
No higher resolution available.
This file is from a shared repository and may be used by other projects.
The description on its file description page there is shown below.
License
Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC 3.0)
Summary
Author:Weitzman SP, Cabanillas ME,Department of Endocrine Neoplasia and Hormonal Disorders, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center(Openi/National Library of Medicine)Source:https://openi.nlm.nih.gov/detailedresult?img=PMC4547654_cmar-7-265Fig1&query=Cabozantinib&it=xg&req=4&npos=9 Description:f1-cmar-7-265: Molecular pathways important in MTC and targets relevant to cabozantinib.Notes: Mutations in RET are the most common drivers of MTC; however, there are other important kinases which are upregulated and are targeted by cabozantinib. For example, cabozantinib is a potent inhibitor of MET and VEGFR2. MET and VEGFR cooperate to drive tumor angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis. Upregulation of MET is associated with the ability of tumors to evade antiangiogenic treatment. Furthermore, osteoblasts and osteoclasts express MET and VEGF receptors. Hepatocyte growth factor, the only known ligand for the MET receptor, may be an important factor directing cross talk between tumor cells and osteoblasts/osteoclasts. Thus, simultaneous inhibition of MET and VEGF receptors may block progression of osteolytic and osteoblastic bone metastases.Abbreviations: MTC, medullary thyroid cancer; RET, rearranged during transfection; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment |
|---|
| current | 20:46, 24 November 2021 | 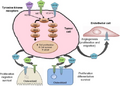 | 512 × 369 (173 KB) | Ozzie10aaaa | Author:Weitzman SP, Cabanillas ME,Department of Endocrine Neoplasia and Hormonal Disorders, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center(Openi/National Library of Medicine)Source:https://openi.nlm.nih.gov/detailedresult?img=PMC4547654_cmar-7-265Fig1&query=Cabozantinib&it=xg&req=4&npos=9 Description:f1-cmar-7-265: Molecular pathways important in MTC and targets relevant to cabozantinib.Notes: Mutations in RET are the most common drivers of MTC; however, there are other important kinases w... |
File usage
The following page uses this file:

