Human penis
| Human penis | |
|---|---|
 A flaccid uncircumcised penis; naturally occurring pubic hair has been deliberately removed to show anatomical detail | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Genital tubercle, urogenital folds |
| System | Genitourinary system, male reproductive system |
| Artery | Dorsal artery of the penis, deep artery of the penis, artery of the urethral bulb, internal pudendal artery |
| Vein | Deep dorsal vein, superficial dorsal vein of the penis, vein of bulb of penis, internal pudendal veins |
| Nerve | Dorsal nerve of the penis, pudendal nerve |
| Lymph | Superficial inguinal lymph nodes |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | penis, pudendum virile, membrum virile |
| MeSH | D010413 |
| TA98 | A09.4.01.001 |
| TA2 | 3662 |
| FMA | 9707 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In human anatomy, the penis (/ˈpiːnɪs/; pl.: penises or penes; from the Latin pēnis, initially "tail"[1]) is an external male sex organ (intromittent organ) that additionally serves as the urinary duct. The main parts are the root, body, the epithelium of the penis including the shaft skin, and the foreskin covering the glans. The body of the penis is made up of three columns of tissue: two corpora cavernosa on the dorsal side and corpus spongiosum between them on the ventral side. The human male urethra passes through the prostate gland, where it is joined by the ejaculatory duct, and then through the penis. The urethra traverses the corpus spongiosum, and its opening, the meatus, lies on the tip of the glans. It is a passage both for urination and ejaculation of semen.
An erection is the stiffening expansion and orthogonal reorientation of the penis, which occurs during sexual arousal. Erections can occur in non-sexual situations; spontaneous non-sexual erections frequently occur during adolescence and sleep. In its flaccid state, the penis is smaller, gives to pressure, and the glans is covered by the foreskin. In its fully erect state, the shaft becomes rigid and the glans becomes engorged but not rigid. An erect penis may be straight or curved and may point at an upward angle, a downward angle, or straight ahead. As of 2015[update], the average erect human penis is 13.12 cm (5.17 in) long and has a circumference of 11.66 cm (4.59 in).[2][3] Neither age nor size of the flaccid penis accurately predicts erectile length. There are several common body modifications to the penis, including circumcision and piercings.
The penis is homologous to the clitoris in females.[4]
Structure

Three main parts of the human penis include:
- Root: It is the attached part, consisting of the bulb in the middle and the crura, one crus on either side of the bulb. It lies within the superficial perineal pouch. The crus is attached to the pubic arch.
- Shaft: The pendulous part of the penis. It has two surfaces: dorsal (posterosuperior in the erect penis) and ventral or urethral (facing downwards and backwards on the flaccid penis). The ventral surface is marked by the penile raphe. The base of the shaft is supported by the suspensory ligament, which is attached to the pubic symphysis.[5]
- Epithelium of the penis consists of the shaft skin, the foreskin, and the preputial mucosa on the inside of it. The foreskin covers and protects the glans and shaft. The epithelium is not attached to the underlying shaft, so it is free to glide to and fro.[6]
The human penis is made up of three columns of erectile tissue: two corpora cavernosa lie next to each other (separated by a fibrous septum) on the dorsal side and one corpus spongiosum lies between them on the ventral side.[7] These columns are surrounded by a fibrous layer of connective tissue called the tunica albuginea. The corpora cavernosa are innervated by lesser and greater cavernous nerves and form most of the penis containing blood vessels that fill with blood to help make an erection.[8] The crura are the proximal parts of the corpora cavernosa. The corpus spongiosum is an erectile tissue surrounding the urethra. The proximal parts of the corpus spongiosum form the bulb and the distal ends form the glans penis.[5]
The enlarged and bulbous-shaped end of the corpus spongiosum forms the glans penis with two specific types of sinusoids, which supports the foreskin, a loose fold of skin that in adults can retract to expose the glans.[9] The area on the underside of the glans, where the foreskin is attached, is called the frenulum. The rounded base of the glans is called the corona.

The urethra, which is the last part of the urinary tract, traverses the corpus spongiosum, and its opening, known as the meatus, lies on the tip of the glans penis. It is a passage both for urine and for the ejaculation of semen. Sperm are produced in the testicles and stored in the attached epididymides. During ejaculation, sperm are propelled up the vasa deferentia, two ducts that pass over and behind the bladder. Fluids are added by the seminal vesicles and the vasa deferentia turn into the ejaculatory ducts, which join the urethra inside the prostate gland. The prostate, as well as the bulbourethral glands, add further secretions, and the semen is expelled through the penis.
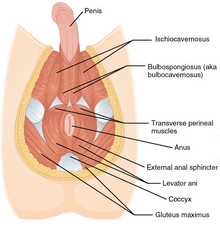
The penile raphe is the visible ridge between the lateral halves of the penis, found on the ventral or underside of the penis, running from the meatus and continuing as the perineal raphe across the scrotum and the perineum (area between scrotum and anus).[10]
The human penis differs from those of most other mammals, as it has no baculum (or erectile bone) and instead relies entirely on engorgement with blood to reach its erect state. A distal ligament buttresses the glans penis and plays an integral role to the penile fibroskeleton, and the structure is called "os analog", a term coined by Geng Long Hsu in the Encyclopedia of Reproduction.[11] It is a remnant of the baculum that has likely evolved due to change in mating practice.[12]
The human penis cannot be withdrawn into the groin, and it is larger than average in the animal kingdom in proportion to body mass. The human penis is reciprocating from a cotton soft to a bony rigidity resulting from penile arterial flow varied between 2–3 to 60–80 mL/Min implies the most ideal milieu to apply Pascal's law in the entire human body; the overall structure is unique.[11]
Size
Penile measurements vary, with studies that rely on self-measurement reporting a significantly higher average size than those which rely on measurements taken by health professional. A 2015 systematic review of 15,521 men in which the subjects were measured by health professionals showed that the average length of an erect human penis is 13.12 cm (5.17 inches) long, while the average circumference of an erect human penis is 11.66 cm (4.59 inches).[2][3]
Among all primates, the human penis is the largest in girth, but is comparable to the chimpanzee penis and the penises of certain other primates in length.[13] Penis size is affected by genetics, but also by environmental factors such as fertility medications[14] and chemical/pollution exposure.[15][16][17]
Normal variations

- Pearly penile papules are raised bumps of somewhat paler color around the base (sulcus) of the glans, which typically develop in males aged 20 to 40. As of 1999, different studies had produced estimates of incidence ranging from 8 to 48 percent of all men.[18] They may be mistaken for warts, but are not harmful or infectious and do not require treatment.[19]
- Fordyce's spots are small, raised, yellowish-white spots 1–2 mm in diameter that may appear on the penis, which again are common and not infectious.
- Sebaceous prominences are raised bumps similar to Fordyce's spots on the shaft of the penis, located at the sebaceous glands and are normal.
- Phimosis is an inability to retract the foreskin fully. It is normal and harmless in infancy and pre-pubescence, occurring in about 8% of boys at age 10. According to the British Medical Association, treatment (topical steroid cream and/or manual stretching) does not need to be considered until age 19.
- Curvature: few penises are completely straight, with curves commonly seen in all directions (up, down, left, right). Sometimes the curve is very prominent but it rarely inhibits sexual intercourse. Curvature as great as 30° is considered normal and medical treatment is rarely considered unless the angle exceeds 45°. Changes to the curvature of a penis may be caused by Peyronie's disease.
Development

When the fetus is exposed to testosterone, the genital tubercle elongates (primordial phallus) and develops into the glans and shaft of the penis and the urogenital folds develop into the penile raphe.[20][21][22][23]
Growth in puberty
On entering puberty, the penis, scrotum and testicles will enlarge toward maturity. During the process, pubic hair grows above and around the penis. A large-scale study assessing penis size in thousands of 17- to 19-year-old males found no difference in average penis size between 17-year-olds and 19-year-olds. From this, it can be concluded that penile growth is typically complete not later than age 17, and possibly earlier.[24]
Physiological functions
Urination
In males, the expulsion of urine from the body is done through the penis. The urethra drains the bladder through the prostate gland where it is joined by the ejaculatory duct, and then onward to the penis. At the root of the penis (the proximal end of the corpus spongiosum) lies the external sphincter muscle. This is a small sphincter of striated muscle tissue and is in healthy males under voluntary control. Relaxing the urethra sphincter allows the urine in the upper urethra to enter the penis properly and thus empty the urinary bladder.
Physiologically, urination involves coordination between the central, autonomic, and somatic nervous systems. In infants, some elderly individuals, and those with neurological injury, urination may occur as an involuntary reflex. Brain centers that regulate urination include the pontine micturition center, periaqueductal gray, and the cerebral cortex.[25] During erection, these centers block the relaxation of the sphincter muscles, so as to act as a physiological separation of the excretory and reproductive function of the penis, and preventing urine from entering the upper portion of the urethra during ejaculation.[26]
Voiding position
The distal section of the urethra allows a human male to direct the stream of urine by holding the penis. This flexibility allows the male to choose the posture in which to urinate. In cultures where more than a minimum of clothing is worn, the penis allows the male to urinate while standing without removing much of the clothing. It is customary for some boys and men to urinate in seated or crouched positions. The preferred position may be influenced by cultural or religious beliefs.[27] Research on the medical superiority of either position exists, but the data are heterogenic. A meta-analysis[28] summarizing the evidence found no superior position for young, healthy males. For elderly males with LUTS, however, the sitting position when compared to the standing position is differentiated by the following:
- the post void residual volume (PVR, ml) was significantly decreased
- the maximum urinary flow (Qmax, ml/s) was increased
- the voiding time (VT, s) was decreased
This urodynamic profile is related to a lower risk of urologic complications, such as cystitis and bladder stones.
Erection
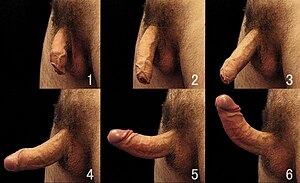

An erection is the stiffening and rising of the penis, which occurs during sexual arousal, though it can also happen in non-sexual situations. Spontaneous erections frequently occur during adolescence due to friction with clothing, a full bladder or large intestine, hormone fluctuations, nervousness, and undressing in a nonsexual situation. It is also normal for erections to occur during sleep and upon waking. (See nocturnal penile tumescence.) The primary physiological mechanism that brings about erection is the autonomic dilation of arteries supplying blood to the penis, which allows more blood to fill the three spongy erectile tissue chambers in the penis, causing it to lengthen and stiffen. After vasocongestion, the now-engorged erectile tissue presses against and constricts the veins that carry blood away from the penis. More blood enters than leaves the penis until an equilibrium is reached where an equal volume of blood flows into the dilated arteries and out of the constricted veins; a constant erectile size is achieved at this equilibrium. The scrotum will usually tighten during erection.
Erection facilitates sexual intercourse though it is not essential for various other sexual activities.
Erection angle
Although many erect penises point upwards (see illustration), it is common and normal for erect penis to curve in any direction. Many penises are curved in right, left, upwards or downwards direction depending upon the tension of the suspensory ligament that holds it in position.
The following table shows how common various erection angles are for a standing male, out of a sample of 81 males aged 21 through 67. In the table, zero degrees is pointing straight up against the abdomen, 90 degrees is horizontal and pointing straight forward, while 180 degrees would be pointing straight down to the feet. An upward pointing angle is most common.[29]
| Angle (°) from vertically upwards |
Percent of males |
|---|---|
| 0–30 | 4.9 |
| 30–60 | 29.6 |
| 60–85 | 30.9 |
| 85–95 | 9.9 |
| 95–120 | 19.8 |
| 120–180 | 4.9 |
Sexual stimulation and ejaculation
The glans and the frenulum are erogenous zones of the penis.[30] The glans has a lot of nerve endings, which makes it the most sensitive.[31] The most effective way to stimulate the penis is through oral (fellatio) or manual stimulation (a handjob or manual masturbation). Frot is mutual penile stimulation between men.
Ejaculation is the ejection of semen from the penis. It is usually accompanied by orgasm. A series of muscular contractions delivers semen, containing male gametes known as sperm cells or spermatozoa, from the penis. Ejaculation usually happens as the result of sexual stimulation, but it can be due to prostatic disease in rare cases. Ejaculation may occur spontaneously during sleep (known as a nocturnal emission). Anejaculation is the condition of being unable to ejaculate.
Ejaculation has two phases: emission and ejaculation proper. The emission phase of the ejaculatory reflex is under control of the sympathetic nervous system, while the ejaculatory phase is under control of a spinal reflex at the level of the spinal nerves S2–4 via the pudendal nerve. A refractory period succeeds the ejaculation, and sexual stimulation precedes it.[32]
The ischiocavernosus muscle helps to stabilize the penis during erection by compressing the crus and slowing the return of blood through the veins. The bulbospongiosus muscle also contributes to erection along with the expulsion of urine and semen.
Evolved adaptations
The human penis has been argued to have several evolutionary adaptations. The purpose of these adaptations is to maximise reproductive success and minimise sperm competition. Sperm competition is where the sperm of two males simultaneously occupy the reproductive tract of a female and they compete to fertilise the egg.[33] If sperm competition results in the rival male's sperm fertilising the egg, cuckoldry could occur. This is the process whereby males unwittingly invest their resources into offspring of another male and, evolutionarily speaking, should be avoided.[34]
The most researched human penis adaptations are testis and penis size, ejaculate adjustment and semen displacement.[35]
Testis and penis size
Evolution has caused sexually selected adaptations to occur in penis and testis size in order to maximise reproductive success and minimise sperm competition.[36][37]
Sperm competition has caused the human penis to evolve in length and size for sperm retention and displacement.[37] To achieve this, the penis must be of sufficient length to reach any rival sperm and to maximally fill the vagina.[37] In order to ensure that the female retains the male's sperm, the adaptations in length of the human penis have occurred so that the ejaculate is placed close to the female cervix.[38] This is achieved when complete penetration occurs and the penis pushes against the cervix.[39] These adaptations have occurred in order to release and retain sperm to the highest point of the vaginal tract. As a result, this adaptation also leaves the sperm less vulnerable to sperm displacement and semen loss. Another reason for this adaptation is that, due to the nature of the human posture, gravity creates vulnerability for semen loss. Therefore, a long penis, which places the ejaculate deep in the vaginal tract, could reduce the loss of semen.[40]
Another evolutionary theory of penis size is female mate choice and its associations with social judgements in modern-day society.[37][41] A study which illustrates female mate choice as an influence on penis size presented females with life-size, rotatable, computer generated males. These varied in height, body shape and flaccid penis size, with these aspects being examples of masculinity.[37] Female ratings of attractiveness for each male revealed that larger penises were associated with higher attractiveness ratings.[37] These relations between penis size and attractiveness have therefore led to frequently emphasized associations between masculinity and penis size in popular media.[41] This has led to a social bias existing around penis size with larger penises being preferred and having higher social status. This is reflected in the association between believed sexual prowess and penis size and the social judgement of penis size in relation to 'manhood'.[41]
Like the penis, sperm competition has caused the human testicles to evolve in size through sexual selection.[36] This means that large testicles are an example of a sexually selected adaptation. The human testicles are moderately sized when compared to other animals such as gorillas and chimpanzees, placing somewhere midway.[42] Large testicles are advantageous in sperm competition due to their ability to produce a bigger ejaculation.[43] Research has shown that a positive correlation exists between the number of sperm ejaculated and testis size.[43] Larger testes have also been shown to predict higher sperm quality, including a larger number of motile sperm and higher sperm motility.[36]
Research has also demonstrated that evolutionary adaptations of testis size are dependent on the breeding system in which the species resides.[44] Single-male breeding systems—or monogamous societies—tend to show smaller testis size than do multi-male breeding systems or extra-pair copulation (EPC) societies. Human males live largely in monogamous societies like gorillas, and therefore testis size is smaller in comparison to primates in multi-male breeding systems, such as chimpanzees. The reason for the differentiation in testis size is that in order to succeed reproductively in a multi-male breeding system, males must possess the ability to produce several fully fertilising ejaculations one after another.[36] This, however, is not the case in monogamous societies, where a reduction in fertilising ejaculations has no effect on reproductive success.[36] This is reflected in humans, as the sperm count in ejaculations is decreased if copulation occurs more than three to five times in a week.[45]
Ejaculate adjustment
One of the primary ways in which a male's ejaculate has evolved to overcome sperm competition is through the speed at which it travels. Ejaculates can travel up to 60 centimetres[quantify] which, when combined with its placement at the highest point of the vaginal tract, acts to increase the probability that an egg will be fertilised by his sperm as opposed to another's, thus maximising his likelihood of paternity.[40]
In addition, males can—and do—adjust their ejaculates in response to sperm competition and according to the likely costs and benefits of mating with a particular female.[46] Research has focused primarily on two fundamental ways in which males go about achieving this: adjusting ejaculate size and adjusting ejaculate quality.
Quantity
The number of sperm in any given ejaculate varies from one ejaculate to another.[47] This variation is hypothesised to be a male's attempt to eliminate, if not reduce, his sperm competition. A male will alter the number of sperm he ejaculates into a female according to his perceived level of sperm competition,[35] ejaculating a higher number of sperm if he suspects a greater level of competition from other males.
In support of ejaculate adjustment, research has shown that a male typically increases the number of sperm he ejaculates into his partner after they have been separated for a period of time.[48] This is largely due to the fact that the less time a couple is able to spend together, the higher the probability the female will be inseminated by another male,[49] hence the likelihood of greater sperm competition. Increasing the number of sperm a male ejaculates into a female increases the probability of his paternity when another's ejaculate may be stored within the female as a result of her potential extra-pair copulations during this separation. This increase in the number of sperm a male produces in response to sperm competition is not observed for masturbatory ejaculates.[35]
Quality
Males also adjust their ejaculates in response to sperm competition in terms of quality. Research has demonstrated, for example, that simply viewing a sexually explicit image of a female and two males (i.e. high sperm competition) can cause males to produce a greater amount of motile sperm than when viewing a sexually explicit image depicting exclusively three females (i.e. low sperm competition).[50] Much like increasing the number, increasing the quality of sperm that one ejaculates into a female maximizes one's likelihood of paternity when the threat of sperm competition is high.
Female phenotypic quality
A female's phenotypic quality is a key determinant of a male's ejaculate investment.[51]
Research has shown that males produce larger ejaculates containing better, more motile sperm when mating with a higher quality female.[46] This is largely to reduce a male's sperm competition, since more attractive females are likely to be approached and subsequently inseminated by more males than are less attractive females. Increasing investment in females with high quality phenotypic traits therefore acts to offset the ejaculate investment of others.[51] In addition, female attractiveness has been shown to be an indicator of reproductive quality, with greater value in higher quality females.[52] It is therefore beneficial for males to increase their ejaculate size and quality when mating with more attractive females, since this is likely to maximise their reproductive success also. Through assessing a female's phenotypic quality, males can judge whether or not to invest (or invest more) in a particular female, which will influence their subsequent ejaculate adjustment.
