017". Sanofi (Press release). 11 December 2017. Archived from the original on 24 February 2020. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
- ↑ "FDA approves Admelog, the first short-acting "follow-on" insulin product to treat diabetes". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 11 December 2017. Archived from the original on 14 June 2019. Retrieved 12 December 2017.
- ↑ "Liumjev: Pending EC decision". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 30 January 2020. Archived from the original on 31 January 2020. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
- ↑ "CHMP Recommends Approval of Lilly's New Fast-Acting Mealtime Insulin to Improve Glycemic Control in Adults with Diabetes". Eli Lilly and Company (Press release). 31 January 2020. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
- ↑ "Liumjev EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 29 January 2020. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 16 April 2020.
- ↑ Langreth, Robert (29 June 2016). "Decoding Big Pharma's Secret Drug Pricing Practices". Bloomberg. Archived from the original on 13 July 2016. Retrieved 15 July 2016.
- ↑ "Drug company announces new version of insulin at half the price". The Hill. 3 April 2019. Archived from the original on 15 April 2019. Retrieved 15 April 2019.
- ↑ "Humalog". MIMS. Archived from the original on 13 January 2017. Retrieved 12 January 2017.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|
|---|
- "Insulin lispro". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 23 February 2020. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
- Pages using duplicate arguments in template calls
- Use dmy dates from February 2020
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- Chem-molar-mass both hardcoded and calculated
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Chemical articles without CAS registry number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs missing an ATC code
- Drug has EMA link
- Drugboxes which contain changes to verified fields
- Chemicals that do not have a ChemSpider ID assigned
- Diabetes
- Eli Lilly and Company brands
- Human proteins
- Insulin receptor agonists
- Insulin therapies
- Peptide hormones
- Recombinant proteins
- RTT