Semen displacement
The shape of the human penis is thought to have evolved as a result of sperm competition.[53] Semen displacement is an adaptation of the shape of the penis to draw foreign semen away from the cervix. This means that in the event of a rival male's sperm occupying the reproductive tract of a female, the human penis is able to displace the rival sperm, replacing it with his own.[54]
Semen displacement has two main benefits for a male. Firstly, by displacing a rival male's sperm, the risk of the rival sperm fertilising the egg is reduced.[55] Secondly, the male replaces the rival's sperm with his own, thereby increasing the probability of his fertilising the egg and successfully reproducing with the female. However, males have to ensure they do not displace their own sperm. It is thought that the relatively quick loss of erection after ejaculation, penile hypersensitivity following ejaculation, and the shallower, slower thrusting of the male after ejaculation prevent this from occurring.[54]
The coronal ridge is the part of the human penis thought to have evolved to allow for semen displacement. Research has studied how much semen is displaced by differently shaped artificial genitals.[55] This research showed that, when combined with thrusting, the coronal ridge of the penis is able to remove the seminal fluid of a rival male from within the female reproductive tract. It does this by forcing the semen under the frenulum of the coronal ridge, causing it to collect behind the coronal ridge shaft.[55] When model penises without a coronal ridge were used, less than half the artificial sperm was displaced, compared to penises with a coronal ridge.[55]
The presence of a coronal ridge alone, however, is not sufficient for effective semen displacement. It must be combined with adequate thrusting to be successful. It has been shown that the deeper the thrusting, the larger the semen displacement. No semen displacement occurs with shallow thrusting.[55] Some have therefore termed thrusting as a semen displacement behaviour.[56]
The behaviours associated with semen displacement, namely thrusting (number of thrusts and depth of thrusts), and duration of sexual intercourse,[56] have been shown to vary according to whether a male perceives the risk of partner infidelity to be high or not. Males and females report greater semen displacement behaviours following allegations of infidelity. In particular, following allegations of infidelity, males and females report deeper and quicker thrusting during sexual intercourse.[55]
Clinical significance
Disorders
- Paraphimosis is an inability to move the foreskin forward over the glans. It can result from fluid trapped in a foreskin left retracted, perhaps following a medical procedure, or accumulation of fluid in the foreskin because of friction during vigorous sexual activity.
- In Peyronie's disease, anomalous scar tissue grows in the soft tissue of the penis, causing curvature. Severe cases can be improved by surgical correction.
- A thrombosis can occur during periods of frequent and prolonged sexual activity, especially fellatio. It is usually harmless and self-corrects within a few weeks.
- Infection with the herpes virus can occur after sexual contact with an infected carrier; this may lead to the development of herpes sores.
- Balanitis is an inflammation, either infectious or not.
- Pudendal nerve entrapment is a condition characterized by pain on sitting and the loss of penile sensation and orgasm. Occasionally, there is a total loss of sensation and orgasm. The pudendal nerve can be damaged by narrow, hard bicycle seats and accidents.
- Penile fracture can occur if the erect penis is bent excessively. A popping or cracking sound and pain is normally associated with this event. Emergency medical assistance should be obtained as soon as possible. Prompt medical attention lowers the likelihood of permanent penile curvature.
- In diabetes, peripheral neuropathy can cause tingling in the penile skin and possibly reduced or completely absent sensation. The reduced sensations can lead to injuries for either partner and their absence can make it impossible to have sexual pleasure through stimulation of the penis. Since the problems are caused by permanent nerve damage, preventive treatment through good control of the diabetes is the primary treatment. Some limited recovery may be possible through improved diabetes control.
- Erectile dysfunction is the inability to develop and maintain an erection sufficiently firm for satisfactory sexual performance. Diabetes is a leading cause, as is natural aging. A variety of treatments exist, most notably including the phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor drugs (such as sildenafil citrate, marketed as Viagra), which work by vasodilation.
- Priapism is a painful and potentially harmful medical condition in which the erect penis does not return to its flaccid state. Priapism lasting over four hours is a medical emergency. The causative mechanisms are poorly understood but involve complex neurological and vascular factors. Potential complications include ischaemia, thrombosis, and impotence. In serious cases the condition may result in gangrene, which may result in amputation. However, that is usually only the case if the organ is broke out and injured because of it. The condition has been associated with a variety of drugs including prostaglandin. Contrary to common knowledge, sildenafil (Viagra) will not cause it.[57]
- Lymphangiosclerosis is a hardened lymph vessel, although it can feel like a hardened, almost calcified or fibrous, vein. It tends not to share the common blue tint with a vein however. It can be felt as a hardened lump or "vein" even when the penis is flaccid, and is even more prominent during an erection. It is considered a benign physical condition. It is fairly common and can follow a particularly vigorous sexual activity for men, and tends to go away if given rest and more gentle care, for example by use of lubricants.
- Carcinoma of the penis is rare with a reported rate of 1 person in 100,000 in developed countries. Some sources state that circumcision can protect against this disease, but this notion remains controversial among medical circles.[58]
- Hard flaccid syndrome is a chronic and painful condition characterized by a semi-rigid penis in the flaccid state, a soft glans when erect, along with various associated symptoms like pelvic pain, low libido, erectile dysfunction, and penile sensory changes.
- Cold glans syndrome is a condition marked by the persistent inability of the glans penis to maintain an erect state during sexual arousal, potentially leading to reduced sensitivity and erection difficulties.
Developmental disorders
- Hypospadias is a developmental disorder where the meatus is positioned wrongly at birth. Hypospadias can also occur iatrogenically by the downward pressure of an indwelling urethral catheter.[59] It is usually corrected by surgery.
- A micropenis is a very small penis caused by developmental or congenital problems.
- Diphallia, or penile duplication (PD), is the rare condition of having two penises.
Alleged and observed psychological disorders
- Penis panic (koro in Malaysian/Indonesian) — delusion of shrinkage of the penis and retraction into the body. This appears to be culturally conditioned and largely limited to Ghana, Sudan, China, Japan, Southeast Asia, and West Africa.
- In April 2008, Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of Congo, the West African police arrested 14 suspected victims (of penis snatching) and sorcerers accused of using black magic or witchcraft to steal (make disappear) or shrink men's penises to extort cash for cure, amid a wave of panic. Arrests were made in an effort to avoid bloodshed seen in Ghana a decade before, when 12 penis snatchers were beaten to death by mobs.[60]
- Penis envy — the contested Freudian belief of all women inherently envying men for having penises.
Society and culture



Terminology
In many cultures, referring to the penis is considered taboo or vulgar, and a variety of slang words and euphemisms are used to talk about it. In English, these include member, dick, cock, prick, johnson, dork, peter, pecker, manhood, stick, rod, thing, third/middle leg, dong, willy, schlong, and todger.[61] Many of these are used as insults—though sometimes playfully—meaning an unpleasant or unworthy person.[62][63] Among these, historically, the most commonly used euphemism for penis in English literature and society was member.[64]
Alteration
The penis is sometimes pierced or decorated by other body art. Other than circumcision, genital alterations are almost universally elective and usually for the purpose of aesthetics or increased sensitivity. Piercings of the penis include the Prince Albert, the apadravya, the ampallang, the dydoe, and the frenum piercing. Foreskin restoration or stretching is a further form of body modification, as well as implants under the shaft of the penis.
Trans women who undergo sex reassignment surgery have their penis surgically modified into a vagina via vaginoplasty. Trans men who undergo such surgery have a phalloplasty or metoidioplasty.
Other practices that alter the penis are also performed, although they are rare in Western societies without a diagnosed medical condition. Apart from penectomy, perhaps the most radical of these is subincision, in which the urethra is split along the underside of the penis. Subincision originated among Australian Aborigines, although it is now done by some in the U.S. and Europe.
Circumcision

The most common form of body modification related to the penis is circumcision: removal of part or all of the foreskin. It is most commonly performed as an elective procedure for prophylactic, cultural, or religious reasons.[65] For infant circumcision, modern devices such as the Gomco clamp, Plastibell, and Mogen clamp are available.[66] Among the world's major medical organizations, there is a consensus that circumcision reduces heterosexual HIV infection rates in high-risk populations,[67][68] and differing perspectives on the prophylactic efficacy and cost effectiveness of circumcision in developed nations.[65] The World Health Organization (WHO; 2007), the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS; 2007), and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC; 2008) state that evidence indicates circumcision reduces the risk of HIV acquisition by men during penile-vaginal sex.[69][70] Circumcision plays a significant role in many of the world's cultures.[71] When performed for religious reasons, it is most common among both Jews and Muslims, among whom it is near-universal.[72]
Potential regeneration
There are efforts by scientists to partially or fully regenerate the structures of the human penis.[73][74][75] Patients who can benefit most from this field are those who have congenital defects, cancer, and injuries that have excised parts of their genitalia.[76][77][78] Some organizations which perform research into, or conduct regeneration procedures, include the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine and the United States Department of Defense.[77][78] The first successful penis allotransplant surgery was done in September 2005 in a military hospital in Guangzhou, China.[79] A man at 44 sustained an injury after an accident and his penis was severed; urination became difficult as his urethra was partly blocked. A recently brain-dead man, aged 23, was selected for the transplant. Despite atrophy of blood vessels and nerves, the arteries, veins, nerves and the corpora spongiosa were successfully matched. But, on 19 September (after two weeks), the surgery was reversed because of a severe psychological problem (rejection) by the recipient and his wife.[80]
In 2009, researchers Chen, Eberli, Yoo and Atala have produced bioengineered penises and implanted them on rabbits.[81] They were able to obtain erection and copulate, with 10 of 12 rabbits achieving ejaculation. This study shows that in the future it could be possible to produce artificial penises for replacement surgeries or phalloplasties. In 2015, the world's first successful penis transplant took place in Cape Town, South Africa in a nine-hour operation performed by surgeons from Stellenbosch University and Tygerberg Hospital. The 21-year-old recipient, who had been sexually active, had lost his penis in a botched circumcision at 18.[82]
See also
- Buried penis
- Castration anxiety
- Dick joke
- Dildo
- Genital modification and mutilation
- Penile enlargement
- Penis envy
- Penis removal
- Phallic architecture
- Preputioplasty
- Stunt cock
- Testicle
- Vulva - external female reproductive system
References
- ^ Harper, Douglas. "penis". Online Etymology Dictionary.
- ^ a b Berezow, Alex B. (March 2, 2015). "Is Your Penis Normal? There's a Chart for That". RealClearScience. Archived from the original on May 24, 2020. Retrieved July 7, 2018.
- ^ a b Veale, D.; Miles, S.; Bramley, S.; Muir, G.; Hodsoll, J. (2015). "Am I normal? A systematic review and construction of nomograms for flaccid and erect penis length and circumference in up to 15 521 men". BJU International. 115 (6): 978–986. doi:10.1111/bju.13010. PMID 25487360. S2CID 36836535.
- ^ Tortora, Gerard J; Anagnostakos, Nicholas P (1987). Principles of anatomy and physiology (5th ed.). New York: Harper & Row. pp. 727–728. ISBN 978-0060466695.
- ^ a b Richard L. Drake; A. Wayne Voglz; Adam W. M. Mitchell (8 March 2019). Gray's anatomy for students fourth edition. Elsevier. p. 461,501,502. ISBN 978-0323393041.
- ^ "Video of gliding action". Circumstitions. Archived from the original on May 7, 2017. Retrieved July 17, 2022.
- ^ Bannister LH, Dyson M. Reproductive system. In: Williams PL, ed. Gray's Anatomy. London: Churchill Livingstone; 1995:1857. OCLC 45217979.
- ^ "corpus cavernosum". U.S.gov. Feb 2011. Archived from the original on 13 February 2022. Retrieved 13 Feb 2022.
- ^ Hsu GL, Brock G, von Heyden B, Nunes L, Lue TF, Tanagho EA (May 1994). "The distribution of elastic fibrous elements within the human penis". British Journal of Urology. 73 (5): 566–571. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.1994.tb07645.x. PMID 8012781.
- ^ Snell RS. The perineum. In: Snell RS, ed. Clinical Anatomy. Philadelphia, Pa: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2004:430–431. Baltimore, MD Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2006. ISBN 9780781791649. Archived from the original on 2019-01-19. Retrieved 2019-01-17.
- ^ a b "M. K. Skinner (Ed.), Encyclopedia of Reproduction. vol. 1, pp. 367–375. Academic Press: Elsevier". Academic Press. Archived from the original on 2021-02-22. Retrieved 2019-01-17.
- ^ "Why Humans Lost Their Penis Bone". Science. 13 December 2016. Archived from the original on 19 June 2022. Retrieved 30 June 2022.
- ^ Dixson, A. F. (2009). Sexual selection and the origins of human mating systems. Oxford University Press. pp. 61–65. ISBN 9780191569739.
- ^ Center of Disease Control. "DES Update: Consumers". Archived from the original on 2014-03-17. Retrieved 2013-11-07.
- ^ Swan SH, Main KM, Liu F, et al. (August 2005). "Decrease in anogenital distance among male infants with prenatal phthalate exposure". Environmental Health Perspectives. 113 (8): 1056–61. doi:10.1289/ehp.8100. PMC 1280349. PMID 16079079.
- ^ Montague, Peter. "PCBs Diminish Penis Size". Rachel's Hazardous Waste News. 372. Archived from the original on 2012-03-03.
- ^ "Hormone Hell". DISCOVER. Archived from the original on 2009-08-13. Retrieved 2008-04-05.
- ^ Brown, Clarence William (February 13, 2014). "Pearly Penile Papules: Epidemiology". Medscape. Archived from the original on 2010-02-15. Retrieved 2014-03-08.
- ^ "Spots on the penis". 3 November 2014. Archived from the original on 20 December 2008. Retrieved 16 January 2017.
- ^ Keith L. Moore, T. V. N. Persaud, Mark G. Torchia, The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology 10th Ed. Elsevier Health Sciences, 2015 ISBN 9780323313483, pp 267-69
- ^ Jones, Richard E.; Lopez, Kristin H. (28 September 2013). Human Reproductive Biology. Academic Press. p. 352. ISBN 978-0-12-382185-0.
- ^ Hodges, Frederick Mansfield S.; Denniston, George C.; Milos, Marilyn Fayre (2007). Male and Female Circumcision: Medical, Legal, and Ethical Considerations in Pediatric Practice. Springer US. p. 10. ISBN 978-0-58539-937-9. Archived from the original on November 24, 2023. Retrieved November 24, 2023.
- ^ Martin, Richard J.; Fanaroff, Avory A.; Walsh, Michele C. (2014). Fanaroff and Martin's Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine E-Book: Diseases of the Fetus and Infant. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 1522. ISBN 978-0-32329-537-6. Archived from the original on November 24, 2023. Retrieved November 24, 2023.
- ^ Ponchietti R, Mondaini N, Bonafè M, Di Loro F, Biscioni S, Masieri L (February 2001). "Penile length and circumference: a study on 3,300 young Italian males". European Urology. 39 (2): 183–6. doi:10.1159/000052434. PMID 11223678. S2CID 46856727.
- ^ Sie JA, Blok BF, de Weerd H, Holstege G (2001). "Ultrastructural evidence for direct projections from the pontine micturition center to glycine-immunoreactive neurons in the sacral dorsal gray commissure in the cat". J. Comp. Neurol. 429 (4): 631–7. doi:10.1002/1096-9861(20010122)429:4<631::AID-CNE9>3.0.CO;2-M. PMID 11135240. S2CID 7570375.
- ^ Schirren, C.; Rehacek, M.; Cooman, S. de; Widmann, H.-U. (24 April 2009). "Die retrograde Ejakulation". Andrologia. 5 (1): 7–14. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0272.1973.tb00878.x. S2CID 83926005.
- ^ Y. de Jong; R.M. ten Brinck; J.H.F.M. Pinckaers; A.A.B. Lycklama à Nijeholt. "Influence of voiding posture on urodynamic parameters in men: a literature review" (PDF). Nederlands Tijdschrift voor urologie. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2014-07-14. Retrieved 2014-07-02.
- ^ de Jong, Y; Pinckaers, JH; Ten Brinck, RM; Lycklama À Nijeholt, AA; Dekkers, OM (2014). "Urinating Standing versus Sitting: Position Is of Influence in Men with Prostate Enlargement. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis". PLOS ONE. 9 (7): e101320. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...9j1320D. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0101320. PMC 4106761. PMID 25051345.
- ^ Sparling J (1997). "Penile erections: shape, angle, and length". Journal of Sex & Marital Therapy. 23 (3): 195–207. doi:10.1080/00926239708403924. PMID 9292834.
- ^ Crooks, Robert; Baur, Karla (2008). Our Sexuality. Thomson/Wadsworth. p. 90. ISBN 978-0-49510-326-4. Archived from the original on 2024-02-24. Retrieved 2024-02-24.
- ^ Olausson, Håkan; Wessberg, Johan; Morrison, India (2016). Affective Touch and the Neurophysiology of CT Afferents. Springer Science+Business Media. p. 305. ISBN 978-1-4939-6418-5.
...the most pleasurable of all body parts when stimulated sexually: the glans (or tip) of the penis.
- ^ Carlson, Neil. (2013). Physiology of Behavior. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Pearson Education, Inc.
- ^ Bleske-Rechek, A. L.; Euler, H. A.; LeBlanc, G. J.; Shackelford, T. K.; Weekes-Shackelford, V. A. (2002). "Psychological adaptation to human sperm competition". Evolution and Human Behavior. 23 (2): 123–138. doi:10.1016/S1090-5138(01)00090-3.
- ^ Ehrke, A. D.; Pham, M. N.; Shackelford, T. K.; Welling, L. L. M. (2013). "Oral sex, semen displacement, and sexual arousal: testing the ejaculate adjustment hypothesis". Evolutionary Psychology. 11 (5): 1130–9. doi:10.1177/147470491301100515. PMC 10429105. PMID 24356208.
- ^ a b c Shackelford, Todd K.; Goetz, Aaron T. (2007-02-01). "Adaptation to Sperm Competition in Humans". Current Directions in Psychological Science. 16 (1): 47–50. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8721.2007.00473.x. ISSN 0963-7214. S2CID 6179167.
- ^ a b c d e Moller, A. P. (1988). "Ejaculate quality, testes size and sperm competition in primates". Journal of Human Evolution. 17 (5): 479–488. doi:10.1016/0047-2484(88)90037-1.
- ^ a b c d e f Mautz, B. S.; Wong, B. B. M.; Peters, R. A.; Jennions, M. D. (April 23, 2013). "Penis size interacts with body shape and height to influence male attractiveness". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 110 (17): 6925–30. Bibcode:2013PNAS..110.6925M. doi:10.1073/pnas.1219361110. JSTOR 42590540. PMC 3637716. PMID 23569234.
- ^ Masters, W. H.; Johnson, V. E. (1966). Human Sexual Response. Boston: Little, Brown and Company. ISBN 9780316549875.
- ^ Schultz, W. W.; van Andel, P.; Sabelis, I.; Mooyaart, E. (December 18, 1999). "Magnetic resonance imaging of male and female genitals during coitus and female sexual arousal". BMJ. 319 (7225): 1596–600. doi:10.1136/bmj.319.7225.1596. PMC 28302. PMID 10600954.
- ^ a b Gallup, G. G.; Burch, R. L. (January 1, 2004). "Semen displacement as a sperm competition strategy in humans". Evolutionary Psychology. 2: 147470490400200. doi:10.1177/147470490400200105.
- ^ a b c Lever, J.; Frederick, D. A.; Peplau, L. A. (2006). "Does size matter? Men's and women's views on penis size across the lifespan". Psychology of Men and Masculinity. 7 (3): 129–143. doi:10.1037/1524-9220.7.3.129.
- ^ Harcourt, A. H.; Purvis, A.; Liles, L. (1995). "Sperm competition: Mating system, not breeding season, affects testes size of primates". Functional Ecology. 9 (3): 469–476. Bibcode:1995FuEco...9..468H. doi:10.2307/2390011. JSTOR 2390011.
- ^ a b Simmons, Leigh W.; Firman, Renée C.; Rhodes, Gillian; Peters, Marianne (2003). "Human sperm competition: testis size, sperm production and rates of extra pair copulations". Animal Behaviour. 68 (2): 297–302. doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2003.11.013. S2CID 52483925.
- ^ Harcourt, A. H.; Harvey, P. H.; Larson, S. G.; Short, R. V. (1981). "Testis weight, body weight and breeding system in primates". Nature. 293 (5827): 55–57. Bibcode:1981Natur.293...55H. doi:10.1038/293055a0. PMID 7266658. S2CID 22902112.
- ^ Freund, M. (1962). "Interrelationships among the characteristics of human semen and facts affecting semen specimen quality". Journal of Reproduction and Fertility. 4 (2): 143–159. doi:10.1530/jrf.0.0040143. PMID 13959612. S2CID 30336265.
- ^ a b Kelly, Clint D.; Jennions, Michael D. (2011-11-01). "Sexual selection and sperm quantity: meta-analyses of strategic ejaculation". Biological Reviews. 86 (4): 863–884. doi:10.1111/j.1469-185X.2011.00175.x. hdl:1885/64047. ISSN 1469-185X. PMID 21414127. S2CID 696117.
- ^ Shackelford, Todd K.; Pound, Nicholas; Goetz, Aaron T. (2005). "Psychological and Physiological Adaptations to Sperm Competition in Humans". Review of General Psychology. 9 (3): 228–248. doi:10.1037/1089-2680.9.3.228. S2CID 37941662. Archived from the original on 2020-11-23. Retrieved 2019-12-04.
- ^ Baker, R. Robin; Bellis, Mark A. (1989-05-01). "Number of sperm in human ejaculates varies in accordance with sperm competition theory". Animal Behaviour. 37 (Pt 5): 867–869. doi:10.1016/0003-3472(89)90075-4. S2CID 53183250.
- ^ Shackelford, T (2002). "Psychological adaptation to human sperm competition". Evolution and Human Behavior. 23 (2): 123–138. doi:10.1016/s1090-5138(01)00090-3.
- ^ Kilgallon, Sarah J.; Simmons, Leigh W. (2005-09-22). "Image content influences men's semen quality". Biology Letters. 1 (3): 253–255. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2005.0324. ISSN 1744-9561. PMC 1617155. PMID 17148180.
- ^ a b Leivers, Samantha; Rhodes, Gillian; Simmons, Leigh W. (2014-09-01). "Context-dependent relationship between a composite measure of men's mate value and ejaculate quality". Behavioral Ecology. 25 (5): 1115–1122. doi:10.1093/beheco/aru093. ISSN 1045-2249.
- ^ Thornhill, Randy; Gangestad, Steven W. (2008). The evolutionary biology of human female sexuality. Oxford; New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199712489.
- ^ Shackelford, Todd K.; Goetz, Aaron T. (2007-02-01). "Adaptation to Sperm Competition in Humans". Current Directions in Psychological Science. 16 (1): 47–50. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8721.2007.00473.x. ISSN 0963-7214. S2CID 6179167.
- ^ a b Burch, R. L.; Gallup, G. G.; Mitchell, T. J. (2006). "Semen displacement as a sperm competition strategy: Multiple mating, self-semen displacement, and timing of in-pair copulations". Human Nature. 17 (3): 253–264. doi:10.1007/s12110-006-1008-9. PMID 26181472. S2CID 31703430.
- ^ a b c d e f Burch, R. L.; Gallup, G. G.; Parvez, R. A.; Stockwell, M. L.; Zappieri, M. L. (2003). "The human penis as a semen displacement device". Evolution and Behaviour. 24 (4): 277–289. doi:10.1016/S1090-5138(03)00016-3.
- ^ a b Euler, H. A.; Goetz, A. T.; Hoier, S.; Shackelford, T. K.; Weekes-Shackelford, V. A. (2005). "Mate retention, semen displacement, and human sperm competition: A preliminary investigation of tactics to prevent and correct female infidelity". Personality and Individual Differences. 38 (4): 749–763. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2004.05.028.
- ^ Goldenberg MM (1998). "Safety and efficacy of sildenafil citrate in the treatment of male erectile dysfunction". Clinical Therapeutics. 20 (6): 1033–48. doi:10.1016/S0149-2918(98)80103-3. PMID 9916601.
- ^ Boczko S, Freed S (November 1979). "Penile carcinoma in circumcised males". New York State Journal of Medicine. 79 (12): 1903–4. PMID 292845.
- ^ Andrews HO, Nauth-Misir R, Shah PJ (March 1998). "Iatrogenic hypospadias—a preventable injury?". Spinal Cord. 36 (3): 177–80. doi:10.1038/sj.sc.3100508. PMID 9554017.
- ^ "Lynchings in Congo as penis theft panic hits capital". Reuters. 22 April 2017. Archived from the original on 7 December 2022. Retrieved 16 January 2017.
- ^ "todger - Definition, meaning & more - Collins Dictionary". Archived from the original on 7 August 2016. Retrieved 16 January 2017.
- ^ Marv Rubinstein, American English Compendium: A Portable Guide to the Idiosyncrasies, Subtleties, Technical Lingo, and Nooks and Crannies of American English, ISBN 1442232838, p. 147
- ^ Ruth Bell, Changing Bodies, Changing Lives: Expanded Third Edition: A Book for Teens on Sex and Relationships, ISBN 0307794067, p. 15
- ^ David M. Friedman (4 September 2008). A Mind of Its Own: A Cultural History of the Penis. Simon and Schuster. p. 43. ISBN 978-1-43-913608-9.
- ^ a b Alan Glasper, Edward; Richardson, James; Randall, Duncan (2021). "Promote, Restore, and Stabilise Health Status in Children". A Textbook of Children's and Young People's Nursing. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 382. ISBN 9780702065033.
- ^ Holman JR, Lewis EL, Ringler RL (August 1995). "Neonatal circumcision techniques". American Family Physician. 52 (2): 511–520. PMID 7625325.
- ^ Chikutsa, Antony; Maharaj, Pranitha (July 2015). "Social representations of male circumcision as prophylaxis against HIV/AIDS in Zimbabwe". BMC Public Health. 15 (1): 603. doi:10.1186/s12889-015-1967-z. ISSN 1471-2458. PMC 4489047. PMID 26133368.
It is now generally accepted in public health spheres that medical male circumcision is efficacious in the prevention of HIV infection.
- ^ Merson, Michael; Inrig, Stephen (2017). The AIDS Pandemic: Searching for a Global Response. Springer Publishing. p. 379. ISBN 9783319471334.
This led to a [medical] consensus that male circumcision should be a priority for HIV prevention in countries and regions with heterosexual epidemics and high HIV and low male circumcision prevalence.
- ^ New Data on Male Circumcision and HIV Prevention: Policy and Programme Implications (PDF) (Report). World Health Organization. March 28, 2007. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-03-02. Retrieved 2007-08-13.
- ^ "Male Circumcision and Risk for HIV Transmission and Other Health Conditions: Implications for the United States". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2008. Archived from the original on 2017-02-20. Retrieved 2013-11-07.
- ^ Benson, Janette (2008). Encyclopedia of Infant and Early Childhood Development: A-F. Academic Press. p. 279. ISBN 9780123704610.
- ^ Ubayd, Anis (2006). The Druze and Their Faith in Tawhid. Syracuse University Press. p. 150. ISBN 9780815630975.
Male circumcision is standard practice, by tradition, among the Druze
- ^ Patel, Manish; Atala, Anthony (2011-12-29). "Tissue Engineering of the Penis". The Scientific World Journal. 11: 2567–2578. doi:10.1100/2011/323989. ISSN 2356-6140. PMC 3253692. PMID 22235188.
- ^ Andrew, Tom W.; Kanapathy, Muholan; Murugesan, Log; Muneer, Asif; Kalaskar, Deepak; Atala, Anthony (October 24, 2019). "Towards clinical application of tissue engineering for erectile penile regeneration". Nature Reviews Urology. 16 (12): 734–744. doi:10.1038/s41585-019-0246-7. ISSN 1759-4820. PMID 31649327. S2CID 204883088. Archived from the original on July 19, 2022. Retrieved November 19, 2020.
- ^ Pozzi, Edoardo; Muneer, Asif; Sangster, Pippa; Alnajjar, Hussain M.; Salonia, Andrea; Bettocchi, Carlo; Castiglione, Fabio; Ralph, David J. (July 2019). "Stem-cell regenerative medicine as applied to the penis". Current Opinion in Urology. 29 (4): 443–449. doi:10.1097/MOU.0000000000000636. ISSN 0963-0643. PMID 31008782. S2CID 128353913. Archived from the original on 2024-03-18. Retrieved 2020-11-21.
- ^ Moore, Lisa; Casper, Monica (2014). The Body: Social and Cultural Dissections. Taylor & Francis. p. 74. ISBN 9781136771798.
- ^ a b Ude, Chinedu Cletus; Miskon, Azizi; Idrus, Ruszymah Bt Hj; Abu Bakar, Muhamad Bin (2018-02-26). "Application of stem cells in tissue engineering for defense medicine". Military Medical Research. 5 (1): 7. doi:10.1186/s40779-018-0154-9. ISSN 2054-9369. PMC 6389246. PMID 29502528.
- ^ a b Ferreira, Becky (October 6, 2014). "How to Grow An Artificial Penis". Vice News. Archived from the original on November 11, 2020. Retrieved November 19, 2020.
- ^ "世界首例异体阴茎移植成功 40岁患者数周后出院·广东新闻·珠江三角洲·南方新闻网". Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 16 January 2017.
- ^ Sample, Ian (2006-09-18). "Man rejects first penis transplant". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on 2018-05-31. Retrieved 2010-05-22.
- ^ Chen KL, Eberli D, Yoo JJ, Atala A (November 2009). "Regenerative Medicine Special Feature: Bioengineered corporal tissue for structural and functional restoration of the penis". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 107 (8): 3346–50. Bibcode:2010PNAS..107.3346C. doi:10.1073/pnas.0909367106. PMC 2840474. PMID 19915140.
- ^ Gallagher, James (13 March 2015). "South Africans perform first 'successful' penis transplant". BBC News. Archived from the original on 17 March 2019. Retrieved 16 January 2017.
External links
- Articles with short description
- Short description matches Wikidata
- Wikipedia indefinitely move-protected pages
- Wikipedia indefinitely semi-protected pages
- Articles containing potentially dated statements from 2015
- All articles containing potentially dated statements
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from March 2022
- Commons category link from Wikidata
- Articles with TA98 identifiers
- Human penis
- Human anatomy
- Human male reproductive system
- Mammal male reproductive system
- Men's health
- Penis
- Urinary system
- Sex organs